|
AlleleID
AlleleID designs oligos for strain differentiation and taxa specific assays. This aids in bacterial identification, pathogen detection and species identification. The software is designed to run on Windows and Macintosh operating system. AlleleID aligns sequences to locate differences in DNA and to find conserved regions and then designs oligos to amplify and detect only the species or strains of interest from the mix. The platforms for which AlleleID includes support are: # Quantitative PCR: Designs species specific and taxa specific qPCR assays # Microarrays: Designs species specific and taxa specific microarrays # xMAP: Designs oligos for Direct Hybridization Assays (DHA) and ASPE assays # MLPA: Designs probes for copy number detection and SNP studies References {{reflist External linksAlleleID Homepage [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms ( SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small bits of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by " -mer" (from Greek ''meros'', "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides (nt) is a hexamer, while one of 25 n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
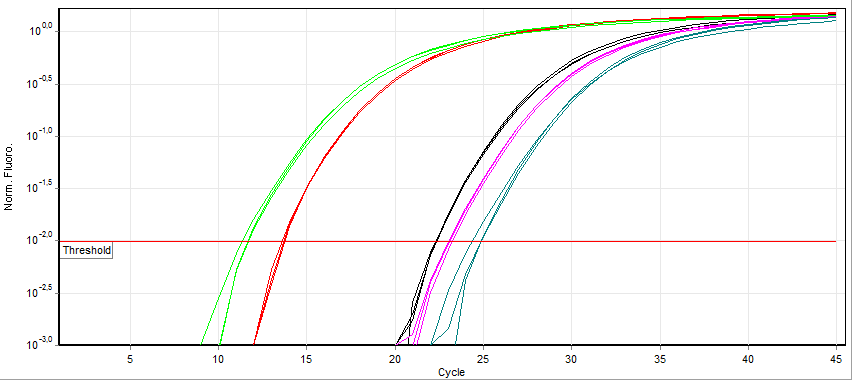
Quantitative PCR
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (quantitative real-time PCR) and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules) (semi-quantitative real-time PCR). Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter, which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence. The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation ''qPCR'' be used for q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10−12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as '' probes'' (or ''reporters'' or '' oligos''). These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called ''target'') under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
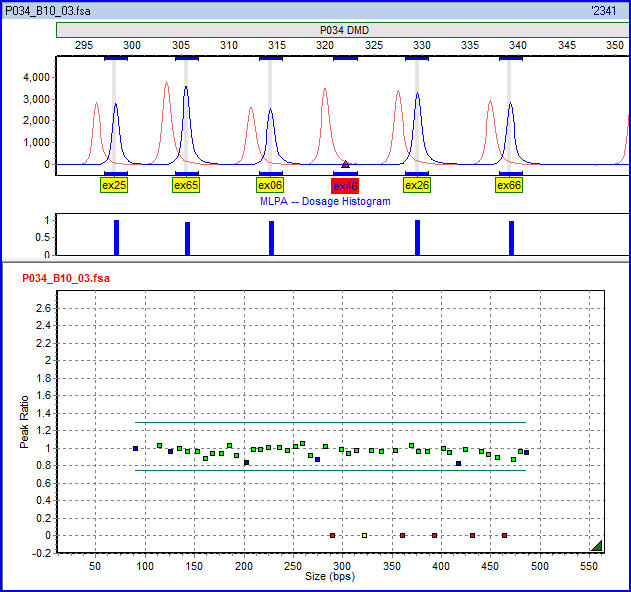
Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) is a variation of the multiplex polymerase chain reaction that permits amplification of multiple targets with only a single primer pair. It detects copy number changes at the molecular level, and software programs are used for analysis. Identification of deletions or duplications can indicate pathogenic mutations, thus MLPA is an important diagnostic tool used in clinical pathology laboratories worldwide. History Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification was invented by Jan Schouten, a Dutch scientist. The method was first described in 2002 in the scientific journal ''Nucleic Acid Research''. The first applications included the detection of exon deletions in the human genes BRCA1, MSH2 and MLH1, which are linked to hereditary breast and colon cancer. Now MLPA is used to detect hundreds of hereditary disorders, as well as for tumour profiling. Description MLPA quantifies the presence of particular sequences in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |