|
Alinjaq Castle
The Alinja Tower, also known as Alinjagala, Alinja-gala () or the Armenian fortress of Yernjak up to the 14th centuryآ«ذڑر€ذµذ؟ذ¾رپر‚رŒ ذ•ر€ذ½ذ´ذ¶ذ°ذ؛ (ذگذ»ذ¸ذ½ذ´ذ¶ذ°-ذ؛ذ°ذ»ذ°)آ» /ذ‘رژذ»ذ»ذµر‚ذµذ½رŒ ذڑذ°ذ²ذ؛ذ°ذ·رپذ؛ذ¾ذ³ذ¾ ذ¸رپر‚ذ¾ر€ذ¸ذ؛ذ¾-ذ°ر€ر…ذµذ¾ذ»ذ¾ذ³ذ¸ر†ذ؛رپذ؛ذ¾ذ³ذ¾ ذ¸ذ½رپر‚ذ¸ر‚رƒر‚ذ° ذ² ذ¢ذ¸ر„ذ»ذ¸رپذµ, ذ’ر‹ذ؟رƒرپذ؛ذ¸ 1-8 / p.16 – ذکذ·ذ´-ذ²ذ¾ ذگذ؛ذ°ذ´ذµذ¼ذ¸رڈ ذ½ذ°رƒذ؛ ذ،ذ،ذ،ذ , 1928 (ذ،ذ»ذ¾ذ²ذ°ر€رŒ ر‚ذ¾ذ؟ذ¾ذ½ذ¸ذ¼ذ¾ذ² ذگر€ذ¼ذµذ½ذ¸ذ¸: ذ¢ذ¾ذ¼ 2. Pages 246-247.), is a tower located to the west of Khanega village, not far from Julfa city in Azerbaijan, on the right coast of the Alinja River (Alinjachay), higher of the Armenian monastery St. Karapet, on the top of Alinja Mountain. The tower was one of the strongest defensive buildings of its time. History The first mentions are in sources from the 1st century. The tower was founded and belonged to the Armenian lords of Syunik. It was one of the important fortress in Armenia. By the 10th century, the tower was in the hands of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanة™gah, Julfa
Xanة™gah (also, Khanagah and Khanegakh) is a village and municipality in the Julfa District of Nakhchivan, Azerbaijan. It is located 37 km in the north from the district center, on both banks of the Alinja River, on the slope of the Zangezur ridge. Its population is busy with vine-growing, farming and animal husbandry. There are secondary school, cultural house, three libraries, communication branch, club, kindergarten and a medical center in the village. It has a population of 1,212. The ''ئڈlincة™أ§ay xanة™gahؤ±'' (Alinja architectural complex) of the Middle Ages is located in the east from the Khanagah village, on the left bank of the Alinja River. Etymology The name of the ''Xanة™gah'' ( Khanagah) is related with common name of Khanagah which were given to the sanctuary, sacred place and the buildings built around the holy graves or to the buildings owned by the pilgrims. The Khanagah means "place for dervishes", and were built on the sacred places. The tombs of the ''Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbelian Dynasty
The House of Orbelian () was a noble family of Armenia and a dynasty of Armenian lords of the province of Syunik, with a long history of political influence documented in inscriptions throughout the provinces of Vayots Dzor and Syunik, and recorded by the family historian Bishop Stepanos in his 1297 ''History of Syunik''. History In historical sources, Ivane Orbeli is mentioned for the first time from this family. The Orbels were especially advanced during the reign of Demetrius I and David V, when their family inherited the name of Amirspasalar, and Lori as a administrative state. For their bravery and loyal service at the Georgian court, the Orbelians received the hereditary title of commander-in-chief ( amirspasalar) of the army and significant territories with a number of fortresses, including the fortress of Orbeti in the south of present-day Georgia, from which the name of the family - Orbeli and then Orbelian - was derived. In 1177-1178, Amirspasalar Ivane Orbeli l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miran Shah
Mirza Jalal-ud-din Miran Shah Beg (1366 – 20 April 1408), commonly known as Miran Shah (), was a son of the Central Asian conqueror Timur, founder of the Timurid Empire. During his father's reign, Miran Shah was initially a powerful regional governor and prominent military commander, having aided Timur in his conquests as well as suppressing several revolts. However, after facing accusations of destructive and hedonistic behaviour, the prince was later deposed from these roles by the emperor. Following Timur's death in 1405, Miran Shah became embroiled in the ensuing war of succession, having thrown his support behind his son Khalil Sultan. He was later killed whilst battling against the Timurid's traditional rivals, the Qara Qoyunlu. Though never ruling in his own right, the line of Miran Shah played a prominent role in the history of the Timurid Empire. His grandson Abu Sa'id Mirza eventually came to rule the majority of Transoxiana in the latter half of the 15th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeated commander, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest military leaders and tacticians in history, as well as one of the most brutal and deadly. Timur is also considered a great patron of art and architecture, for he interacted with intellectuals such as Ibn Khaldun, Hafez, and Hafiz-i Abru and his reign introduced the Timurid Renaissance. Born into the Turkicized Mongol confederation of the Barlas in Transoxiana (in modern-day Uzbekistan) in the 1320s, Timur gained control of the western Chagatai Khanate by 1370. From that base he led military campaigns across Western, South, and Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Southern Russia, defeating in the process the Khans of the Golden Horde, the Mamluks of Egypt and Syria, the emerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Seljuq Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qأ¯nأ¯q branch of Oghuz Turks. The empire spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia in the north to the Persian Gulf in the south, and it spanned the time period 1037–1308, though Seljuk rule beyond the Anatolian peninsula ended in 1194. The Seljuk Empire was founded in 1037 by Tughril (990–1063) and his brother Chaghri (989–1060), both of whom co-ruled over its territories; there are indications that the Seljuk leadership otherwise functioned as a triumvirate and thus included Musa Yabghu, the uncle of the aforementioned two. During the formative phase of the empire, the Seljuks first advanced from their original homelands near the Aral Sea into Khorasan and then into the Iranian mainland, where they would become largely based as a Persianate socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the Iraq–Kuwait border, southeast, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest, and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The country covers an area of and has Demographics of Iraq, a population of over 46 million, making it the List of countries by area, 58th largest country by area and the List of countries by population, 31st most populous in the world. Baghdad, home to over 8 million people, is the capital city and the List of largest cities of Iraq, largest in the country. Starting in the 6th millennium BC, the fertile plains between Iraq's Tigris and Euphrates rivers, referred to as Mesopotamia, fostered the rise of early cities, civilisations, and empires including Sumer, Akkadian Empire, Akkad, and Assyria. Known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eldiguzids (Atabegs Of Azerbaijan)
The Ildegizids, EldiguzidsC.E. Bosworth, "Ildenizids or Eldiguzids", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Edited by P.J. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs et al., Encyclopأ¦dia of Islam, 2nd Edition., 12 vols. with indexes, etc., Leiden: E. J. Brill, 1960–2005. Vol 3. pp 1110-111. Excerpt 1: "Ildenizids or Eldiguzids, a line of Atabegs of Turkish slave commanders who governed most of northwestern Persia, including Arran, most of Azarbaijan, and Djibal, during the second half of the 6th/12th century and the early decades of the 7th/13th century". Excerpt 2: "The Turkish Ildenizids shared to the full in the Perso-Islamic civilization" or Ildenizids, also known as Atabegs of Azerbaijan ( ''Atabakan-e ؤ€zarbayjan)'' were an Atabegate of the Seljuk Empire, and a Sunni Muslim Turkic dynastyBritannica. ArticleEldegأ¼zid dynasty Eldegأ¼zid dynasty, also spelled Ildigأ¼zid, Ildegأ¼zid, Ildegizid, or Ildenizid, (1137–1225), Iranian atabeg dynasty of Turk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Peoples
Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the Turkic subfamily...". "The Turkic peoples represent a diverse collection of ethnic groups defined by the Turkic languages." According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in the Altai-Sayan region, Mongolia or Tuva.: "The ultimate Proto-Turkic homeland may have been located in a more compact area, most likely in Eastern Mongolia": "The best candidate for the Turkic Urheimat would then be northern and western Mongolia and Tuva, where all these haplogroups could have intermingled, rather than eastern and southern Mongolia..." Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers; they later became nomadic Pastoralism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
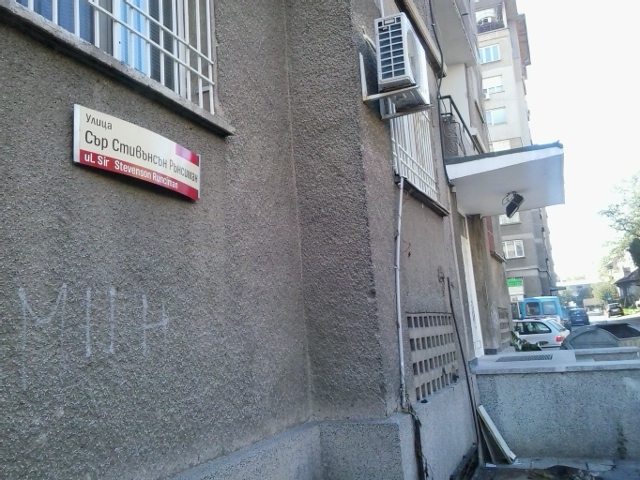
Steven Runciman
Sir James Cochran Stevenson Runciman (7 July 1903 – 1 November 2000), known as Steven Runciman, was an English historian best known for his three-volume '' A History of the Crusades'' (1951–54). His works had a profound impact on the popular conception of the Crusades. Biography Born in Northumberland, he was the second son of Walter and Hilda Runciman. His parents were members of the Liberal Party and the first married couple to sit simultaneously in Parliament. His father was created Viscount Runciman of Doxford in 1937. His paternal grandfather, Walter Runciman, 1st Baron Runciman, was a shipping magnate. He was named after his maternal grandfather, James Cochran Stevenson, the MP for South Shields. Eton and Cambridge Runciman said that he started reading Greek at the age of seven or eight. Later he came to be able to make use of sources in other languages as well: Arabic, Turkish, Persian, Hebrew, Syriac, Armenian and Georgian. A King's Scholar at Eton College, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goghtn
Goght’n (; also mentioned in sources as Goght’an, , and alternatively transliterated as ) was a canton () located in the province of Vaspurakan in historical Armenia. Its borders roughly corresponded to the modern Ordubad Rayon of Nakhichevan, Azerbaijan. Goght’n was well known for winemaking, the quality of its grape and fruit orchards. The region also was the birthplace of a number of prominent Armenian '' gusans'' (minstrels). The ancestors of the renowned twentieth-century Armenian composer and music ethnologist Komitas Vardapet were originally from Goght’n. Some of the region's oldest towns and villages have survived to this day, including Jugha (now Julfa) and Ordvat’ (modern-day Ordubad). History Early to medieval According to Movses Khorenatsi, King Tigran Ervanduni (of the Orontid line) of Armenia settled his wife and his daughters in an area to the east of ( Ararat) and up to Goght’n, in Tambat, Oskiokh, Djaghguyn and other settlements giving them also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julfa, Azerbaijan (city)
Julfa (), formerly Jugha (Armenian: ص‹ص¸ض‚ص²ص،, also transliterated as ''Djugha''), is a city and the capital of the Julfa District of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of Azerbaijan. Julfa is separated by the Aras River from its namesake, the town of Jolfa on the Iranian side of the border. The two towns are linked by a road bridge and a railway bridge. Both Azerbaijan's absolute minimum temperature () and the absolute maximum temperature () were observed in Julfa (and also in Ordubad). History The city is known as ''Jugha'' () in Armenian. The modern-day town of Julfa is located a few kilometers east of the ruins of the historical settlement of Julfa/Jugha, which are situated on a rocky strip of land in between the left bank of the Aras and a steep mountain range.Ghougassian, Vazken S. ï؟½JULFA i. SAFAVID PERIOD†''Encyclopaedia Iranica'', XV/2, pp. 217–224 and XV/3, pp. 225–231. The medieval Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi wrote that Julfa was founded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smbat I Of Armenia
Smbat I (; 850–912/14), sometimes Smbat A Martyr () was the second king of the medieval Kingdom of Armenia of the Bagratuni dynasty, and son of Ashot I. He is the father of Ashot II (known as Ashot Yerkat) and Abas I. Rule Smbat I was crowned king in 892 in Shirakavan (Yerazgavors), following a brief attempt by his uncle Abas to disrupt his succession to the throne. Smbat continued his father's policy of maintaining cordial relations with the Byzantine Empire but remained mindful of the Arabs' fears of the Armeno-Byzantine alliance. Speaking with the Arab '' ostikan'' (governor) Muhammad Ibn Abi'l-Saj (Afshin), Smbat convinced him that the alliance would not only be for the dual benefit of Byzantium and Armenia but would also work to the economic favor of the Arabs. Smbat also achieved a major victory when on April 21, 892, he recaptured the former Armenian capital of Dvin from the Arabs. In some of these endeavors Smbat received strong support from his neighbor to the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |