|
Alice Springs Orogeny
The Alice Springs Orogeny was a major intraplate tectonic (mountain building) episode in central Australia responsible for the formation of a series of large mountain ranges. The deformation associated with the Alice Spring Orogeny caused the vertically-tilted sandstone layers of the iconic Uluru/Ayers Rock. Duration The Alice Springs Orogeny was a long lived event, beginning approximately 450 million years ago and concluding about 300 million years ago,Bradshaw JD, Evans PR (1988). "Palaeozoic tectonics, Amadeus Basin, central Australia". The APEA Journal 28: 267–282 and it involved less than 100 km of distributed shortening. Extent The Alice Springs orogeny was centred in an area that had previously been a marine sedimentary basin, and involved the thrusting up of the underlying metamorphic and igneous rocks of Proterozoic age. The Alice Springs Orogeny had its beginnings in the Late Ordovician, continuing during the Silurian and Devonian, and by the Carboniferous t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons. These processes include those of mountain-building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Principles of tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles can help geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth-surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (also spelled Palaeoproterozoic) is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic eon, and also the longest era of the Earth's geological history, spanning from (2.5–1.6 Ga). It is further subdivided into four geologic periods, namely the Siderian, Rhyacian, Orosirian and Statherian. Paleontological evidence suggests that the Earth's rotational rate ~1.8 billion years ago equated to 20-hour days, implying a total of ~450 days per year. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized. Atmosphere The Earth's atmosphere was originally a weakly reducing atmosphere consisting largely of nitrogen, methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide and inert gases, in total comparable to Titan's atmosphere. When oxygenic photosynthesis evolved in cyanobacteria during the Mesoarchean, the increasing amount of byproduct dioxygen began to deplete the reductants in the ocean, land surface and the atmosphere. Eventually all surface reductant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Orogenies
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period Ma (million years ago) to the start of the Silurian Period Ma. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Northern Territory
The geology of Australia includes virtually all known rock types, spanning a geological time period of over 3.8 billion years, including some of the oldest rocks on earth. Australia is a continent situated on the Indo-Australian plate. Components Australia's geology can be divided into several main sections: the Archaean cratonic shields, Proterozoic fold belts and sedimentary basins, Phanerozoic sedimentary basins, and Phanerozoic metamorphic and igneous rocks. Australia as a separate continent began to form after the breakup of Gondwana in the Permian, with the separation of the continental landmass from the African continent and Indian subcontinent. Australia rifted from Antarctica in the Cretaceous. The current Australian continental mass is composed of a thick subcontinental lithosphere, over thick in the western two-thirds and thick in the younger eastern third. The Australian continental crust, excluding the thinned margins, has an average thickness of , with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
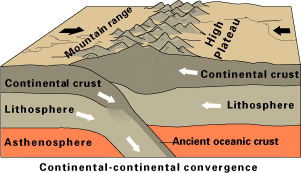
Orogenies Of Australia
Orogeny () is a mountain-building process that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic (or synkinematic) process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word ''orogeny'' comes . Although it was used before him, the American geologist G. K. Gilbert used the term in 1890 to mean the process of mountain-building, as distinguished from epeirogeny. Tectonics Orogeny takes place on the convergent margi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macdonnell Ranges
The MacDonnell Ranges, or Tjoritja in Arrernte language, Arrernte, is a mountain range located in southern Northern Territory. MacDonnell Ranges is also the name given to an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia, interim Australian bioregion broadly encompassing the mountain range, with an area of .IBRA Version 6.1 data The range is a long series of mountains in central Australia, consisting of parallel ridges running to the east and west of Alice Springs. The mountain range contains many spectacular gaps and gorges as well as areas of Indigenous Australian, Aboriginal significance. The ranges were named after Sir Richard Graves MacDonnell, Richard MacDonnell (the Governor of South Australia at the time) by John McDouall Stuart, whose 1860 expedition reached them in April of that year. The Horn Exped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohorovičić Discontinuity
The Mohorovičić discontinuity ( ; )usually called the Moho discontinuity, Moho boundary, or just Mohois the boundary between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's mantle, mantle of Earth. It is defined by the distinct change in velocity of seismic waves as they pass through changing densities of rock. The Moho lies almost entirely within the lithosphere (the hard outer layer of the Earth, including the crust). Only beneath mid-ocean ridges does it define the lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary (the depth at which the mantle becomes significantly ductile). The Mohorovičić discontinuity is below the ocean floor, and beneath typical continental crusts, with an average of . Named after the pioneering Croats, Croatian seismologist Andrija Mohorovičić, the Moho separates both the oceanic crust and continental crust from the underlying mantle. The Mohorovičić discontinuity was first identified in 1909 by Mohorovičić, when he observed that seismograms from Depth of focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraplate Deformation
Intraplate deformation is the folding, breaking, or flow of the Earth's crust within plates instead of at their margins. This process usually occurs in areas with especially weak crust and upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, such as the Tibetan Plateau (Figure 1). Intraplate deformation brings another aspect to Plate tectonics, plate tectonic theory. Crustal deformation processes The theory of plate tectonics states that the Earth's lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) is made up of rigid plates that "float" on top of the asthenosphere (lower mantle) and move relative to one another. As the plates move, the crust deforms dominantly along the plate margins. Intraplate deformation differs from that respect by the observation that deformation can occur anywhere the crust is weak and not just at plate margins. Deformation is the folding, breaking, or flow of rocks. There are many different types of crustal deformation depending on whether the rocks are brittle or Ductility, ductile. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petermann Orogeny
The Petermann Orogeny was an Australian intracontinental event that affected basement rocks of the northern Musgrave Province and Ediacaran (Proterozoic) sediments of the (now) southern Amadeus Basin between 630-520 Ma. The remains are seen today in the Petermann Ranges. Prior to the Petermann Orogeny, which resulted in exhumation of the Musgrave Block, the Amadeus Basin was contiguous with the Officer Basin in South Australia. The extent and effect of the Petermann Orogen appears to be relatively confined, occurring most pervasively within the central northern-Musgrave Block. Here, older Musgravian (~1200-1150 Ma) fabrics are partially to completely overprinted by sub-eclogite-facies mineral assemblages (11-12 kbar at 650 °C). The Woodroofe Thrust, Davenport Shear Zone and Mann Fault accommodated much of the 30–40 km exhumation. Exhumation of the Musgrave Block (and overlying sediments) resulted in successive unroofing and deposition of rock types suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogenic
Orogeny () is a mountain-building process that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic (or synkinematic) process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word ''orogeny'' comes . Although it was used before him, the American geologist G. K. Gilbert used the term in 1890 to mean the process of mountain-building, as distinguished from epeirogeny. Tectonics Orogeny takes place on the convergent margi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |