|
Alfred Lämmerhirt
Carl Louis Alfred Traugott Lämmerhirt (; 21 April 1839 – 10 July 1899) was a German industrialist, engineer and founding member of Westfalia Dinnendahl Gröppel, initially based in Bochum. He was the father-in-law of Hugo Siepmann and Robert Fricke. Early life and education Lämmerhirt was born 21 April 1839 in Stolberg (Harz), Kingdom of Prussia (presently Germany), the eldest of six children, to Christian Lämmerhirt, a district court secretary and later vice mayor of Suhl, and Karoline Lisette (née Steher). He completed the Real school whilst living with a great-uncle in Nordhausen due to the provincial location of his hometown and limited educational possibilities. After he completed a technical apprenticeship in Erfurt, he decided to become an engineer. He enrolled and studied mechanical engineering at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology where he belonged to the Fidelitas fraternity. Career After his graduation, he initially worked as stoker/fireman, for the Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
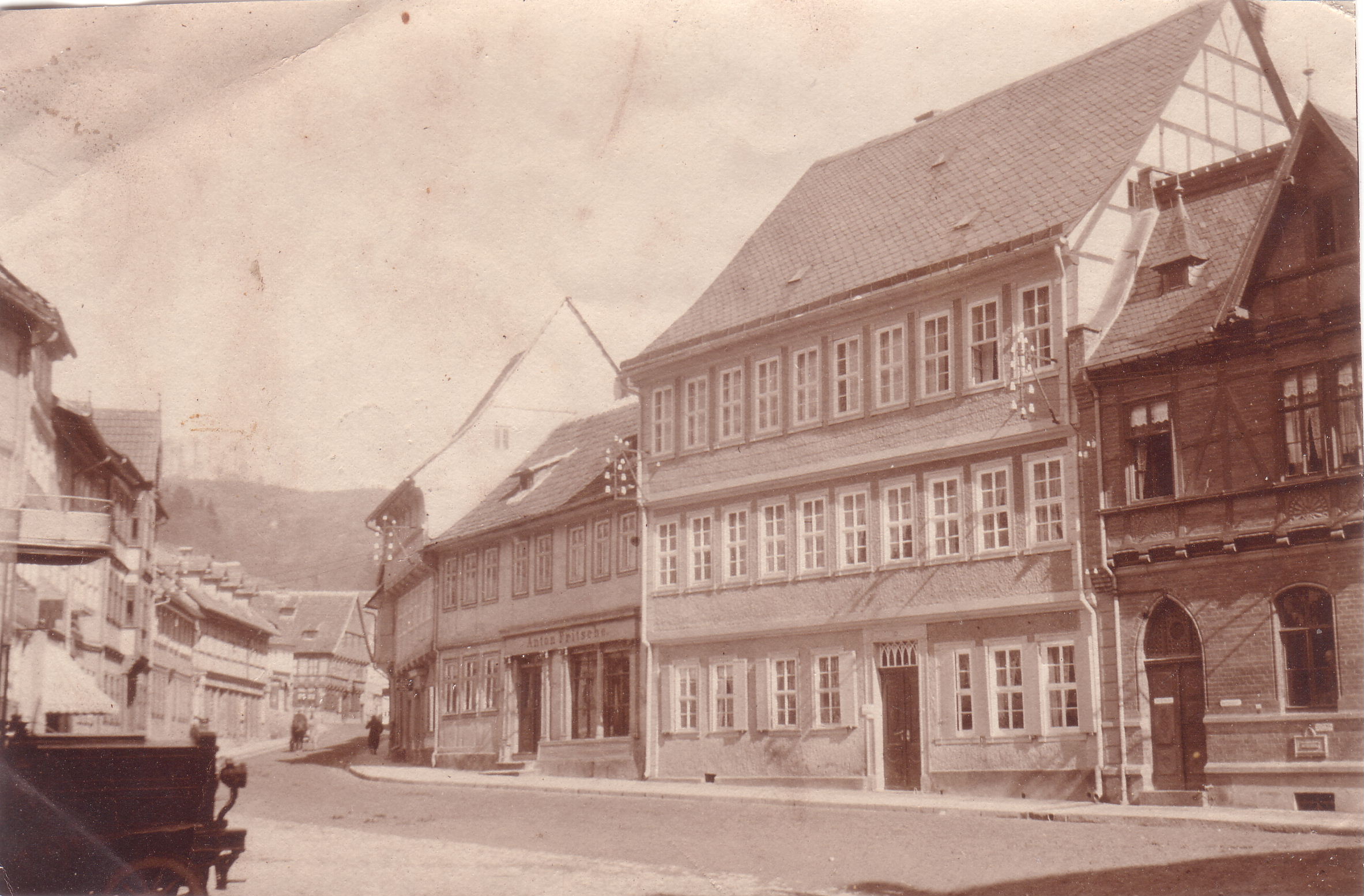
Stolberg (Harz)
Stolberg (pronounced Stoul-berg ) is a town (sometimes itself called 'Harz' in historical references) and a former municipality in the district of Mansfeld-Südharz, in the German State of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated in the southern part of the Harz mountains, about west of Sangerhausen, and northeast of Nordhausen. Since 1 September 2010, it has been part of the municipality of Südharz. History Stolberg was established as a settlement for miners in around AD 1000, although there is evidence of mining in the area as far back as 794. The name is derived from the German words ''Stollen'' = " ininggallery" and ''Berg'' = "hill". Iron, copper, silver, tin and gold were extracted there. Town status was awarded to Stolberg (Harz) before 1300. During the German Peasants' War, Stolberg was the site of several battles, the peasants being led by Thomas Müntzer who was born in the town. On 2 May 1525, rebellious peasants invaded the town and forced the ruling Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne-Minden Railway Company
The Cologne-Minden Railway Company (German, old spelling: ''Cöln-Mindener Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', ''CME'') was along with the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company and the Rhenish Railway Company one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Founding The founding of the Cologne-Minden Railway Company in 1843 in Cologne ended a long struggle for a railway line between the Rhineland and the German North Sea ports, as well as the Prussian capital of Berlin. From the 1830s several railway committees in the cities of Düsseldorf, Cologne and Aachen attempted to find a solution with each other and the Prussian government. The focus of all these efforts was to avoid the Dutch duties on trade on the Rhine, which significantly increased the cost of import and export of goods via the Rhine. Some of the Cologne committee members under David Hansemann (1790–1864)—a merchant and banker fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siepmann
Siepmann Industries (; ; colloquially referred to as Siepmann) is a German industrial concern headquartered in Warstein, Germany. Founded in 1891, Siepmann is primarily known for being active in the coal, steel, ammunition, armaments industry as well as important supplier to the automotive, maritime and energy industries. The concern is primarily made up by two arms Siepmann-Werke GmbH & Co KG ( drop steel foundry) and PERSTA-Stahlarmaturen GmbH & Co KG (valves) and historically belonged among the most important employers of the region, at peak employing over 3,000 employees, and important supplier to Germany during World War I and World War II, such as for curb chains and tanks. Siepmann was the second largest drop steel foundry after the Krupp concern. Overview Siepmann is primarily controlled by the Hugo Siepmann branch of the family. The descendants of Emil Siepmann are non-active minority owners. The operations are still at the same location where it moved in 1909, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city (by area and population) of the Ruhr as well as the largest city of Westphalia. It lies on the Emscher and Ruhr (river), Ruhr rivers (tributaries of the Rhine) in the Rhine-Ruhr, Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region, the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, second biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union, and is considered the administrative, commercial, and cultural centre of the eastern Ruhr. Dortmund is the second-largest city in the Low German dialect area, after Hamburg. Founded around 882,:File:Boevinghausen erwaehnung.jpg, Wikimedia Commons: First documentary reference to Dortmund-Bövinghausen from 882, contribution-list of the Werden Abbey (near Essen), North-Rhine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krupp
Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer during both world war, world wars. It produced battleship, battleships, U-boats, tanks, howitzers, guns, utilities, and hundreds of other commodities. The company also produced steel used to build railroads in the United States and to cap the Chrysler Building. After the Nazi Germany, Nazis seized power in Germany, Krupp supported the regime and was one of many German businesses that profited from forced labour under German rule during World War II, slave labor during World War II. Upon the war's end, the head of the company, Alfried Krupp, was tried and convicted as a war criminal for employing prisoners of war, foreign civilians and concentration camp inmates under inhumane conditions in support of the Nazi war effort. Despite being senten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin-Wannsee
Wannsee () is a locality in the southwestern Berlin borough of Steglitz-Zehlendorf, Germany. It is the westernmost locality of Berlin. In the quarter there are two lakes, the larger ''Großer Wannsee'' (Greater Wannsee) and the '' Kleiner Wannsee'' (Little Wannsee), located on the Havel and separated by the Wannsee Bridge. The larger of the two lakes covers an area of and has a maximum depth of . The municipality is the location of the compound where the mass extermination of Europe's Jewish population, known as the "Final Solution", was planned and approved at the Wannsee Conference in early 1942 by the Nazi Party's highest-ranking officials, including Reinhard Heydrich and Adolf Eichmann. Geography Overview At the western rim of the Wannsee locality the Glienicke Bridge connects it with the city of Potsdam. The late neoclassical Glienicke Palace as well as the Pfaueninsel are nearby. Since 1990 these palaces and parks have formed part of the Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Officer
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air force, air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-General, Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies, General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently grante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants. The territory of the region is almost identical with the historic Province of Westphalia, which was a part of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815 to 1918 and the Free State of Prussia from 1918 to 1946. In 1946, Westphalia merged with North Rhine, another former part of Prussia, to form the newly created state of North Rhine-Westphalia. In 1947, the state with its two historic parts was joined by a third one: Lippe, a former Principality of Lippe, principality and Free State of Lippe, free state. The seventeen Districts of Germany, districts and nine Independent city#Germany, independent cities of Westphalia and Lippe (district), the single district of Lippe are members of the North Rhine-Westphalia#Subdivisions, Westphalia-Lippe Regional Association (''Landschaftsverband Westfalen-Lippe''). Previo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotthard Tunnel
The Gotthard Tunnel (, ) is a railway tunnel that forms the summit of the Gotthard Railway in Switzerland. It connects Göschenen with Airolo and was the first tunnel through the Saint-Gotthard Massif in order to bypass the St Gotthard Pass. It was built as single bore tunnel accommodating a standard gauge double-track railway throughout. When opened in 1882, the Gotthard Tunnel was the longest tunnel in the world. The tunnel rises from the northern portal at Göschenen () and the highest point () is reached after approximately . After two more kilometers, the border between the cantons of Uri and Ticino is passed; after another , the tunnel ends at the southern portal near to Airolo (). The trip takes about seven to eight minutes by train. Services are operated by the Swiss Federal Railways. History Background The origins of the Gotthard Tunnel and its construction can be traced back to the widely-felt desire to improve interconnectivity between the European nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, highest population within its city limits of any city in the European Union. The city is also one of the states of Germany, being the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country by area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.6 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region, as well as the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, fifth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulzer (manufacturer)
Sulzer Ltd. is a Swiss industrial engineering and manufacturing firm, founded by Salomon Sulzer-Bernet in 1775 and established as Sulzer Brothers Ltd. (Gebrüder Sulzer) in 1834 in Winterthur, Switzerland. Today it is a publicly traded company with some 180 manufacturing facilities and service centers around the world. The company's shares are listed on the Swiss Stock Exchange. Sulzer specializes in technologies for fluids of all types. The company's inventions includes the first precision valve steam engine (1876), the Sulzer diesel engine (1898) and artificial hip joints (1965). Sulzer Brothers helped develop shuttleless weaving and their core business in the 1970s and 1980s was loom manufacturing. Rudolf Diesel worked for Sulzer in 1879 and in 1893 Sulzer bought certain rights to diesel engines. Sulzer built their first diesel engine in 1898. Organization Corporate structure The company is organized into three divisions: * Flow: Pumping solutions - it produces pumps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |