|
Alexey Kuznetsov
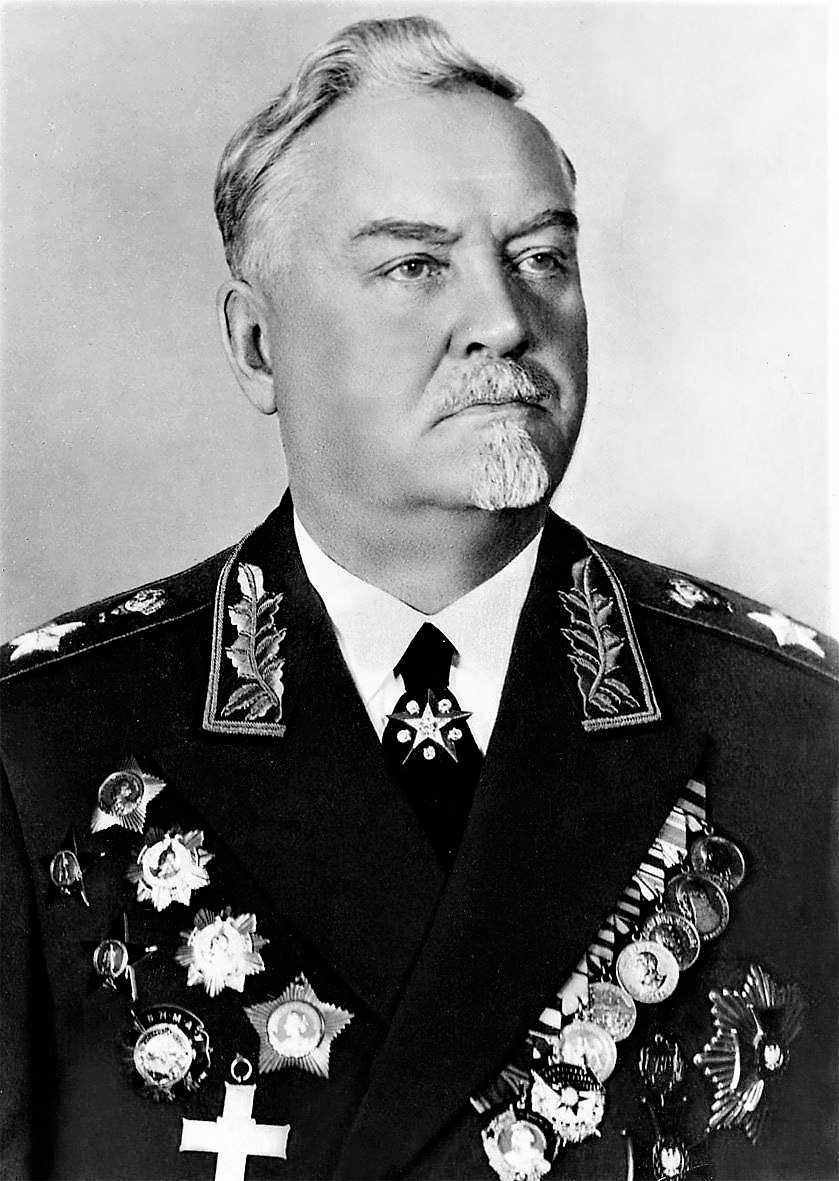
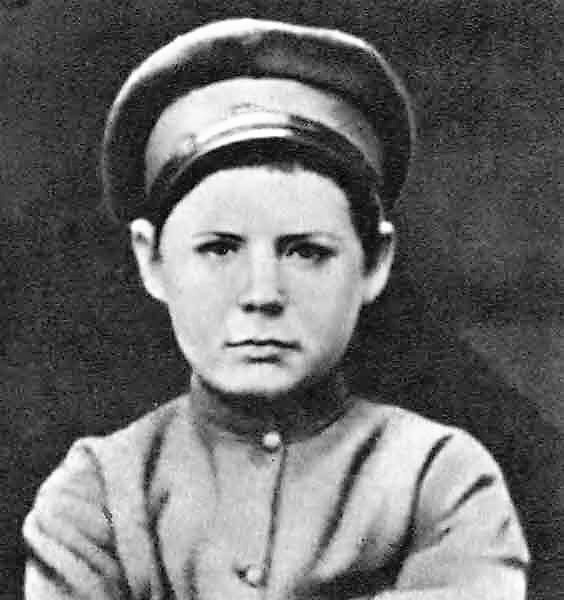
Alexey Alexandrovich Kuznetsov (, in Borovichi – 1 October 1950, in Moscow) was a Soviet statesman, CPSU (since 1925) functionary, Lieutenant General, member of CPSU Central Committee (1939-1949). He was Second Secretary (deputy leader) to Leningrad CPSU ''gorkom'' (city committee) and '' obkom'' (oblast committee), and, during the Siege of Leningrad, helped organize the city's defense. For his work during the siege, he was promoted to First Secretary in 1945. Zhdanov was thought to want Kuznetsov to replace him as CC Party Chairman. Kuznetsov was also believed to be a possible replacement for Stalin on the latter's death. He was a strong supporter of Stalin, who appointed him to head the security functions of the party, showing how much the Soviet leader trusted him. The beginning of Kuznetsov’s fall came when Stalin demoted him and returned him to a minor post in Leningrad (a frequent sign that the subject was destined for a final fall). This may have been because Kuzne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad Regional Committee Of The Communist Party Of The Soviet Union
The Leningrad Regional Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, commonly referred to as the Leningrad CPSU obkom, was the position of highest authority in Leningrad Oblast during most of the existence of the Soviet Union. The position was created on 1 August 1927, and abolished on 29 August 1991 although most authority was lost in June that year to the position of Governor of Leningrad Oblast. The First Secretary was a de facto appointed position usually by the Politburo or the General Secretary himself. First Secretaries The following individuals served as first secretaries of the Leningrad Regional Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Second Secretary See also *Leningrad City Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union The Leningrad City Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, commonly referred to as the Leningrad CPSU gorkom, was the position of highest authority in the city of Leningrad (until January 26, 1924 Petrograd) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Committee
Central committee is the common designation of a standing administrative body of communist parties, analogous to a board of directors, of both ruling and nonruling parties of former and existing socialist states. In such party organizations, the committee would typically be made up of delegates elected at a party congress. In those states where it constituted the state power, the central committee made decisions for the party between congresses and usually was (at least nominally) responsible for electing the politburo. In non-ruling communist parties, the central committee is usually understood by the party membership to be the ultimate decision-making authority between congresses once the process of democratic centralism has led to an agreed-upon position. Non-communist organizations are also governed by central committees, such as the right-wing Likud party in Israel, the North American Mennonite Church and Alcoholics Anonymous, the Chinese Kuomintang as well as the former Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The Communist Party Of The Soviet Union Executed By The Soviet Union
Member may refer to: * Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon * Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set * In object-oriented programming, a member of a class ** Field (computer science), entries in a database ** Member variable, a variable that is associated with a specific object * Limb (anatomy), an appendage of the human or animal body ** Euphemism for penis * Structural component of a truss, connected by nodes * User (computing), a person making use of a computing service, especially on the Internet * Member (geology), a component of a geological formation * Member of parliament * The Members, a British punk rock band * Meronymy, a semantic relationship in linguistics * Church membership, belonging to a local Christian congregation, a Christian denomination and the universal Church * Member, a participant in a club or learned society A learned society (; also learned academy, scholarly society, or academic association) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian People Executed By The Soviet Union
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including: *Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and people of Russia, regardless of ethnicity *Russophone, Russian-speaking person (, ''russkogovoryashchy'', ''russkoyazychny'') * Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *Russian alphabet * Russian cuisine *Russian culture *Russian studies Russian may also refer to: * Russian dressing *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith * Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series * Russian (solitaire), a card game * "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album '' '' by Caravan Palace *Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 *The South African name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Politicians
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medal "For The Defence Of Leningrad"
The Medal "For the Defence of Leningrad" (russian: Медаль «За оборону Ленинграда») was a World War II campaign medal of the Soviet Union established on December 22, 1942 by decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR to recognise the valour and hard work of the Soviet civilian and military defenders of Leningrad during the 872-day siege of the city by the German armed forces between September 8, 1941 and January 27, 1944. The medal's statute was later amended by Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet on March 8, 1945. and again one last time on July 18, 1980 by decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR № 2523-X. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orders Of Lenin
The Order of Lenin (russian: Орден Ленина, Orden Lenina, ), named after the leader of the Russian October Revolution, was established by the Central Executive Committee on April 6, 1930. The order was the highest civilian decoration bestowed by the Soviet Union. The order was awarded to: * Civilians for outstanding services rendered to the State * Members of the armed forces for exemplary service * Those who promoted friendship and cooperation between people and in strengthening peace * Those with meritorious services to the Soviet state and society From 1944 to 1957, before the institution of a specific length of service medals, the Order of Lenin was also used to reward 25 years of conspicuous military service. Those who were awarded the titles "Hero of the Soviet Union" and " Hero of Socialist Labour" were also given the order as part of the award. It was also bestowed on cities, companies, factories, regions, military units, and ships. Various educational institut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rehabilitate (Soviet)
Rehabilitation (russian: реабилитация, transliterated in English as ''reabilitatsiya'' or academically rendered as ''reabilitacija'') was a term used in the context of the former Soviet Union and the post-Soviet states. Beginning after the death of Stalin in 1953, the government undertook the political and social restoration, or political rehabilitation, of persons who had been repressed and criminally prosecuted without due basis. It restored the person to the state of acquittal. In many cases, rehabilitation was posthumous, as thousands of victims had been executed or died in labor camps. The government also rehabilitated several minority populations which it had relocated under Stalin, and allowed them to return to their former territories and in some cases restored their autonomy in those regions. Post-Stalinism epoch The government started mass amnesty of the victims of Soviet repressions after the death of Joseph Stalin. In 1953, this did not entail any form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Bulganin
Nikolai Alexandrovich Bulganin (russian: Никола́й Алекса́ндрович Булга́нин; – 24 February 1975) was a Soviet politician who served as Minister of Defense (1953–1955) and Premier of the Soviet Union (1955–1958) under Nikita Khrushchev, following service in the Red Army and as defence minister under Joseph Stalin. Early life and career Bulganin was born in 1895 in Nizhny Novgorod. The son of an office worker, he was of Russian ethnicity. He joined the Bolshevik Party in March 1917 and was recruited in 1918 into the Cheka, the Bolshevik regime's political police, where he served until 1922. During the summer of 1918, he worked with Lazar Kaganovich, the local communist leader, in imposing the Red Terror in Nizhny Novgorod. He worked with Kaganovich again in Turkestan in 1920. After the Russian Civil War (1917-1923), Bulganin became an industrial manager and worked in the electricity administration until 1927. He was the director of the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Kirov
Sergei Mironovich Kirov ( né Kostrikov; 27 March 1886 – 1 December 1934) was a Soviet politician and Bolshevik revolutionary whose assassination led to the first Great Purge. Kirov was an early revolutionary in the Russian Empire and member of the Bolshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. Kirov became an Old Bolshevik and personal friend to Joseph Stalin, rising through the Communist Party of the Soviet Union ranks to become head of the party in Leningrad and a member of the Politburo. On 1 December 1934, Kirov was shot and killed by Leonid Nikolaev at his offices in the Smolny Institute for unknown reasons; Nikolaev and several suspected accomplices were convicted in a show trial and executed less than 30 days later. Kirov's death was later used as a pretext for Stalin's escalation of political repression in the Soviet Union and the events of the Great Purge, with complicity as a common charge for the condemned in the Moscow Trials. Kirov's ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet Union, Soviet city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II. Nazi Germany, Germany's Army Group North advanced from the south, while the German-allied Finnish Army, Finnish army invaded from the north and completed the ring around the city. The siege began on 8 September 1941, when the Wehrmacht severed the last road to the city. Although Soviet forces managed to open a narrow land corridor to the city on 18 January 1943, the Red Army did not lift the siege until 27 January 1944, 872 days after it began. The blockade became one of the List of sieges, longest and most destructive sieges in history, and it was possibly the List of battles by casualties#Sieges and urban combat, cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)