|
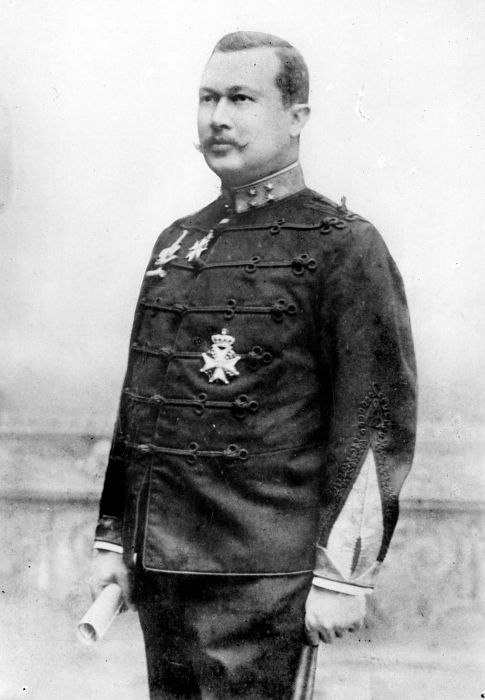
Alexander Willem Frederik Idenburg
Alexander Willem Frederik Idenburg (23 July 1861 – 28 February 1935) was a Dutch military officer and politician of the Anti Revolutionary Party who served as Governor-General of Suriname from 1905 until 1908, and the Dutch East Indies from 1909 until 1916. He also served as Minister of Colonies on three occasions between 1902 and 1919. Idenburg served on the Council of State from 1925 until his death in 1935.A.W.F. Idenburg ''Parlement & Politiek''. Retrieved on 17 January 2015. Biography Idenburg was born on 23 July 1861 in Rotterdam, Netherlands. At the age of 16, he was send to Koninklij ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of State (Netherlands)
The Council of State ( nl, ) is a constitutionally established advisory body in the Netherlands to the government and States General that officially consists of members of the royal family and Crown-appointed members generally having political, commercial, diplomatic or military experience. It was founded in 1531, making it one of the world's oldest still-functioning state organisations. The Council of State must be consulted by the cabinet on proposed legislation before a law is submitted to parliament. The Council of State Administrative Law division also serves as one of the four highest courts of appeal in administrative matters. The King is president of the Council of State but he seldom chairs meetings. The Vice-President of the Council of State chairs meetings in his absence and is the ''de facto'' major personality of the institution. Under Dutch constitutional law, the Vice-President of the Council is acting head of state when there is no monarch such as if the royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huygens Institute For The History Of The Netherlands
The Huygens Institute for the History of the Netherlands was formed on January 1, 2011 through a merger of the Institute of Dutch History ( nl, 'Instituut voor Nederlandse Geschiedenis', ING) a research institute of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research, and the Huygens Instituut of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (founded in 1808). The institute is located in Amsterdam, Netherlands, in the Spinhuis building. The institute is made up of three thematically oriented sections: one for the study of political and institutional history, one for the study of the history of science, and a third one for the study of literature. The first section dates back to 1902, when it was established as the "Commissie van Advies voor de 's Rijks Geschiedkundige Publicatien" (Advisory Commission for Publications in the History of the Empire), under the directorship of the historian Herman Theodoor Colenbrander. Huygens ING researches texts and sources from the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Douwes Dekker
Ernest François Eugène Douwes Dekker also known as '' Setyabudi'' or ''Setiabudi'' (8 October 1879 – 28 August 1950) was an Indonesian- Dutch nationalist and politician of Indo descent. He was related to the famous Dutch anti-colonialism writer Multatuli, whose real name was Eduard Douwes Dekker ("Douwes Dekker" being their surname). In his youth, he fought in the Second Boer War in South Africa on the Boer side. His thoughts were highly influential in the early years of the Indonesian freedom movement. After Indonesian independence, he adopted the Sundanese name Danoedirdja Setiaboedi. Early years Douwes Dekker was born in Pasuruan, in the north east of Java, 80 km south of Surabaya. His father was Auguste Henri Edouard Douwes Dekker, a broker and bank agent, of a Dutch family living in the then- Dutch East Indies. His Indo (Eurasian) mother was Louisa Margaretha Neumann, of half-German and half- Javanese descent. Douwes Dekker's great-uncle was the famous writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarekat Islam
Sarekat Islam or Syarikat Islam ( 'Islamic Association' or 'Islamic Union'; SI) was an Indonesian socio-political organization founded at the beginning of the 20th Century during the Dutch colonial era. Initially, SI served as a cooperative of Muslim Javanese batik traders to compete with the Chinese-Indonesian big traders. From there, SI rapidly evolved into a nationalist political organization that demanded self-governance against the Dutch colonial regime and gained wide popular support. SI was especially active during the 1910s and the early 1920s. By 1916, it claimed 80 branches with a total membership of around 350,000. SI was eventually embroiled in an internal conflict between the Islamic moderates and the radical communist members who urged firmer anti-colonialist and anti-capitalist actions. In 1921, the organization was split and communist members founded a separate entity known as the Sarekat Islam Merah (Red Islamic Association) which was absorbed into the Commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampung (village)
A kampong (''kampung'' in Malay and Indonesian) is the term for a village in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore and a "port" in Cambodia. The term applies to traditional villages, especially of the indigenous people, and has also been used to refer to urban slum areas and enclosed developments and neighbourhoods within towns and cities in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Cambodia, Sri Lanka and Christmas Island. The traditional ''kampong'' village designs and architecture have been targeted for reform by urbanists and modernists and have also been adapted by contemporary architects for various projects. The English word " compound", when referring to a development in a town, is derived from the Malay word of . Brunei In Brunei, the term kampong (also kampung) primarily refers to the third- and lowest-level subdivisions after districts ( ms, daerah) and mukim (equivalent to subdistrict). Some kampong divisions are sufficiently villages by anthropologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotfried Coenraad Ernst Van Daalen
Gotfried Coenraad Ernst "Frits" van Daalen (23 March 1863 – 22 February 1930) was an Indo people, Indo (Eurasian) Lieutenant General of the Royal Dutch East Indies Army who served in the Dutch East Indies. He was also the appointed Governor of Aceh, Governor of Aceh from 1905 until 1908. Biography Van Daalen was named after his Dutch father ''Gotfried Coenraad Ernst (Frits) van Daalen'' (born in 's-Hertogenbosch, the Netherlands 23 July 1836 and died in Surabaya, 13 May 1889), also a famous, decorated KNIL officer and veteran of the Aceh War, who was discharged from service as a consequence of a scandal where he publicly offended the Governor-General of the colony. As a young officer in the rank of Lieutenant and Captain Van Daalen was awarded several prestigious military distinctions for proven bravery. He first became ''Knight of the Military William Order'' in 1890, was awarded the ''Honorary Sabre'' by the Dutch monarch in 1897, followed by becoming an ''Officer of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surinamese Guilder
The guilder ( nl, gulden; ISO 4217 code: ''SRG'') was the currency of Suriname until 2004, when it was replaced by the Surinamese dollar. It was divided into 100 cents. Until the 1940s, the plural in Dutch was ''cents'', with ''centen'' appearing on some early paper money, but after the 1940s the Dutch plural became ''cent''. History The Surinamese guilder was initially at par with the Dutch guilder. In 1940, following the occupation of the Netherlands, the currency (along with the Netherlands Antillean guilder) was pegged to the U.S. dollar at a rate of 1.88585 guilders = 1 dollar. The Surinamese guilder began to lose value from high inflation in the beginning of the 1980s, when a currency black market emerged. It was replaced by the Surinamese dollar on 1 January 2004 at a rate of 1 dollar = 1,000 guilders. To save cost of manufacturing, coins of less than 5 guilders (all denominated in cents) were made legal for their face value in the new currency. Thus, these coins increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunday Law
Blue laws, also known as Sunday laws, Sunday trade laws and Sunday closing laws, are laws restricting or banning certain activities on specified days, usually Sundays in the western world. The laws were adopted originally for religious reasons, specifically to promote the observance of the Christian day of worship, but since then have come to serve secular purposes as well. Blue laws commonly ban certain business and recreational activities on Sundays and impose restrictions on the retail sale of hard goods and consumables, particularly alcoholic beverages An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The c .... The laws also place limitations on a range of other endeavors, including travel, fashions, hunting, professional sports, theatre, stage performances, motion pictures, movie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New West Indian Guide
The ''New West Indian Guide'' (''Nieuwe West-Indische Gids'') is a peer-reviewed academic journal founded by the Royal Netherlands Institute of Southeast Asian and Caribbean Studies. It was established in 1919 by Herman Benjamins and covers research on anthropology, art, archaeology, economics, geography, history, political science, and linguistics Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Lingu ... of the Caribbean. Brill acquired the journal in 2012. See also * Open access in the Netherlands References External links New West Indian Guide at University of Florida Digital Collections English-language journals Publications established in 1919 Caribbean studies journals Quarterly journals Brill Publishers academic journals {{area-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Representatives (Netherlands)
The House of Representatives (, pronounced ; commonly referred to as the ', literally "Second Chamber of the States General") is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of the Netherlands, the States General, the other one being the Senate. It has 150 seats, which are filled through elections using party-list proportional representation. Generally, the house is located in the Binnenhof in The Hague, however, it has temporarily moved to the former building of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs at Bezuidenhoutseweg 67 in the Hague while the Binnenhof is being renovated. Name Although the body is officially called the "House of Representatives" in English, it is not a direct translation of its official Dutch name, the "Second Chamber of the States General", "Second Chamber" or more colloquially just the "Chamber". Rather than "representative" (''afgevaardigde''), a member of the House is referred to as ''(Tweede) Kamerlid'', or "member of the (Second) Chamber". Functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Kuyper
Abraham Kuyper (; ; 29 October 1837 – 8 November 1920) was the Prime Minister of the Netherlands between 1901 and 1905, an influential neo-Calvinist theologian and a journalist. He established the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands, which upon its foundation became the second largest Calvinist denomination in the country behind the state-supported Dutch Reformed Church. In addition, he founded the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, the Anti-Revolutionary Party, and a newspaper. In religious affairs, he sought to adapt the Dutch Reformed Church to challenges posed by the loss of state financial aid and by increasing religious pluralism in the wake of splits that the church had undergone in the 19th century, rising Dutch nationalism, and the Arminian religious revivals of his day which denied predestination. He vigorously denounced modernism in theology as a fad that would pass away. In politics, he dominated the Anti-Revolutionary Party (ARP) from its founding in 1879 to his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |