|
Alexander Kompaneyets
Alexander Solomonovich Kompaneyets (Russian: Александр Соломонович Компанеец) was born on January 4, 1914, in Ekaterinoslav, Russian Empire (now Dnipro, Ukraine) and died on August 19, 1974, in Palanga, Lithuania. He was a prominent physicist, author of a number of textbooks, and collaborator on the Soviet atomic bomb project who lived mainly in Moscow. Life Kompaneyets was a student of Lev Landau in Kharkiv in the 1930s, where he dealt with solid state physics (electrical conductivity in metals and semiconductors). In 1936 he received his doctorate (candidate title) and habilitated in 1939 (Russian doctorate). He was a professor at the Institute of Chemical Physics at the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow (where he worked from 1946 until the end of his life) and is best known for his introductory textbook on theoretical physics. He also dealt with the physics of detonation, which he wrote about in a book with Yakov Zeldovich, and generally about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnipro
Dnipro is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper River, Dnipro River, from which it takes its name. Dnipro is the Capital (political), administrative centre of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. It hosts the administration of Dnipro urban hromada. Dnipro has a population of Archeological evidence suggests the site of the present city was settled by Cossacks, Cossack communities from at least 1524. Yekaterinoslav ("glory of Catherine") was established by decree of the Emperor of all the Russias, Russian Empress Catherine the Great in 1787 as the administrative center of Novorossiya Governorate, Novorossiya. From the end of the 19th century, the town attracted foreign capital and an international, multi-ethnic workforce exploiting Kryvbas iron ore and Donbas coal. Renamed Dnipropetrovsk in 1926 after the Ukrainian Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Communist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkiv
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.Kharkiv "never had eastern-western conflicts" , ''Euronews'' (23 October 2014) Located in the northeast of the country, it is the largest city of the historic region of Sloboda Ukraine. Kharkiv is the administrative centre of Kharkiv Oblast and Kharkiv Raion. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine in early 2022, it had an estimated population of 1,421,125. Founded in 1654 as a Cossacks, Cossack fortress, by late 19th century Kharkiv had developed within the Russian Empire as a major commercial and industrial centre. From December 1919 to January 1934, Kharkiv was the capital of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Physicists
This list of Russian physicists includes the famous physicists from the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation. Alphabetical list __NOTOC__ A *Alexei Alexeyevich Abrikosov, Alexei Abrikosov, discovered how magnetic flux can penetrate a superconductor (the Abrikosov vortex), Nobel Prize winner *Franz Aepinus, related electricity and magnetism, proved the electric nature of pyroelectricity, explained electric polarization and electrostatic induction, invented Achromatic lens, achromatic microscope *Zhores Alferov, inventor of modern heterotransistor, Nobel Prize winner *Sergey Alekseenko, director of the Kutateladze Institute of Thermophysics, Global Energy Prize recipient *Artem Alikhanian, a prominent researcher of cosmic rays, inventor of wide-gap track spark chamber *Abram Alikhanov, nuclear physicist, a prominent researcher of cosmic rays, built the first nuclear reactors in the USSR, founder of Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP) *S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yulii Khariton
Yulii Borisovich Khariton (; 27 February 1904 – 18 December 1996) was a Russian people, Russian physicist who was a leading scientist in the former Soviet atomic bomb project, Soviet program of nuclear weapons. Since the initiation of the Soviet program of developing the Soviet atomic bomb project, atomic bomb by Joseph Stalin in 1943, Khariton was the "chief nuclear weapon designer" and remained associated with the Soviet program for nearly History of the Soviet Union, four decades. In honour of the centennial of his birthday in 2004, his image appeared on a Russian postal stamp by the Government of Russia, Russian government. Biography Family, early life and education Yulii Borisovich Khariton was born in Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire, to an ethnic middle class History of the Jews in Russia, Russian Jewish family, on 27 February 1904. His father, Boris Osipovich Khariton, was a Political journalism, political journalist, editor, and publisher who had attained a LLB, law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunyaev–Zeldovich Effect
The Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect (named after Rashid Sunyaev and Yakov B. Zeldovich and often abbreviated as the SZ effect) is the spectral distortion of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) through inverse Compton scattering by high-energy electrons in galaxy clusters, in which the low-energy CMB photons receive an average energy boost during collision with the high-energy cluster electrons. Observed distortions of the cosmic microwave background spectrum are used to detect the disturbance of density in the universe. Using the Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect, dense clusters of galaxies have been observed. Overview The Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect was predicted by Rashid Sunyaev and Yakov Zeldovich to describe anisotropies in the CMB. The effect is caused by the CMB interacting with high energy electrons. These high energy electrons cause inverse Compton scattering of CMB photons which causes a distortion in the radiation spectrum of the CMB. The Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect is mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashid Sunyaev
Rashid Alievich Sunyaev (, ; born 1 March 1943 in Tashkent, USSR) is a German, Soviet, and Russian astrophysicist of Tatar descent. He got his MS degree from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) in 1966. He became a professor at MIPT in 1974. Sunyaev was the head of the High Energy Astrophysics Department of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and has been chief scientist of the Academy's Space Research Institute since 1992. He has also been a director of the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Garching, Germany since 1996, and Maureen and John Hendricks Distinguished Visiting Professor in the School of Natural Sciences at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton since 2010. In February 2022, he signed an open letter from Russian scientists and science journalists condemning Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Works Sunyaev and Yakov B. Zeldovich developed the theory for the evolution of density fluctuations in the early universe. They predicted the patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Atomic Bomb Project
The Soviet atomic bomb project was authorized by Joseph Stalin in the Soviet Union to develop nuclear weapons during and after World War II. Russian physicist Georgy Flyorov suspected that the Allied powers were secretly developing a " superweapon" since 1939. Flyorov urged Stalin to start a nuclear program in 1942. Early efforts mostly consisted of research at Laboratory No. 2 in Moscow, and intelligence gathering of Soviet-sympathizing atomic spies in the US Manhattan Project. Subsequent efforts involved plutonium production at Mayak in Chelyabinsk and weapon research and assembly at KB-11 in Sarov. After Stalin learned of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the nuclear program was accelerated through intelligence gathering about the Manhattan Project and German nuclear weapon project. Espionage coups, especially via Klaus Fuchs and David Greenglass, included detailed descriptions of the implosion-type Fat Man bomb and plutonium production. In the final mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compton Scattering
Compton scattering (or the Compton effect) is the quantum theory of high frequency photons scattering following an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. Specifically, when the photon hits electrons, it releases loosely bound electrons from the outer valence shells of atoms or molecules. The effect was discovered in 1923 by Arthur Holly Compton while researching the scattering of X-rays by light elements, and earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927. The Compton effect significantly deviated from dominating classical theories, using both special relativity and quantum mechanics to explain the interaction between high frequency photons and charged particles. Photons can interact with matter at the atomic level (e.g. photoelectric effect and Rayleigh scattering), at the nucleus, or with just an electron. Pair production and the Compton effect occur at the level of the electron. When a high frequency photon scatters due to an interaction with a charged part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
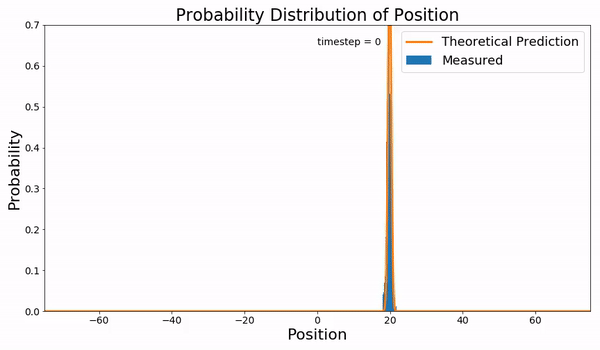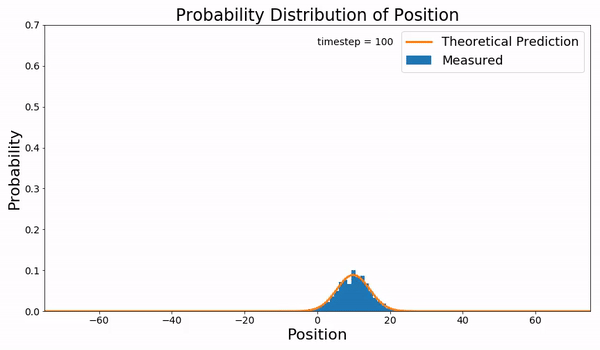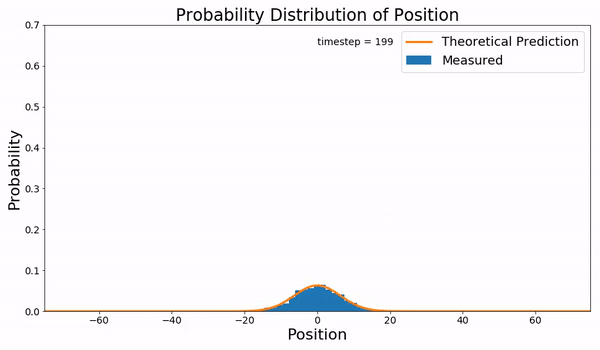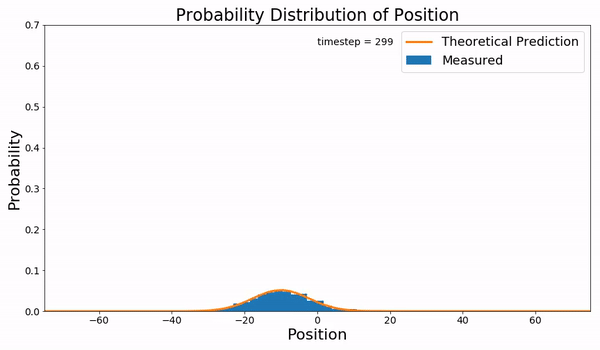
Fokker–Planck Equation
In statistical mechanics and information theory, the Fokker–Planck equation is a partial differential equation that describes the time evolution of the probability density function of the velocity of a particle under the influence of drag (physics), drag forces and random forces, as in Brownian motion. The equation can be generalized to other observables as well. The Fokker–Planck equation has multiple applications in information theory, graph theory, data science, finance, economics etc. It is named after Adriaan Fokker and Max Planck, who described it in 1914 and 1917. It is also known as the Kolmogorov forward equation, after Andrey Kolmogorov, who independently discovered it in 1931. When applied to particle position distributions, it is better known as the Smoluchowski equation (after Marian Smoluchowski), and in this context it is equivalent to the convection–diffusion equation. When applied to particle position and momentum distributions, it is known as the Klein–Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakov Zeldovich
Yakov Borisovich Zeldovich (, ; 8 March 1914 – 2 December 1987), also known as YaB, was a leading Soviet people, Soviet Physics, physicist of Belarusians, Belarusian origin, who is known for his prolific contributions in physical Physical cosmology, cosmology, physics of Plasma physics, thermonuclear reactions, combustion, and Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamical phenomena. From 1943, Zeldovich, a self-taught physicist, started his career by playing a crucial role in the development of the former Soviet atomic bomb project, Soviet program of nuclear weapons. In 1963, he returned to academia to embark on pioneering contributions on the fundamental understanding of the Black hole thermodynamics, thermodynamics of black holes and expanding the scope of physical cosmology. Biography Early life and education Yakov Zeldovich was born into a History of the Jews in Belarus, Belarusian Jewish family in his grandfather's house in Minsk. However, in mid-1914, the Zeldovich family moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few Academy name changes, ending as The Imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |