|
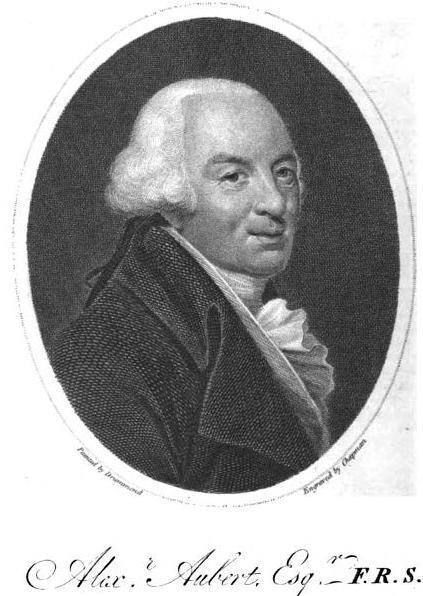
Alexander Aubert
Alexander Aubert FRS FSA, (1730–1805), was an English amateur astronomer and businessman. Life He was born at Austin Friars, London, 11 May 1730. The appearance of the Great Comet of 1744 gave him, then a schoolboy at Geneva, a permanent bias towards astronomy; but he diligently prepared for a mercantile career in counting-houses at Geneva, Leghorn, and Genoa, and visited Rome in the jubilee year (1750). Returning to London in 1751, he was in the following year taken into partnership by his father. In 1753 he became a director, and some years later governor, of the London Assurance Company. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1772, and of the Society of Antiquaries in 1784. In 1793 he received a diploma of admission to the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences. He observed the transit of Venus of 3 June 1769 at Austin Friars, and that of Mercury, 4 May 1786(''Phil. Trans''. Lxxvii. 47) at an observatory built by him at Loampit Hill, near Deptford, and furnished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Aubert From Eur Mag 34
Alexander () is a male name of Greek origin. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander, Oleksandr, Oleksander, Aleksandr, and Alekzandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexsander, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa, Aleksandre, Alejandro, Alessandro, Alasdair, Sasha, Sandy, Sandro, Sikandar, Skander, Sander and Xander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islington
Islington ( ) is an inner-city area of north London, England, within the wider London Borough of Islington. It is a mainly residential district of Inner London, extending from Islington's #Islington High Street, High Street to Highbury Fields and Regent's Canal, encompassing the area around the busy High Street, Upper Street, Essex Road, and Southgate Road to the east. History Etymology The manor of Islington was named by the Saxons ''Giseldone'' (1005), then ''Gislandune'' (1062). The name means "Gīsla's hill" from the Old English personal name ''Gīsla'' and ''dun (fortification), dun'' ("hill", "Downland, down"). The name later mutated to ''Isledon'', which remained in use well into the 17th century when the modern form arose. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The Society Of Antiquaries Of London
Fellows may refer to Fellow, in plural form. Fellows or Fellowes may also refer to: Places *Fellows, California, USA *Fellows, Wisconsin, ghost town, USA Other uses * Fellowes, Inc., manufacturer of workspace products *Fellows, a partner in the firm of English canal carriers, Fellows Morton & Clayton *Fellows (surname) *Mount Fellows, a mountain in Alaska See also *North Fellows Historic District The North Fellows Historic District is a historic district located in Ottumwa, Iowa, United States. The city experienced a housing boom after World War II. This north side neighborhood of single-family brick homes built between 1945 and 1959 ..., listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Wapello County, Iowa * Justice Fellows (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the Fellows of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Overview Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to :Fellows of the Royal Society, around 8,000 fellows, including eminent scientists Isaac Newton (1672), Benjamin Franklin (1756), Charles Babbage (1816), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Jagadish Chandra Bose (1920), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis (1945), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955), Satyendra Nath Bose (1958), and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century English Businesspeople
The 18th century lasted from 1 January 1701 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCI) to 31 December 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinking culminated in the Atlantic Revolutions. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures. The Industrial Revolution began mid-century, leading to radical changes in Society, human society and the Natural environment, environment. The European colonization of the Americas and other parts of the world intensified and associated mass migrations of people grew in size as part of the Age of Sail. During the century, History of slavery, slave trading expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, while declining in Russian Empire, Russia and Qing dynasty, China. Western world, Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Lewis (topographer)
Samuel Lewis or Sam Lewis may refer to: Politics * Samuel Lewis (educator) (1799–1854), American politician, Ohio Superintendent of Common Schools and Liberty Party candidate * Samuel A. Lewis (1831–1913), American politician and philanthropist * Samuel Lewis (barrister) (1843–1903), Sierra Leonean politician, lawyer, first African to be knighted * Samuel S. Lewis (1874–1959), Secretary of the Pennsylvania Department of Forest and Waters in 1951–1954 * Sam Lewis (trade unionist) (1901–1976), Australian trade unionist * Samuel W. Lewis (1930–2014), American diplomat * Samuel W. Lewis (politician), American politician * Samuel Lewis Navarro (born 1957), vice president of Panama Other * Samuel Lewis, early South Australian stonemason who carved the cross on William Light's first memorial * Samuel Lewis (publisher) (c. 1782–1865), editor and publisher of topographical dictionaries and maps * Samuel Lewis (financier) (1837–1901), English money-lender and philan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Lysons (antiquarian)
Daniel Lysons (1762–1834) was an English antiquarian and topographer, who published, amongst other works, the four-volume ''Environs of London'' (1792–96). He collaborated on several antiquarian works with his younger brother Samuel Lysons (1763–1819). Life The son of the Reverend Samuel Lysons (1730–1804) and Mary Peach Lysons of Rodmarton, Gloucestershire, Lysons studied at Bath Grammar School and St Mary Hall, Oxford, graduating MA in 1785, and followed in his father's footsteps to become a curate in Putney, west London from 1789 to 1800. While at Putney, Lysons began his survey of the area around London, in which he was encouraged by Horace Walpole, who appointed him as his 'chaplain'. In 1800, he inherited the family estates at Hempsted, near Gloucester, from his uncle Daniel Lysons (1727–1800). First marriage and children Lysons married Sarah Carteret Hardy (c.1780–1808), the daughter of Lt Col Thomas Carteret Hardy, in Bath on 12 May 1801. A portr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Gentleman's Magazine
''The Gentleman's Magazine'' was a monthly magazine founded in London, England, by Edward Cave in January 1731. It ran uninterrupted for almost 200 years, until 1907, ceasing publication altogether in 1922. It was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (from the French language, French ''magazine'', meaning "storehouse") for a periodical. Samuel Johnson's first regular employment as a writer was with ''The Gentleman's Magazine''. History The original complete title was ''The Gentleman's Magazine: or, Trader's monthly intelligencer''. Cave's innovation was to create a monthly digest of news and commentary on any topic the educated public might be interested in, from commodity prices to Latin poetry. It carried original content from a stable of regular contributors, as well as extensive quotations and extracts from other periodicals and books. Cave, who edited ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' under the pen name "Sylvanus Urban", was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (meaning "st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the second journal in the world exclusively devoted to science, after the '' Journal des sçavans'', and therefore also the world's longest-running scientific journal. It became an official society publication in 1752. The use of the word ''philosophical'' in the title refers to natural philosophy, which was the equivalent of what would now be generally called ''science''. Current publication In 1887 the journal expanded and divided into two separate publications, one serving the physical sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'') and the other focusing on the life sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences''). Both journals now publish theme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topham Beauclerk
Topham Beauclerk ( ; 22 December 1739 – 11 March 1780) was a celebrated English wit and a friend of Samuel Johnson and Horace Walpole. Early life Topham Beauclerk was born on 22 December 1739 in Pall Mall, London. He was the only son of Lord Sidney Beauclerk and a great-grandson of King Charles II. He was christened on 19 January 1740 in St James's Church, Piccadilly, in Westminster. In 1744, his father died and the four-year-old Topham, and his widowed mother, Mary Beauclerk, moved to Upper Brook Street in London and lived there until 1753. Between 1753 and 1757, Topham Beauclerk probably attended Eton College (this is not completely certain as only his surname, Beauclerk, is noted in the college's register). It seems he did not live in the school as a boarder, but in the family home in nearby Windsor. In November 1757 he matriculated at Trinity College, Oxford, which had been attended by his father. His date of leaving is unknown, but he was still there in 1759, when he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
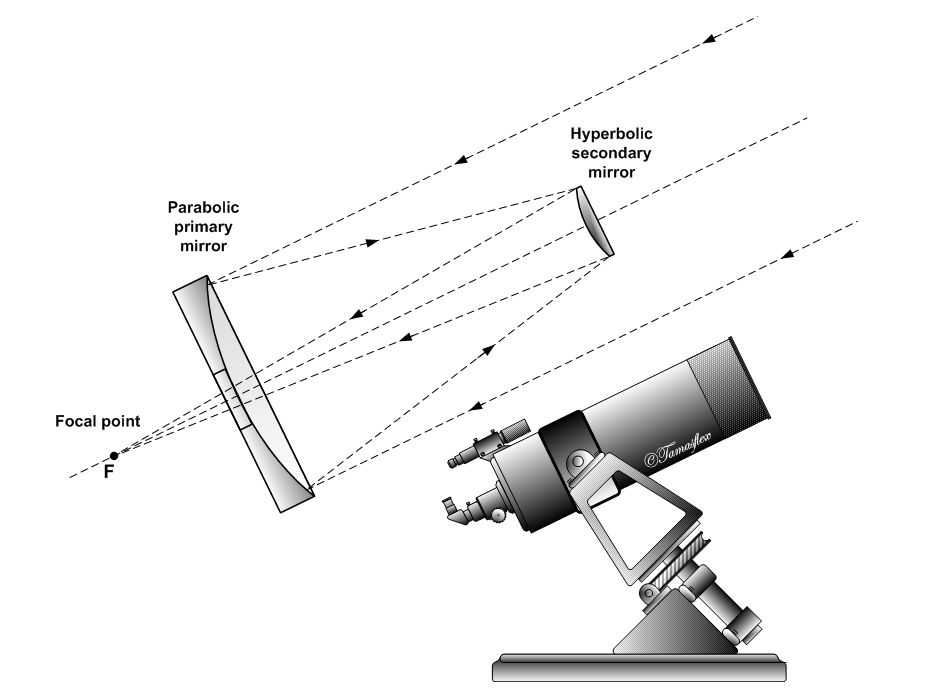
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and Antenna (radio), radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the Focus (optics), focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a Telephoto lens, telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatic Lens
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens (optics), lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic aberration, chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red and blue) into focus on the same plane. Wavelengths in between these two then have better focus error than could be obtained with a simple lens. The most common type of achromat is the achromatic doublet, which is composed of two individual lenses made from glasses with different amounts of Dispersion (optics), dispersion. Typically, one element is a negative (Lens (optics)#Types of simple lenses, concave) element made out of flint glass such as F2, which has relatively high dispersion, and the other is a positive (Lens (optics)#Types of simple lenses, convex) element made of Crown glass (optics), crown glass such as BK7, which has lower dispersion. The lens elements are mounted next to each other, often cemented together, and shaped so that the chromati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |