|
Aldehyde Oxidase
Aldehyde oxidase (AO) is a metabolizing enzyme, located in the cytosolic compartment of tissues in many organisms. AO catalyzes the oxidation of aldehydes into carboxylic acid, and in addition, catalyzes the hydroxylation of some heterocycles. It can also catalyze the oxidation of both cytochrome P450 and monoamine oxidase (MAO) intermediate products. AO plays an important role in the metabolism of several drugs. Reaction AO catalyzes the conversion of an aldehyde in the presence of oxygen and water to an acid and hydrogen peroxide. * an aldehyde + H2O + O2 ⇌ a carboxylate + H2O2 + H+ Though the enzyme uses molecular oxygen as an electron acceptor, the oxygen atom that is incorporated into the carboxylate product is from water; however, the exact mechanism of reduction is still not known for AO. The AO also catalyzes the oxidation of heterocycles, which involves a nucleophilic attack located at the carbon atom beside the heteroatom. This means that susceptibility to nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde Oxidase 1
Aldehyde oxidase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AOX1'' gene. Aldehyde oxidase produces hydrogen peroxide and, under certain conditions, can catalyze the formation of superoxide. Clinical significance Aldehyde oxidase is a candidate gene for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i .... See also * MOCOS References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * EC 1.2.3 {{gene-2-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nrf2
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), also known as nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2, is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''NFE2L2'' gene. NRF2 is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) protein that may regulate the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage triggered by injury and inflammation, according to preliminary research. ''In vitro'', NRF2 binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoter regions of genes encoding cytoprotective proteins. NRF2 induces the expression of heme oxygenase 1 ''in vitro'' leading to an increase in phase II enzymes. NRF2 also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome. NRF2 appears to participate in a complex regulatory network and performs a pleiotropic role in the regulation of metabolism, inflammation, autophagy, proteostasis, mitochondrial physiology, and immune responses. Several drugs that stimulate the NFE2L2 pathway are being studied for treatment of diseases tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine (CPZ), marketed under the brand names Thorazine and Largactil among others, is an antipsychotic medication. It is primarily used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Other uses include the treatment of bipolar disorder, severe behavioral problems in children including those with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, nausea and vomiting, anxiety before surgery, and hiccups that do not improve following other measures. It can be given orally (by mouth), by intramuscular injection (injection into a muscle), or intravenously (injection into a vein). Chlorpromazine is in the typical antipsychotic class, and, chemically, is one of the phenothiazines. Its mechanism of action is not entirely clear but is believed to be related to its ability as a dopamine antagonist. It has antiserotonergic and antihistaminergic properties. Common side effects include movement problems, sleepiness, dry mouth, low blood pressure upon standing, and incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clozapine
Clozapine, sold under the brand name Clozaril among others, is a psychiatric medication and was the first atypical antipsychotic to be discovered. It is used primarily to treat people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder who have had an inadequate response to two other antipsychotics, or who have been unable to tolerate other drugs due to extrapyramidal side effects. In the US, clozapine is also approved for use in people with recurrent suicidal behavior in people with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. It is also used for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease. Clozapine is recommended by multiple international treatment guidelines, after resistance to two other antipsychotic medications, and is the only treatment likely to result in improvement if two (or one) other antipsychotic has not had a satisfactory effect. Long term follow-up studies from Finland show significant improvements in terms of overall mortality including from suicide and all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethinyl Estradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. Ethinylestradiol was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disorders, and certain hormone-sensitive cancers. It is usually taken by mouth but is also used as a patch and vaginal ring. The general side effects of ethinylestradiol include breast tenderness and enlargement, headache, fluid retention, and nausea among others. In males, ethinylestradiol can additionally cause breast development, feminization in general, hypogonadism, and sexual dysfunction. Rare but serious side effects include blood clots, liver damage, and cancer of the uterus. Ethinylestradiol is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol. It is a synthetic derivative of estradiol, a natural estrogen, and differs from it in various ways. Compared to estradiol, ethiny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given Oral administration, by mouth or by injection. Common side effects include nausea, feeling tired, fever, increased risk of infection, leukopenia, low white blood cell counts, and ulcerative stomatitis, breakdown of the skin inside the mouth. Other side effects may include liver disease, lung disease, lymphoma, and severe skin rashes. People on long-term treatment should be regularly checked for side effects. It is not safe during breastfeeding. In those with kidney problems, lower doses may be needed. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziprasidone
Ziprasidone, sold under the brand name Geodon among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It may be used by mouth and by injection into a muscle (IM). The intramuscular form may be used for acute agitation in people with schizophrenia. Common side effects include tremors, tics, dizziness, dry mouth, restlessness, nausea, and mild sedation. Although it can also cause weight gain, the risk is much lower than for other atypical antipsychotics. How it works is not entirely clear but is believed to involve effects on serotonin and dopamine in the brain. Ziprasidone was approved for medical use in the United States in 2001. The pills are made up of the hydrochloride salt, ziprasidone hydrochloride. The intramuscular form is the mesylate, ziprasidone mesylate trihydrate, and is provided as a lyophilized powder. In 2020, it was the 282nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaleplon
Zaleplon, sold under the brand name Sonata among others, is a sedative and hypnotic which is used to treat insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine or Z-drug of the pyrazolopyrimidine class. It was developed by King Pharmaceuticals and approved for medical use in the United States in 1999. Medical uses Zaleplon is slightly effective in treating insomnia, primarily characterized by difficulty falling asleep. Zaleplon significantly reduces the time required to fall asleep by improving sleep latency and may therefore facilitate sleep induction rather than sleep maintenance. Due to its ultrashort elimination half-life, zaleplon may not be effective in reducing premature awakenings; however, it may be administered to alleviate middle-of-the-night awakenings. However, zaleplon has not been empirically shown to increase total sleep time. Zaleplon does not significantly affect driving performance the morning following bedtime administration or 4 hours after middle-of-the-night administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific substance after administration. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is based on mathematical modeling that places great emphasis on the relationship between drug plasma concentration and the time elapsed since the drug's administration. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects the drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a Native metal, free metal on Earth; in its minerals, it is found only in oxidation state, oxidized states. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the List of elements by melting point, sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which may be in the form of FAD or flavin mononucleotide (FMN). Many flavoproteins are known: components of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. FAD can exist in four redox states, which are the flavin-N(5)-oxide, quinone, semiquinone, and hydroquinone. FAD is converted between these states by accepting or donating electrons. FAD, in its fully oxidized form, or quinone form, accepts two electrons and two protons to become FADH2 (hydroquinone form). The semiquinone (FADH·) can be formed by either reduction of FAD or oxidation of FADH2 by accepting or donating one electron and one proton, respectively. Some proteins, however, generate and maintain a super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
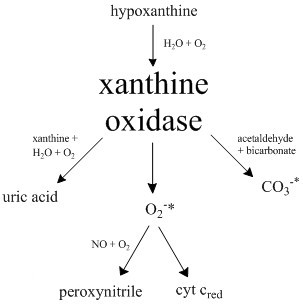
Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine oxidase (XO or XAO) is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans. Xanthine oxidase is defined as an ''enzyme activity'' (EC 1.17.3.2). The same protein, which in humans has the HGNC approved gene symbol ''XDH'', can also have xanthine dehydrogenase activity (EC 1.17.1.4). Most of the protein in the liver exists in a form with xanthine dehydrogenase activity, but it can be converted to xanthine oxidase by reversible sulfhydryl oxidation or by irreversible proteolytic modification. "XDH xanthine dehydrogenase" Reaction The following chemical reactions are catalyzed by xanthine oxidase: * hypoxanthine + H2O + O2 xanthine + H2O2 * xanthine + H2O + O2 uric acid + H2O2 * Xanthine oxidase ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |