|
Alchemical
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of " base metals" (e.g., lead) into " noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Alchemy
Chinese alchemy (煉丹術 ''liàndānshù'' "method for refining cinnabar") is a historical Chinese approach to alchemy. According to original texts such as the Cantong qi, the body is understood as the focus of cosmological processes summarized in the five agents of change, or Wuxing, the observation and cultivation of which leads the practitioner into alignment and harmony with the Tao. Therefore, the traditional view in China is that alchemy focuses mainly on longevity and the purification of one's spirit, mind and body, providing, health, longevity and wisdom, through the practice of Qigong and wuxingheqidao. The consumption and use of various concoctions known as alchemical medicines or elixirs, each of which having different purposes but largely were concerned with immortality. ''Pao zhi'' (炮制; ''Pao chi'') or Processing (Chinese materia medica) is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine, such as honey or wine frying and roasting with toxic metals such as mercury, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophers' Stone
The philosopher's stone is a mythic alchemical substance capable of turning base metals such as mercury into gold or silver; it was also known as "the tincture" and "the powder". Alchemists additionally believed that it could be used to make an elixir of life which made possible rejuvenation and immortality. For many centuries, it was the most sought-after goal in alchemy. The philosopher's stone was the central symbol of the mystical terminology of alchemy, symbolizing perfection at its finest, divine illumination, and heavenly bliss. Efforts to discover the philosopher's stone were known as the Magnum Opus ("Great Work"). Antiquity The earliest known written mention of the philosopher's stone is in the ''Cheirokmeta'' by Zosimos of Panopolis (). Alchemical writers assign a longer history. Elias Ashmole and the anonymous author of ''Gloria Mundi'' (1620) claim that its history goes back to Adam, who acquired the knowledge of the stone directly from God. This knowledge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy And Chemistry In Medieval Islam
Alchemy in the medieval Islamic world refers to both traditional alchemy and early practical chemistry (the early chemical investigation of nature in general) by Science in medieval Islam, Muslim scholars in the medieval Islamic world. The word ''alchemy'' was derived from the Arabic word (), which itself Chemistry (etymology), may derive either from the Egyptian language, Egyptian word ''kemi'' ('black') or from the Ancient Greek, Greek word ('fusion').. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Islamic conquest of Roman Egypt, the focus of alchemical development moved to the Caliphate and the Islamic Golden Age, Islamic civilization. Definition and relationship with medieval western sciences In considering Islamic sciences as a distinct, local practice, it is important to define words such as "Arabic", "Islamic", "alchemy", and "chemistry" in order to gain an understanding of what these terms mean historically. This may also help to clear up any misconception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
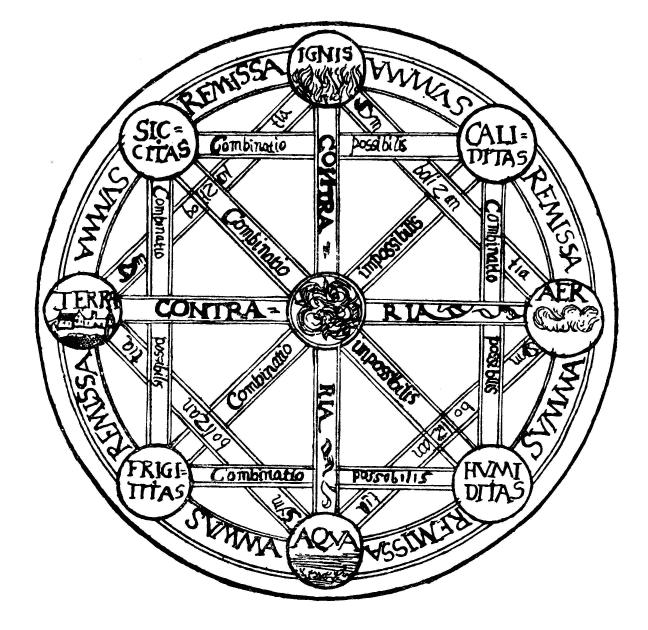
Four Elements
The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the elements to be divisible into infinitely small pieces without changing their nature. While the classification of the material world in ancient India, Hellenistic Egypt, and ancient Greece into air, earth, fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rasayana
In early ayurvedic medicine, ''rasāyana'' (Pali and Sanskrit: रसायन, "path of essence") is one of the eight areas of medicine in Sanskrit literature. The 11th-century Persian scholar Abū Rayhān Bīrūnī noted an Indian science named ''Rasāyana'', focused on restoring health and rejuvenation through plant-derived medicines. Nagarjunacharya conducted experiments in his laboratory called "Rasashala" and authored ''Rasaratanakaram'', detailing alchemical transformations of metals. Al-Bīrūnī conflated the earlier rasāyana practices with rasaśāstra alchemy. Rasaśāstra utilized alchemical processes involving substances like mercury and cinnabar. This practice extended beyond metals, incorporating the preparation of medical tinctures from plants. Rasaśāstra's goals included longevity, health, cognitive enhancement, virility, and extraordinary abilities. Its historical influence was evident in the Ajanta and Ellora cave paintings, the Vishnustambha monumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elixir Of Life
The elixir of life (Medieval Latin: ' ), also known as elixir of immortality, is a potion that supposedly grants the drinker Immortality, eternal life and/or eternal youth. This elixir was also said to Panacea (medicine), cure all diseases. Alchemy, Alchemists in various ages and cultures sought the means of formulating the elixir. History Ancient Mesopotamia An early mention of an elixir of life is found in the Epic of Gilgamesh (from the 2nd millennium BC) in which Gilgamesh comes to fear his own declining years following the death of his beloved companion Enkidu. He seeks out Utnapishtim, a figure in Mesopotamian mythology known for surviving a great flood sent by the gods and being granted immortality. Gilgamesh is directed by Utnapishtim to find a plant at the bottom of the sea, but he loses it to a serpent before he can use it himself. This legend is an archaic explanation for snakes shedding their skin, seen as mystical rejuvenation. China Many rulers of ancient C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnum Opus (alchemy)
In alchemy, the Magnum Opus or Great Work is a term for the process of working with the prima materia to create the philosopher's stone. It has been used to describe personal and spiritual chrysopoeia, transmutation in the Hermeticism, Hermetic tradition, attached to laboratory processes and chemical color changes, used as a model for the individuation process, and as a device in art and literature. The magnum opus has been carried forward in New Age and neo-Hermetic movements which sometimes attached new symbolism and significance to the processes. The original process philosophy has four stages: *''nigredo'', the blackening or melanosis *''Albedo (alchemy), albedo'', the whitening or leucosis *''citrinitas'', the yellowing or xanthosis *''rubedo'', the reddening, purpling, or iosis The origin of these Humorism, four phases can be traced at least as far back as the first century. Zosimus of Panopolis wrote that it was known to Mary the Jewess. The development of black, white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Translations Of The 12th Century
Latin translations of the 12th century were spurred by a major search by European scholars for new learning unavailable in western Europe Renaissance of the 12th century, at the time; their search led them to areas of southern Europe, particularly in Taifa of Toledo, central Spain and Sicily#Arab period (827–1091), Sicily, which recently had come under Christian rule following their reconquest in the late 11th century. These areas had been under Muslim rule for a considerable time, and still had substantial Arabic-speaking populations to support their search. The combination of this accumulated knowledge and the substantial numbers of Arabic-speaking scholars there made these areas intellectually attractive, as well as culturally and politically accessible to Latin scholars. A typical story is that of Gerard of Cremona (c. 1114–87), who is said to have made his way to Toledo, well after its reconquest by Christians in 1085, because he: Many Christian theologians were highly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysopoeia
In alchemy, the term chrysopoeia () refers to the artificial production of gold, most commonly by the alleged transmutation of base metals such as lead. A related term is argyropoeia (), referring to the artificial production of silver, often by transmuting copper. Although alchemists pursued many different goals, the making of gold and silver remained one of the defining ambitions of alchemy throughout its history, from Zosimus of Panopolis (c. 300) to Robert Boyle (1627–1691). The word was used in the title of a brief alchemical work, the ''Chrysopoeia of Cleopatra'' attributed to Cleopatra the Alchemist, which was probably written in the first centuries of the Christian era, but which is first found on a single leaf in a tenth-to-eleventh century manuscript in the Biblioteca Marciana, Venice, MS Marciana gr. Z. 299. The document features an ouroboros containing the words "the all is one" (, '), a concept that is related to Hermeticism. Stephen of Alexandria wrote a work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Techniques
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools, universities, privately owned research institutions, corporate research and testing facilities, government regulatory and forensic investigation centers, physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, regional and national referral centers, and even occasionally personal residences. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that describe the relationship between the soul and the body are Interactionism (philosophy of mind), interactionism, Psychophysical parallelism, parallelism, and epiphenomenalism. Anthropology, Anthropologists and Psychology, psychologists have found that most humans are naturally inclined to believe in the existence of the soul and that they have interculturally distinguished between souls and bodies. The soul has been the central area of interest in philosophy since Ancient history, ancient times. Socrates envisioned the soul to possess a rational faculty, its practice being man's most godlike activity. Plato believed the soul to be the person's real self, an immaterial and immortal dweller of our lives that continues and thinks even after d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |