|
Albrecht Schrauf
Albrecht Schrauf (14 December 1837, Vienna – 29 November 1897, Vienna) was an Austrian mineralogist and crystallographer. Biography Schrauf studied mathematics, physics and mineralogy at the University of Vienna, where one of his instructors was Wilhelm Josef Grailich. Several years later, he became "custos-adjunct" at the "Imperial Hofmineralien Cabinet" in Vienna. In 1867 he was named first curator of the mineral cabinet, and in 1874 was appointed professor and director of the mineralogical museum at the University of Vienna. Known for his investigations in the field of crystallography, he was a proponent of the crystallographic index developed by William Hallowes Miller. In the mid-1860s, he published his best works, "''Atlas der Krystallformen des Mineralreiches''" and an award-winning textbook titled "''Lehrbuch der physikalischen Mineralogie''". In Vienna, he collaborated with Gustav Tschermak in publication of the journal "''Mineralogische Mitteilungen''". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Vienna
The University of Vienna (, ) is a public university, public research university in Vienna, Austria. Founded by Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, Duke Rudolph IV in 1365, it is the oldest university in the German-speaking world and among the largest institutions of higher learning in Europe. The university is associated with 17 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel Prize winners and has been the home to many scholars of historical and academic importance. History Middle Ages to the Enlightenment The university was founded on March 12, 1365, by Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, hence the name "Alma Mater Rudolphina". After the Charles University in Prague (1347) and Jagiellonian University in Kraków (1364), the University of Vienna is the third oldest university in Central Europe and the oldest university in the contemporary German-speaking world; it remains a question of definition as the Charles University in Prague was German-speaking when founded, too. However, Pope Urban V did not ratify th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
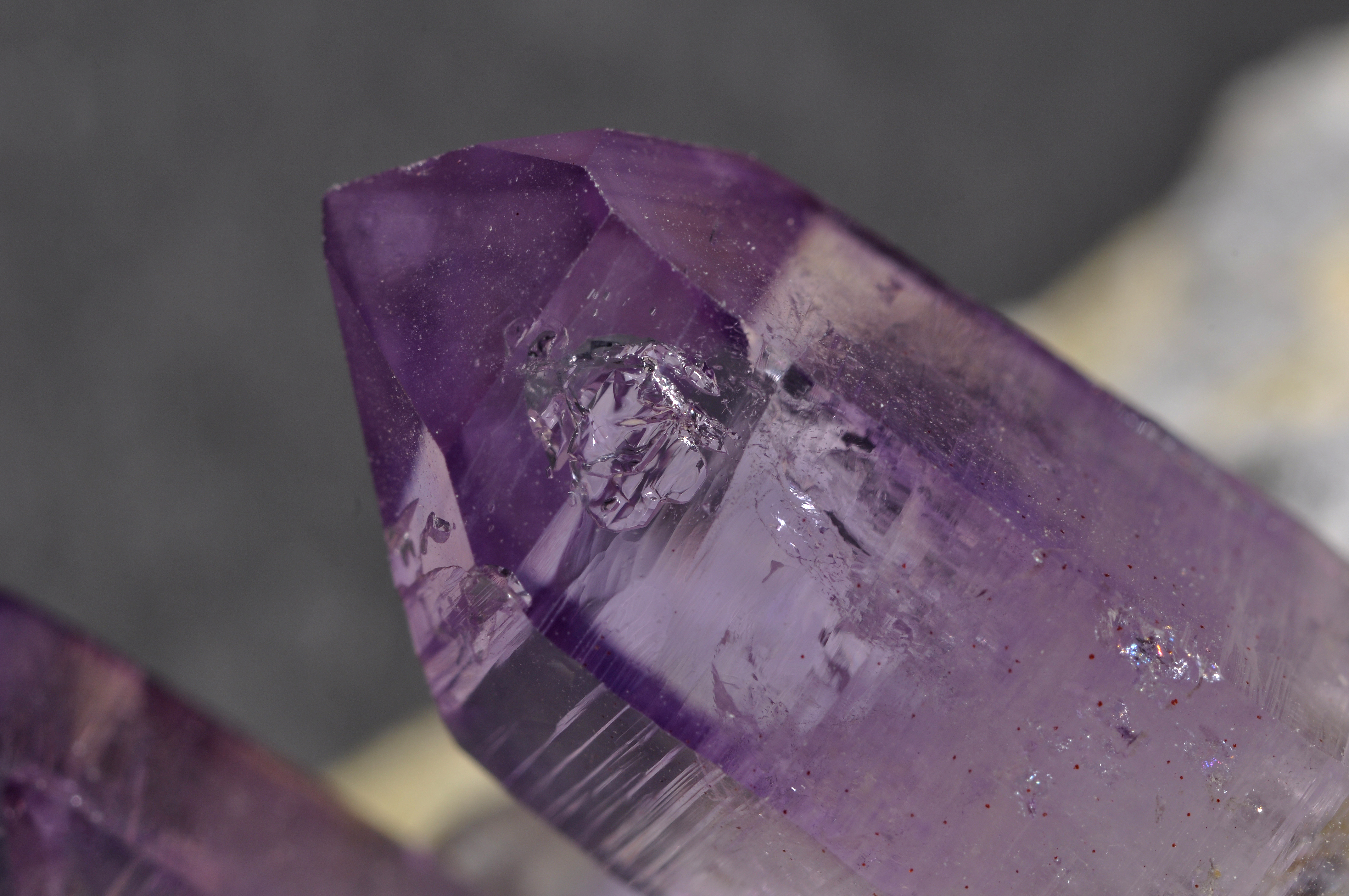
Crystal Form
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallographers
A crystallographer is a type of scientist who practices crystallography, in other words, who studies crystals. Career paths The work of crystallographers spans several academic disciplines, including the life sciences, chemistry, physics, and materials science. They may work in research and manufacturing, which could include growing crystals for use in computer chips, solar cells, or medications. Within the life sciences, they may crystallize biological materials (such as proteins or viruses) or drugs. They may also come in hand in forensic science. They may also study materials using materials simulations. Most working crystallographers have a graduate degree. There are very few opportunities for those with a bachelor's degree or associate degree. By country Germany In 2013, one working group, the Young Crystallographers, was established within the German Crystallographic Society (DGK). As of 2024, the Young Crystallographers have about 250 members. The working group also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologists From Austria-Hungary
A geologist is a scientist who studies the structure, composition, and history of Earth. Geologists incorporate techniques from physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, and geography to perform research in the field and the laboratory. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors to exploit natural resources. They monitor environmental hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Geologists are also important contributors to climate change discussions. History James Hutton is often viewed as the first modern geologist. In 1785 he presented a paper entitled ''Theory of the Earth'' to the Royal Society of Edinburgh. In his paper, he explained his theory that the Earth must be much older than had previously been supposed to allow enough time for mountains to be eroded and for sediments to form new rocks at the bottom of the sea, which in turn were raised up to become dry land. Hutton published a two-volume version of his ideas in 1795Vol. 1 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From Vienna
A scientist is a person who researches to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales ( 624–545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. History The roles of "scientists", and their predecessors before the emergence of modern scientific disciplines, have evolved considerably over time. Scientists of different eras (and before them, natural philosophers, mathematicians, natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1897 Deaths
Events January * January 2 – The International Alpha Omicron Pi sorority is founded, in New York City. * January 4 – A British force is ambushed by Chief Ologbosere, son-in-law of the ruler. This leads to a punitive expedition against Benin City, Benin. * January 7 – A 1897 Darwin cyclone, cyclone destroys Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin, Australia. * January 8 – Lady Flora Shaw, future wife of Governor General Frederick Lugard, 1st Baron Lugard, Lord Lugard, officially proposes the name "Nigeria" in a newspaper contest, to be given to the British Niger Coast Protectorate. * January 22 – In this date's issue of the journal ''Engineering'', the word ''computer'' is first used to refer to a mechanical calculation device. * January 31 – The Czechoslovak Trade Union Association is founded in Prague. February * February 10 – Freedom of religion is proclaimed in Madagascar. * February 16 – The French conquer the island of Raia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1837 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The destructive Galilee earthquake causes thousands of deaths in Ottoman Syria. * January 26 – Michigan becomes the 26th state admitted to the United States. * February 4 – Seminoles attack Fort Foster in Florida. * February 25 – In Philadelphia, the Institute for Colored Youth (ICY) is founded, as the first institution for the higher education of black people in the United States. * February – Charles Dickens's '' Oliver Twist'' begins publication in serial form in London. * March 1 – The Congregation of Holy Cross is formed in Le Mans, France, by the signing of the Fundamental Act of Union, which legally joins the Auxiliary Priests of Blessed Basil Moreau, CSC, and the Brothers of St. Joseph (founded by Jacques-François Dujarié) into one religious association. April–June * April 12 – The conglomerate of Procter & Gamble has its origins, when British-born businessmen William Procter and James Gamble begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Crystallography Before X-rays
Physical crystallography before X-rays describes how physical crystallography developed as a science up to the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen in 1895. In the period before X-rays, crystallography can be divided into three broad areas: geometric crystallography culminating in the discovery of the 230 space groups in 1891–4, chemical crystallography and physical crystallography. Physical crystallography is concerned with the Mineralogy#Physical properties, physical properties of crystals, such as their Crystal optics, optical, electrical, and magnetic properties. The effect of electromagnetic radiation on crystals is covered in the following sections: #Double refraction, double refraction, #Rotary polarization, rotary polarization, #Conical refraction, conical refraction, #Absorption and pleochroism, absorption and pleochroism, #Luminescence, fluorescence and phosphorescence, luminescence, fluorescence and phosphorescence, #Reflection from opaque materials, reflecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrechtschraufite
Albrechtschraufite ( IMA symbol: Asf) is a very rare complex hydrated calcium and magnesium-bearing uranyl fluoride carbonate mineral with formula Ca4Mg(UO2)2(CO3)6F2·17H2O. Its molar weight is 1,428.98 g, color yellow-green, streak white, density 2.6 g/cm3, Mohs hardness 2–3, and luster is vitreous (glassy). It is named after Albrecht Schrauf (1837–1897), Professor of Mineralogy, University of Vienna. Its type locality is Jáchymov, Jáchymov District, Krušné Hory Mountains, Karlovy Vary Region, Bohemia, Czech Republic. See also *List of minerals *List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition of the mineral follows the name. A * Abelsonite: – American physicist Philip Hauge Abelson (1913–2004) * Abswurmbachite: – German mineralogist Irmgard Abs-Wurmbac ... References Magnesium minerals Calcium minerals Fluorine minerals Carbonate minerals Uranium(VI) minerals 17-18 Triclinic minerals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Josef Grailich
Wilhelm Joseph Grailich (16 February 1829, in Pressburg – 13 September 1859, in Vienna) was an Austrian physicist, mineralogist and crystallographer. Education From 1847, Grailich studied sciences at the polytechnic institute in Vienna. Career Grailich served as an assistant to Andreas von Ettingshausen in the institute of physics at the University of Vienna. In 1856 he became an assistant at the ''Hofmineraliencabinett'', where soon afterwards, he succeeded Gustav Adolf Kenngott as " kustos-adjunkt". In 1857 he became an associate professor of higher physics at the university, and in 1859, was chosen as a member of the Vienna Academy of Sciences. Grailich, Wilhelm Joseph @ NDB/ADB Deutsche Biographie In 1910, a thoroughfare in the Lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Tschermak
Gustav Tschermak von Seysenegg (19 April 1836 – 24 May 1927) was an Austrian mineralogist. Biography He was born in Litovel, Moravia, and studied at the University of Vienna, where he obtained a teaching degree. He studied mineralogy at Heidelberg and Tübingen and obtained a PhD. He returned to Vienna as a lecturer in mineralogy and chemistry and, in 1862 was appointed second vice curator of the Imperial Mineralogical Cabinet, becoming director in 1868. He resigned as director in 1877. He was also professor of petrography at the University of Vienna. He was appointed professor in 1873 and a member of the Imperial Academy of Sciences, a member of the American Philosophical Society in 1882, and a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1905. He died in 1927, aged 91. Work He did useful work on many minerals and on meteorites. The mineral tschermakite is named in his honour. In 1871 he established the ''Mineralogische Mitteilungen'' (Mineralogical Reports), publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |