|
Albanian Riviera
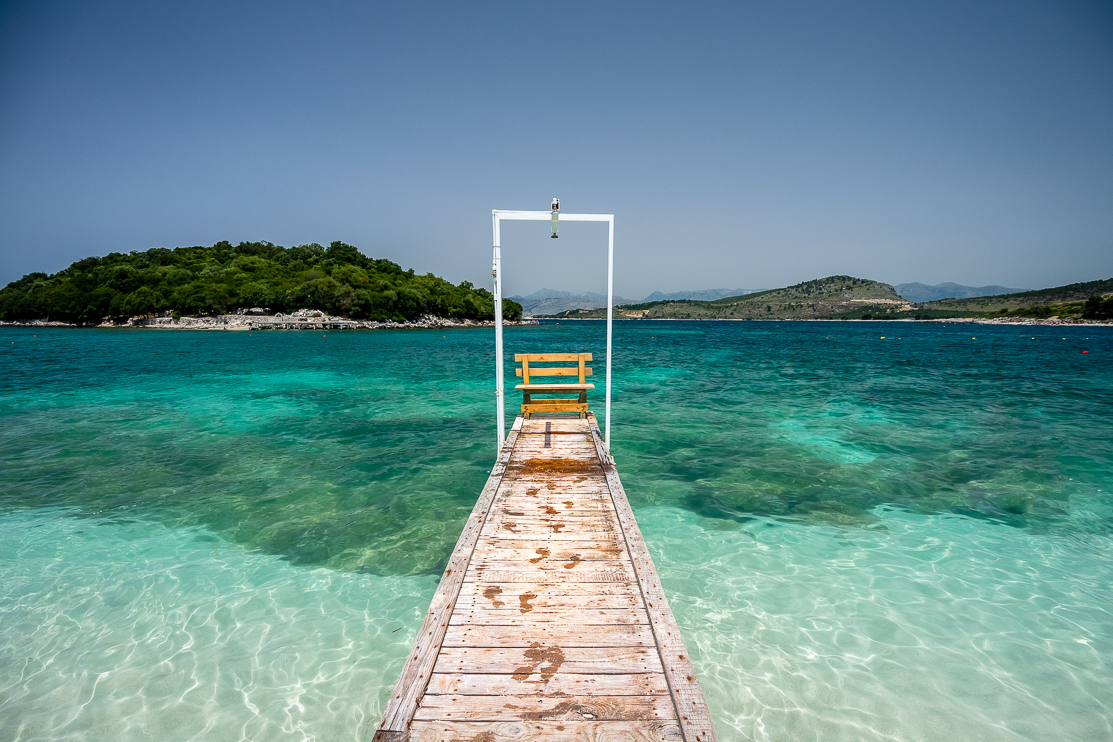
The Albanian Riviera (, ), also popularly known as Bregu, is a coastline along the north-eastern Ionian Sea in the Mediterranean Sea, encompassing the districts of Sarandë and Vlorë in south-western Albania. It forms an important section of the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast, dotted with the villages of Palasë, Kondraq, Dhërmi, Ilias, Vuno, Himara, Pilur, Kudhës, Qeparo, Borsh, Piqeras, Sasaj, Lukovë, Shën Vasil and Nivicë-Bubari. The riviera should not be confused with the entire coastline of the country, which includes the Ionian Sea Coast, and the mostly flat Adriatic Sea Coast in the north. The Ceraunian Mountains separate the coast from the hinterland. The area is a major nightlife, ecotourist, and elite retreat destination in Albania. It features traditional Mediterranean villages, ancient castles, churches, monasteries, secluded turquoise beaches, bays, mountain passes, seaside canyons, coves, rivers, underwater fauna, caves, and orange, lemon, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceraunian Mountains
The Ceraunian Mountains (, , 'Thunderbolt Mountains') are a coastal mountain range in southwestern Albania, within the Vlorë County. The mountain range rises on the northeastern bank of the Ionian Sea and protrudes into the Adriatic Sea. It extends for approximately in a southeast-northwest direction near Sarandë, along the Albanian Riviera, close to Orikum. Geologically, the Karaburun Peninsula belongs to the Ceraunian Mountains, and is separated from the rest by the Llogara Pass () forming the western part of the Ceraunian mountain range, called Acroceraunian Mountains (). The mountains are about long and about wide. The highest peak is Çikë with an elevation of . Name In classical antiquity, the name of the mountains was recorded in Ancient Greek as ''Keraunia ore'', meaning "thunder-split peaks". The western part of the mountain chain is called ''Akrokeraunia'', meaning 'Cape Thunder' which referred to the modern Karaburun peninsula. Both names Ceraunia and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bays Of Albania
Albania is a country in southeastern Europe that lies along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, with a coastline spanning approximately . Situated on the Balkan Peninsula, it is one of the most mountainous countries in Europe. It is bounded by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the southeast and south. Most of Albania rises into mountains and hills, tending to run the length of the country from north to south, as for instance the Albanian Alps in the north, the Sharr Mountains in the northeast, the Skanderbeg Mountains in the center, the Korab Mountains in the east, the Pindus Mountains in the southeast, and the Ceraunian Mountains in the southwest. Plains and plateaus extend in the west along the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea Coast. Some of the most considerable and oldest bodies of freshwater of Europe can be found in Albania. The second largest lake of Southern Europe, the Lake of Shkodër, is located in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Ionian Sea Coast
The Albanian Ionian Sea Coast ( — ) is a coastline of the north-eastern Ionian Sea, that encompasses the south-western border of the Albania, Republic of Albania, stretching from the southern half of Karaburun Peninsula, Albania, Karaburun Peninsula, across the historical region of Labëria, the city of Sarandë, the mountains of the Ceraunian Mountains, Ceraunians, and the Albanian Riviera, to the Lake of Butrint, where the Straits of Corfu, Strait of Corfu separates the country from Greece. Albania is located in Southern Europe, Southern and Southeast Europe, South-eastern Europe in the western section of the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. It borders on Montenegro to the north-west, Kosovo to the north-east, North Macedonia to the east, Greece to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. The coastline occupies a total length of and explicitly marked by a mountainous landscape supplied with deep bays, numerous islands, high cliffs, Rocky coast, rocky and sand, sandy coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borsh
Borsh (; sq-definite, Borshi, ) is a maritime village, in the Albanian Riviera, in the former Lukovë municipality, Vlorë County, Albania. At the 2015 local government reform, it became part of the Himarë municipality. The village is inhabited by ethnic Albanians,Kallivretakis, Leonidas (1995).Η ελληνική κοινότητα της Αλβανίας υπό το πρίσμα της ιστορικής γεωγραφίας και δημογραφίας [The Greek Community of Albania in terms of historical geography and demography" In Nikolakopoulos, Ilias, Kouloubis Theodoros A. & Thanos M. Veremis (eds). ''Ο Ελληνισμός της Αλβανίας [The Greeks of Albania]''. University of Athens. p. 51. " AM Αλβανοί Μουσουλμάνοι”; p.53. “BORSH ΜΠΟΡΣΙ 1243 AM" many of whom have traditionally been Bektashi Order, Bektashi. In Borsh, the Lab dialect of Albanian is spoken. Borsh borders with Fterra, Qeparo, Piqeras, Kuç, Çorraj, Kalasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the " Sonoran Desert fauna" or the " Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Modern Greek equivalent of fauna (πανίς or rather πανίδα). ''Fauna'' is also the word fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River
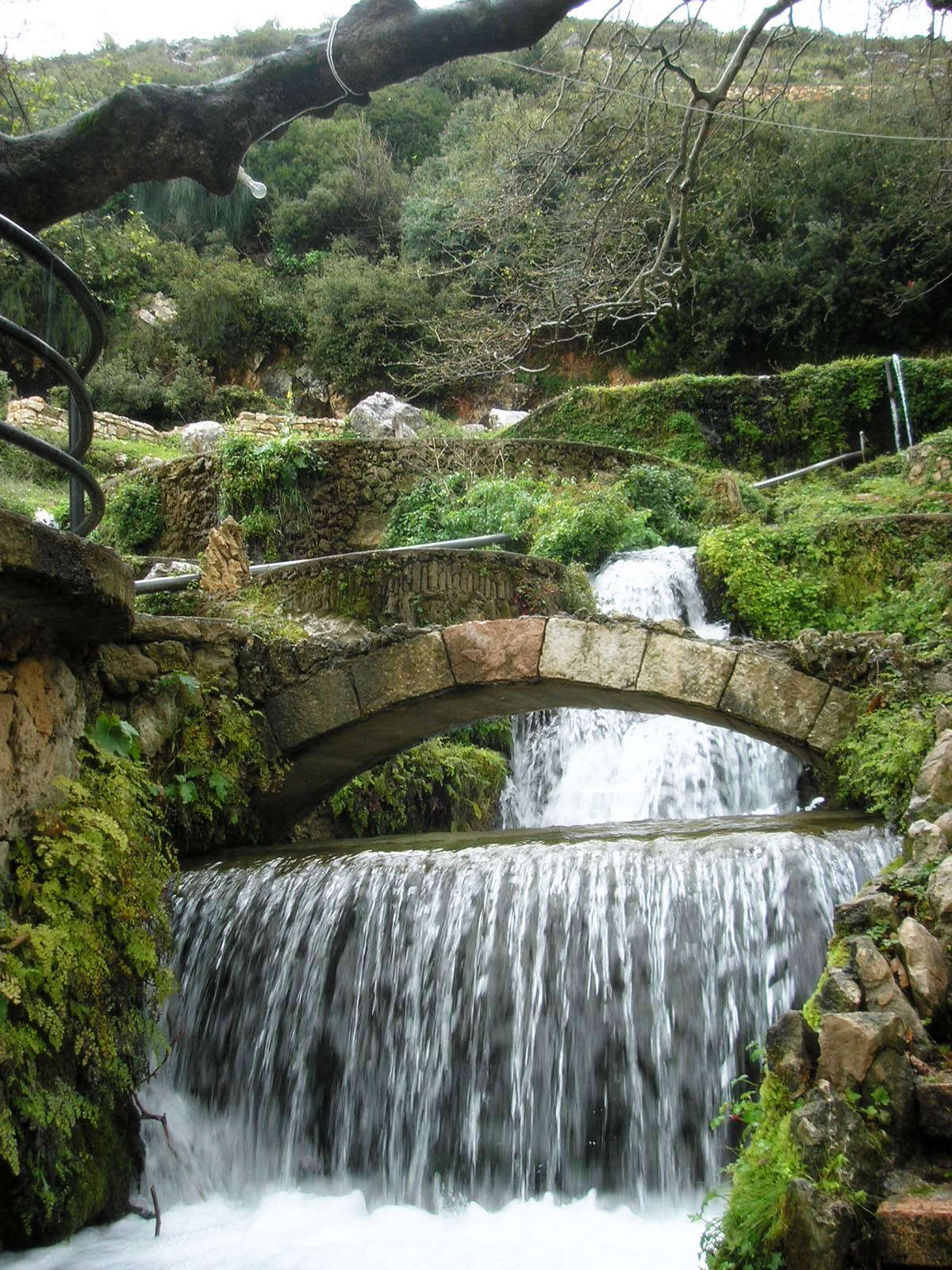
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the Runoff (hydrology), runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their Bank (geography), banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cove
A cove is a small bay or coastal inlet. They usually have narrow, restricted entrances, are often circular or oval, and are often situated within a larger bay. Small, narrow, sheltered bays, inlets, creek (tidal), creeks, or recesses in a coast are often considered coves. Colloquially, the term can be used to describe a sheltered bay. Geomorphology describes coves as precipitously walled and rounded cirque-like openings like a valley extending into or down a mountainside, or in a hollow or nook of a cliff or steep mountainside. A cove can also refer to a corner, nook, or cranny, either in a river, road, or wall, especially where the wall meets the floor. Formation Coves are formed by differential erosion, which occurs when softer rocks are worn away faster than the harder rocks surrounding them. These rocks further erode to form a circular bay with a narrow entrance, called a ''cove''. Another way is that waves can transport rocks and sediment towards cliffs or rock faces, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyon
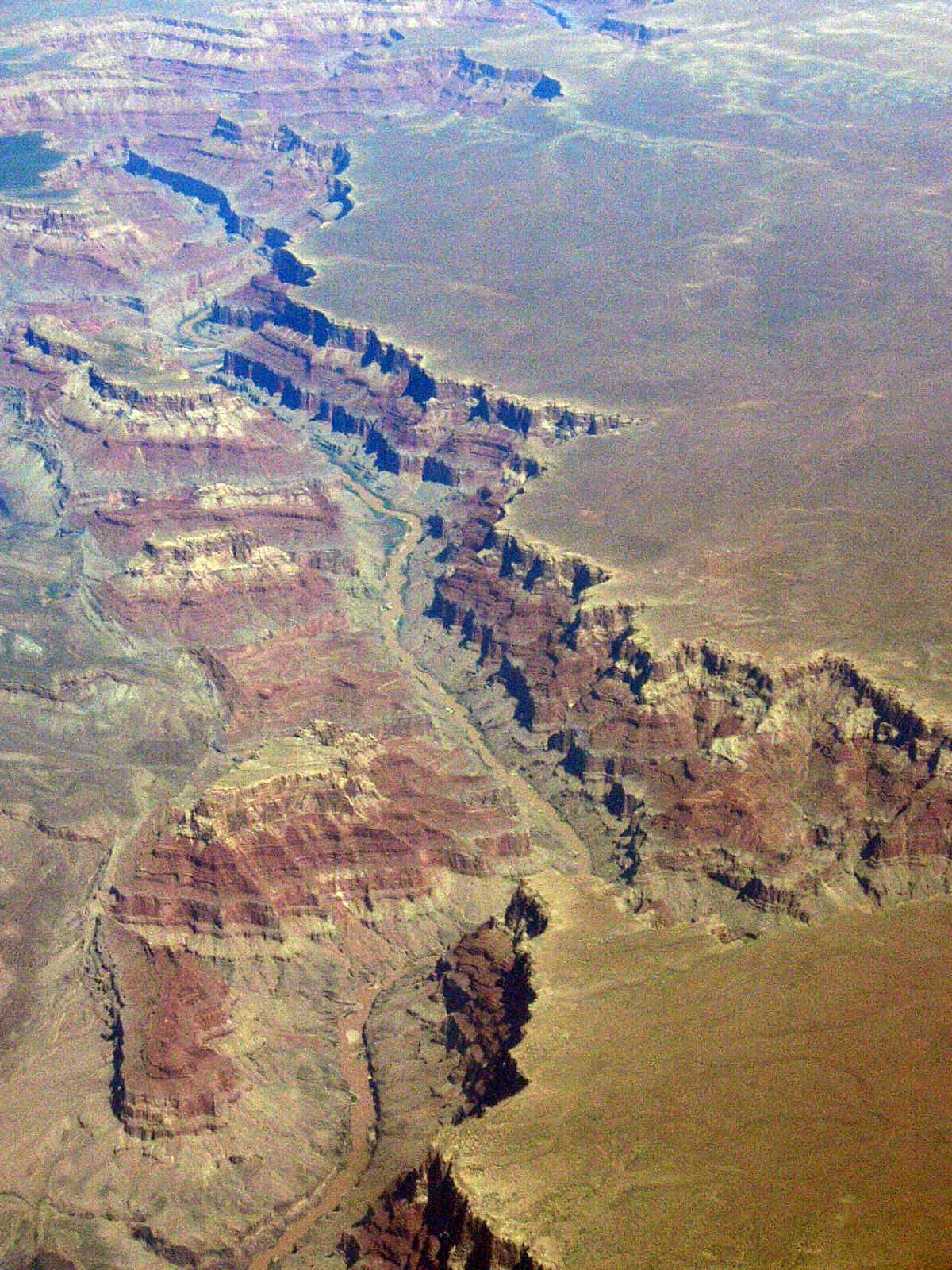
A canyon (; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), gorge or chasm, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examples of mountain- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since mountain ranges can present formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human and animal migration throughout history. At lower elevations it may be called a hill pass. A mountain pass is typically formed between two volcanic peaks or created by erosion from water or wind. Overview Mountain passes make use of a gap (landform), gap, saddle (landform), saddle, col or notch (landform), notch. A topographic saddle is analogous to the mathematical concept of a saddle surface, with a saddle point marking the minimum high point between two valleys and the lowest point along a ridge. On a topographic map, passes can be identified by contour lines with an hourglass shape, which indicates a low spot between two higher points. In the high mountains, a difference of between the summit and the mountain is defined as a mountain pass. Passes are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
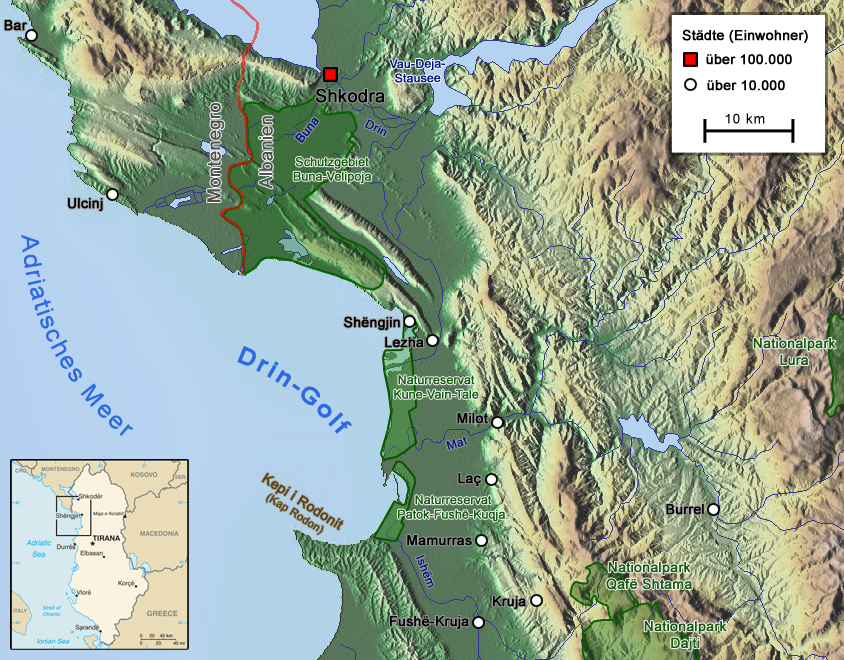
Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast
The Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast ( — ) stretches in the south-eastern Adriatic Sea beginning at the Gulf of Drin in the north, across the port cities of Shëngjin, Durrës, and Vlorë, to the Bay of Vlorë in the south, where the Albanian Riviera and the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast begin. Albania is geographically located in Southern and South-eastern Europe within the Balkan Peninsula. It borders on Montenegro to the north-west, Kosovo to the north-east, North Macedonia to the east, Greece to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. The total length of the coastline is approximately , of which are taken up by white sandy beaches and the rest by various other landforms. The Adriatic Sea is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending all the way from the Strait of Otranto in the south up to the Po Valley in the north. The sea is apportioned into two major basins, wherein Albania is entirely located within the deepest and the southernmost. The coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |