|
Albaconazole
Albaconazole (development code UR-9825) is an experimental triazole antifungal. It has potential broad-spectrum activity. The drug blocks a number of CYP450 liver enzymes. It has also been studied as an antiprotozoal Antiprotozoal agents ( ATC code: ATC P01) is a class of pharmaceuticals used in treatment of protozoan infection. A paraphyletic group, protozoans have little in common with each other. For example, '' Entamoeba histolytica'', a unikont eukary ... agent. References Chloroarenes Fluoroarenes Lactams Lanosterol 14α-demethylase inhibitors Phenylethanolamines Quinazolines Tertiary alcohols Triazole antifungals {{antiinfective-agent-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
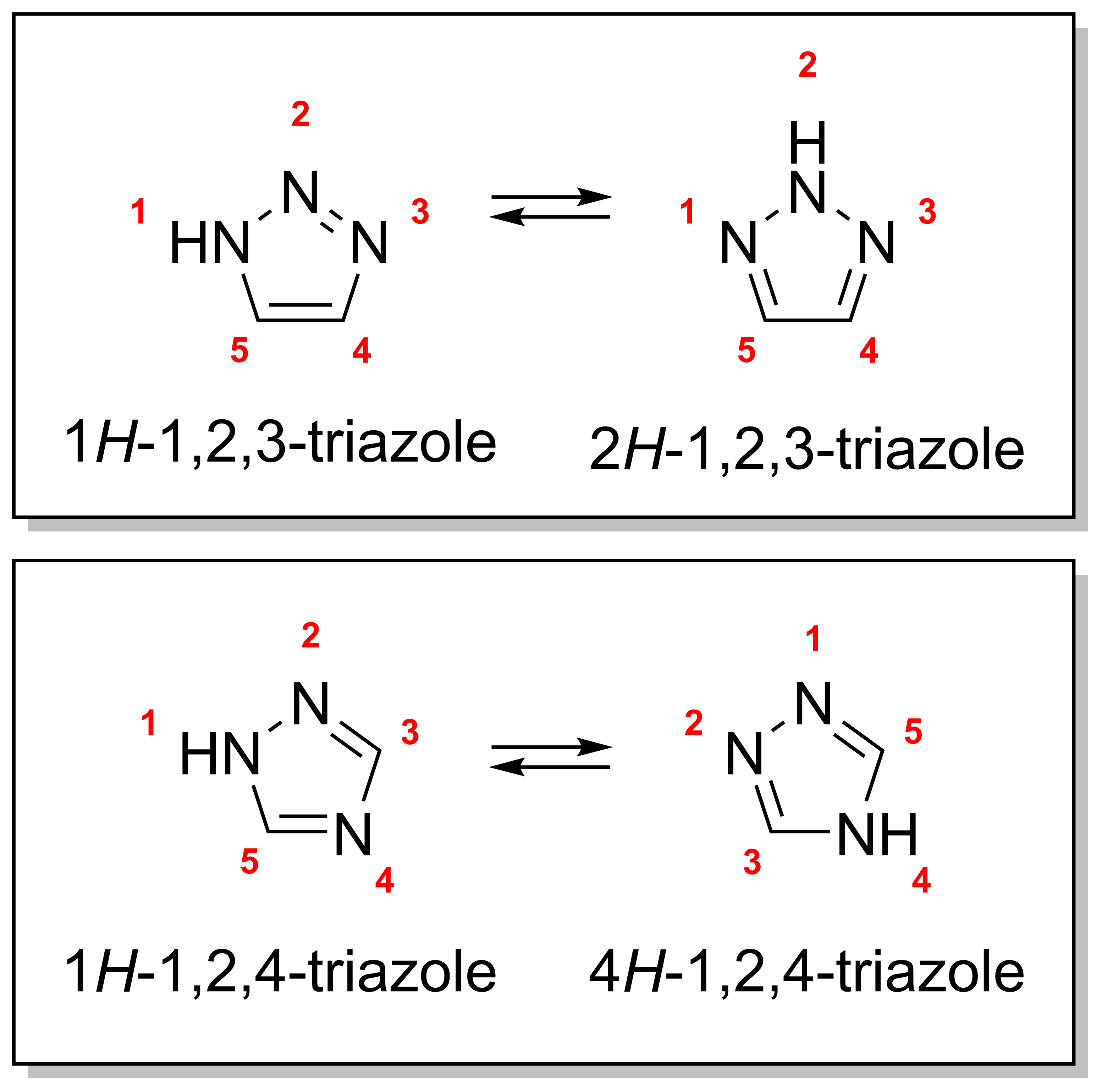
Triazole
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial Isomer, isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to Azide, azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as Piano stool complex, haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of Tautomer, tautomers. In the 1,2,3-Triazole, 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-Triazole, 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. In mammals, these enzymes oxidize steroids, fatty acids, xenobiotics, and participate in many biosyntheses. By hydroxylation, CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. P450s are, in general, the terminal oxidase enzymes in electron transfer chains, broadly categorized as P450-containing systems. The term "P450" is derived from the spectrophotometric peak at the wavelength of the absorption maximum of the enzyme (450 nm) when it is in the reduced state and complexed with carbon monoxide. Most P450s require a protein partner to deliver one or more electrons to reduce the iron (and eventually molecular oxygen). Nomenclature Genes encoding P450 enzymes, and the enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiprotozoal
Antiprotozoal agents ( ATC code: ATC P01) is a class of pharmaceuticals used in treatment of protozoan infection. A paraphyletic group, protozoans have little in common with each other. For example, '' Entamoeba histolytica'', a unikont eukaryotic organism, is more closely related to ''Homo sapiens'' (humans), which also belongs to the unikont phylogenetic group, than it is to '' Naegleria fowleri'', a "protozoan" bikont. As a result, agents effective against one pathogen may not be effective against another. Antiprotozoal agents can be grouped by mechanism or by organism. Recent papers have also proposed the use of viruses to treat infections caused by protozoa. Overuse or misuse of antiprotozoals can lead to the development of antiprotozoal resistance. Medical uses Antiprotozoals are used to treat protozoal infections, which include amebiasis, giardiasis, cryptosporidiosis, microsporidiosis, malaria, babesiosis, trypanosomiasis, Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as a haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide ion (such as fluorine F''−'', chlorine Cl−1,−3,−5, bromine Br−1, or iodine I−). Aryl halides are distinct from haloalkanes (alkyl halides) due to significant differences in their methods of preparation, chemical reactivity, and physical properties. The most common and important members of this class are aryl chlorides, but the group encompasses a wide range of derivatives with diverse applications in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Classification according to halide Aryl fluorides Aryl fluorides are used as synthetic intermediates, e.g. for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and liquid crystals. The conversion of diazonium salts is a well established route to aryl fluorides. Thus, anilines are precursors to aryl fluorides. In the classic Schiemann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactams
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid through cyclization reactions. The term is a portmanteau of the words '' lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size. This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that hydrolysis of an α-lactam gives an α-amino acid and that of a β-Lactam gives a β-amino acid, and so on. Synthesis General synthetic methods are used for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclohexanone with hydrazoic acid, forms ε - Caprolactum, which upon treatment with excess acid forms Cardiazole, a heart stimulant. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanosterol 14α-demethylase Inhibitors
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, having a role in maintaining health of the lens. Lanosterol is the precursor to cholesterol. Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of lanosterol has been intensively investigated. Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to other steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by CYP51 eventually yields cholesterol. Research as an eye drop supplement As a molecule naturally enriched in the eye lens, lanosterol is a component involved in maintenance of lens clarity. Its proposed mechanism of action is to inhibit the aggregation of crystallin proteins, which contribute to the clouding of vision by forming cataracts. Lanosterol is under research for its potential as a therapeutic additive in eye drops to inhibit the aggregation of crystallin p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylethanolamines
Phenylethanolamine (sometimes abbreviated PEOH), or β-hydroxyphenethylamine, is a trace amine with a structure similar to those of other trace phenethylamines as well as the catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. As an organic compound, phenylethanolamine is a β-hydroxylated phenethylamine that is also structurally related to a number of synthetic drugs in the substituted phenethylamine class. In common with these compounds, phenylethanolamine has strong cardiovascular activity and, under the name ''Apophedrin'', has been used as a drug to produce topical vasoconstriction.''The Merck Index, 10th Ed.'' (1983), p. 1051, Merck & Co., Rahway. In appearance, phenylethanolamine is a white solid. Phenylethanolamine is perhaps best known in the field of bioscience as part of the enzyme name " phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase", referring to an enzyme which is responsible for the conversion of norepinephrine into epinephrine, as well as other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinazolines
Quinazoline is an organic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is an aromatic heterocycle with a bicyclic structure consisting of two fused six-membered aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. It is a light yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Also known as 1,3-diazanaphthalene, quinazoline received its name from being an aza derivative of quinoline. Though the parent quinazoline molecule is rarely mentioned by itself in technical literature, substituted derivatives have been synthesized for medicinal purposes such as antimalarial and anticancer agents. Quinazoline is a planar molecule. It is isomeric with the other diazanaphthalenes of the benzodiazine subgroup: cinnoline, quinoxaline A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinazoline, phthalazine and c ..., and phtha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |