|
Al-Tamimi (physician)
Muhammad ibn Sa'id al-Tamimi (), (died 990), known by his kunya, "Abu Abdullah," but more commonly as Al-Tamimi, was a tenth-century physician, who came to renown on account of his medical works. Born in Jerusalem, Al-Tamimi spent his early years in and around Jerusalem where he studied medicine under the tutelage of two local physicians, Al-Hasan ibn Abi Nu'aym, and a Christian monk, Anba Zecharia ben Thawabah. Al-Tamimi possessed an uncommon knowledge of plants and their properties, such that his service in this field was highly coveted and brought him to serve as the personal physician of the Ikhshidid Governor of Ramla, al-Hassan bin Abdullah bin Tughj al-Mastouli, before being asked to render his services in Old Cairo, Egypt. Around 970, Al-Tamimi had settled in Fustat, Egypt, and there prospered in his medical field, writing a medical work for the vizier, Ya'qub ibn Killis (930–991), a Baghdadi Jew who came to work in Egypt under the auspices of the Fatimids. He specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and is considered Holy city, holy to the three major Abrahamic religions—Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital city; Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there, while Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Neither claim is widely Status of Jerusalem, recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Siege of Jerusalem (other), besieged 23 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, and attacked 52 times. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The part of Jerusalem called the City of David (historic), City of David shows first signs of settlement in the 4th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunya (Arabic)
A () is a teknonym in an Arabic name, the name of an adult derived from their eldest son. A kunya is used as a component of an Arabic name, a type of epithet. Literally it refers to the bearer's first-born son or daughter, and this is the usual case. But it may instead have hypothetical or metaphorical references: an example would be Abu Hurayra, “father of the kitten”, the invariable name used for one of the companions of Muhammad who was known for his pet cat. Use of a kunya implies a familiar but respectful setting. A kunya is expressed by the use of '' abū'' (father) or '' umm'' (mother) in a genitive construction, i.e. "father of" or "mother of" as an honorific in place of or alongside given names in the Arab world and the Islamic world more generally. Medieval Jewish names generally had stock kunyas referencing the biblical eponym and not any relative. Those named Abraham received "abu Ishaq", those named Jacob, "abu Yusuf," and so on. In some cases the word ''ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (; ; 973after 1050), known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously "Father of Comparative Religion", "Father of modern geodesy", Founder of Indology and the first anthropologist. Al-Biruni was well versed in physics, mathematics, astronomy, and natural sciences, and also distinguished himself as a historian, chronologist, and linguist. He studied almost all the sciences of his day and was rewarded abundantly for his tireless research in many fields of knowledge. Royalty and other powerful elements in society funded al-Biruni's research and sought him out with specific projects in mind. Influential in his own right, al-Biruni was himself influenced by the scholars of other nations, such as the Greeks, from whom he took inspiration when he turned to the study of philosophy. A gifted linguist, he was conversant in Khwarezmian, Persian, Arabic, and Sanskri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
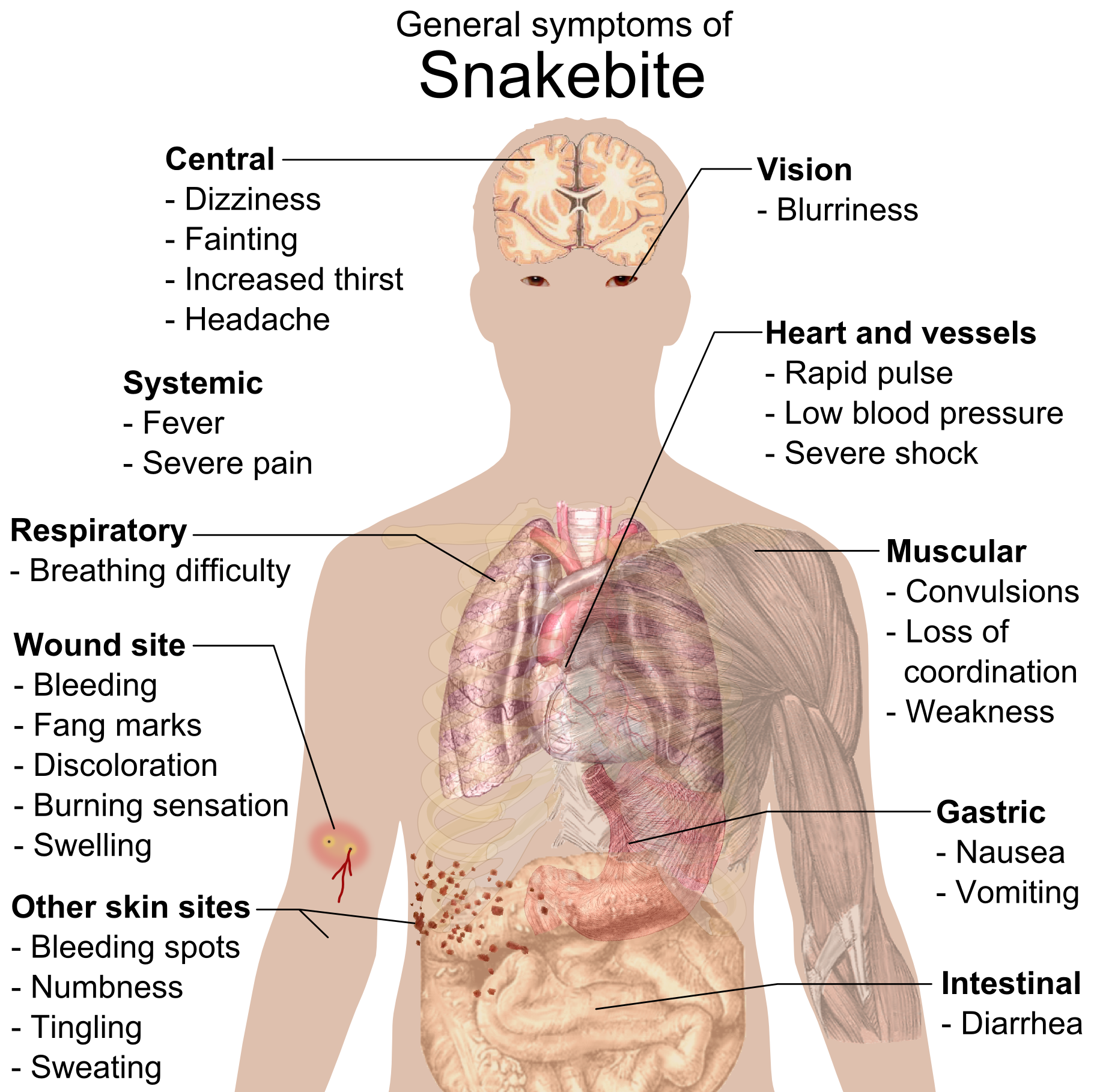
Snakebite
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death. The outcome depends on the type of snake, the area of the body bitten, the amount of snake venom injected, the general health of the person bitten, and whether or not anti-venom serum has been administered by a doctor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theriac
Theriac or theriaca is a medical concoction originally labelled by the Greeks in the 1st century AD and widely adopted in the ancient world as far away as Persia, China and India via the trading links of the Silk Route. It was an alexipharmic, or antidote for a variety of poisons and diseases. It was also considered a panacea, a term for which it could be used interchangeably: in the 16th century Adam Lonicer wrote that garlic was the rustic's theriac or Heal-All. The word ''theriac'' comes from the Greek term θηριακή (''thēriakē''), a feminine adjective signifying "pertaining to animals", from θηρίον (''thērion''), "wild animal, beast". The ancient bestiaries included information—often fanciful—about dangerous beasts and their bites. When cane sugar was an exotic Eastern commodity, the English recommended the sugar-based treacle as an antidote against poison, originally applied as a salve. By extension, ''treacle'' could be applied to any healing prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids traced their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shia, Shi'a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids initially conquered Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia and north-eastern Algeria). They extended their rule across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ya'qub Ibn Killis
Abu'l-Faraj Ya'qub ibn Yusuf ibn Killis (, ), (c. 930 in Baghdad – 991), commonly known simply by his patronymic surname as Ibn Killis, was a high-ranking official of the Ikhshidids who went on to serve as vizier under the Fatimids from 979 until his death in 991. Ya'qub ibn Yusuf ibn Killis was born in Baghdad in about 930 in a Jewish family. After his family moved to Syria he came to Egypt in 943 and entered the service of the Regent Kafur. As soon as he became the household and property administrator, he was in charge of the Egyptian state's finances. Despite converting to Islam in 967, he was imprisoned by Kafur's successors after losing their favor. He was able however to purchase his freedom and went to Ifriqiya, where he put himself at the service of the Fatimid Caliph al-Mu'izz. After the Fatimid conquest of Egypt in 969, Ibn Killis returned to Egypt and was put in charge of the economy, where he was able to regularise the state finances. After the dismissal of Jawhar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a helper but afterwards became the representative and successor of the ''dapir'' (official scribe or secretary) of the Sasanian Empire, Sassanian kings. In modern usage, the term has been used for government Minister (government), ministers in much of the Middle East and beyond. Several alternative spellings are used in English, such as ''vizir'', ''wazir'', and ''vezir''. Etymology Vizier may be derived from the Arabic ''wazara'' (), from the Semitic root ''W-Z-R''. The word is mentioned in the Quran, where Aaron is described as the ''wazir'' (helper) of Moses, as well as the word ''wizr'' (burden) which is also derived from the same root. It was later adopted as a title, in the form of ''wazīr āl Muḥammad'' () by the proto-Shi'a leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fustat
Fustat (), also Fostat, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, though it has been integrated into Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by the Rashidun Muslim general 'Amr ibn al-'As immediately after the Muslim conquest of Egypt in AD 641, and featured the Mosque of Amr, the first mosque built in Egypt. The city reached its peak in the 12th century, with a population of approximately 200,000.Williams, p. 37 It was the centre of administrative power in Egypt, until it was ordered burnt in 1168 by its own vizier, Shawar, to keep its wealth out of the hands of the invading Crusaders. The remains of the city were eventually absorbed by nearby Cairo, which had been built to the north of Fustat in 969 when the Fatimids conquered the region and created a new city as a royal enclosure for the Caliph. The area fell into disrepair for hundreds of years and was used as a rubbish dump. Today, Fustat is a suburb that lies within the modern district of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramla
Ramla (), also known as Ramle (, ), is a city in the Central District of Israel. Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with significant numbers of both Jews and Arabs. The city was founded in the early 8th century CE by the Umayyad caliph Sulayman ibn Abd al-Malik as the capital of Jund Filastin, the district he governed in Bilad al-Sham before becoming caliph in 715. The city's strategic and economic value derived from its location at the intersection of the '' Via Maris'', connecting Cairo with Damascus, and the road connecting the Mediterranean port of Jaffa with Jerusalem. It rapidly overshadowed the adjacent city of Lydda, whose inhabitants were relocated to the new city. Not long after its establishment, Ramla developed as the commercial centre of Palestine, serving as a hub for pottery, dyeing, weaving, and olive oil, and as the home of numerous Muslim scholars. Its prosperity was lauded by geographers in the 10th–11th centuries, when the city was ruled by the Fati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikhshidid Dynasty
The Ikhshidid dynasty (, ) was a Turkic dynasty of governors of mamluk origin, who governed Egypt and parts of the Levant from 935 to 969 on behalf of the Abbasid Caliphate. The dynasty carried the Arabic title "Wāli" reflecting their position as governors on behalf of the Abbasids. The Ikhshidids came to an end when the Fatimid army conquered Fustat in 969. Muhammad ibn Tughj al-Ikhshid, a Turkic mamluk soldier, was appointed governor by the Abbasid Caliph al-Radi. The Ikhshidid family tomb was in Jerusalem. Max Van Berchem, MIFAO 44 - Matériaux pour un Corpus Inscriptionum Arabicarum Part 2 Syrie du Sud T.2 Jérusalem Haram (1927), p13-14 (no.146): “L’émir Muhammad mourut à Damas en 334 (946) et son corps fut transporté et inhumé à Jérusalem. L’émir Unūdjūr mourut en 349 (960) et son corps fut porté à Jérusalem et inhumé à côté de celui de son père. L’émir ‘Ali mourut en 355 (966) et son corps fut transporté à Jérusalem et inhumé à côté de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip K
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularized the name include List of kings of Macedonia, kings of Macedonia and one of the apostles of early Christianity. ''Philip'' has #Philip in other languages, many alternative spellings. One derivation often used as a surname is Phillips (surname), Phillips. The original Greek spelling includes two Ps as seen in Philippides (other), Philippides and Philippos, which is possible due to the Greek endings following the two Ps. To end a word with such a double consonant—in Greek or in English—would, however, be incorrect. It has many diminutive (or even hypocorism, hypocoristic) forms including Phil, Philly (other)#People, Philly, Phillie, Lip (other), Lip, and Pip (other), Pip. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |