|
Al-Hira
Al-Hira ( Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient Lakhmid Arabic city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq. The Sasanian government established the Lakhmid state (Al-Hirah) on the edge of the Arabian Desert near Iraq in order to both prevent direct confrontation between the two empires (Persian and Rome) and to gain its support in battles against Rome. archive.org Etymology and Names It is widely believed that the name ''Al-Hira'' is derived from the Syriac word ''Harta'' (ܚܪܬܐ), meaning "camp" or "encampment". As the city grew in prominence, it came to be known as "Al-Hira, the city of the Arabs," and also as "Hirat al-Nu'man," referring to several kings who bore the name Nu'man and resided there. Linguists and histor ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Conquest Of Iran
As part of the early Muslim conquests, which were initiated by Muhammad in 622, the Rashidun Caliphate conquered the Sasanian Empire between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been the official religion of Persia (or Iran) since the time of the Achaemenid Empire. The persecution of Zoroastrians by the early Muslims during and after this conflict prompted many of them to flee eastward to India, where they were granted refuge by various kings. While Arabia was experiencing the rise of Islam in the 7th century, Persia was struggling with unprecedented levels of political, social, economic, and military weakness; the Sasanian army had greatly exhausted itself in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. Following the execution of Sasanian shah Khosrow II in 628, Persia's internal political stability began deteriorating at a rapid pace. Subsequently, ten new royal claimants were enthroned within the next four years.The Muslim Conquest of Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000. Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya and Najaf, Kufa is one of five Iraqi cities that are of great importance to Shia Islam, Shi'ite Muslims. The city was founded in 638 Common Era, CE (17 Hijra (Islam), Hijrah) during the reign of the second Rashidun Caliph, Umar ibn Al-Khattab, and it was the final capital of the last Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun Caliph, Ali ibn Abi Talib. Kufa was also the founding capital of the Abbasid Caliphate. During the Islamic Golden Age it was home to the grammarians of Kufa. Kufic, Kufic script is named for the city. The Palestinian keffiyeh, also known as kufiya and worn by Arab men, was Cultural appropriation, appropriated from Kufa, and is worn today to convey Cultural diversity, diverse political sentiments. Due to heightened global consumer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
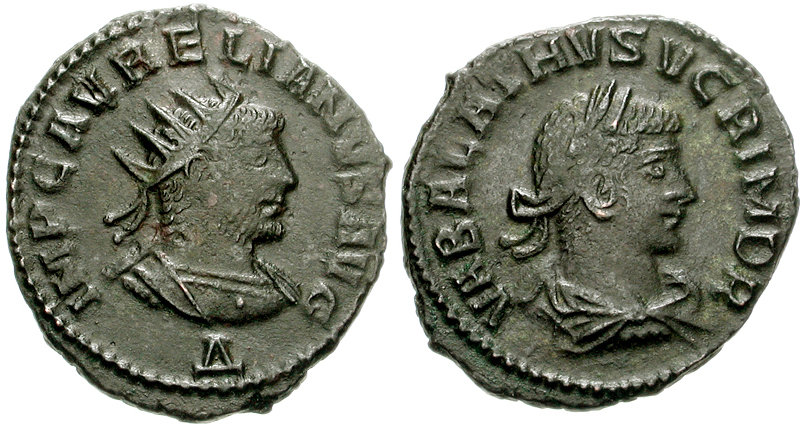
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late antiquity.Norman A. Stillman ''The Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hira
The Battle of Hira () was fought between the Sasanian Empire and the Rashidun Caliphate in 633. It was one of the early battles of the Muslim conquest of Persia, and the loss of the frontier city on the Euphrates River opened the way to the Sasanian capital at Ctesiphon on the Tigris River. Context The city of Al-Hirah, widely known for its size and wealth, had been capital of the Lakhmid kingdom for centuries. It was annexed as a Sasanian frontier province in 602. During the expansion of the Caliphate in 633, Caliph Abu Bakr, sent Khalid ibn al-Walid to capture the lands south of the Euphrates (the as-Sawad Sawad was the name used in early Islamic times (7th–12th centuries) for southern Iraq. It means "black land" or "arable land" and refers to the stark contrast between the alluvial plain of Mesopotamia and the Arabian Desert. Under the Umayyad ...). After taking Ullais in May, the Muslim army under Khalid ibn al-Walid attacked the city of Hira in the last week of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakhmids
The Lakhmid kingdom ( ), also referred to as al-Manādhirah () or as Banū Lakhm (), was an Arab kingdom that was founded and ruled by the Lakhmid dynasty from to 602. Spanning Eastern Arabia and Sawad, Southern Mesopotamia, it existed as a dependency of the Sasanian Empire, though the Lakhmids held al-Hira as their own capital city and governed from there independently. The kingdom was a participant in the Roman–Persian Wars, in which it fought as a Persian ally against the Ghassanids, Ghassanid kingdom, which was ruled by a rival Arab tribe and existed as a dependency of the Roman Empire. While the term "Lakhmids" has been applied to this kingdom's ruling dynasty, more recent scholarship prefers to refer to them as the Naṣrids. The Nasrid dynasty's authority extended over to their Arab allies in Eastern Arabia, Al-Bahrain (eastern cost of Arabia) and Al-Yamama. In 602, the Persian king Khosrow II deposed and executed the last Nasrid ruler Al-Nu'man III ibn al-Mundhir, Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II, also Nebuchadrezzar II, meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir", was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from the death of his father Nabopolassar in 605 BC to his own death in 562 BC. Often titled Nebuchadnezzar the Great, he is regarded as the empire's greatest king, famous for his military campaigns in the Levant and their role in Jewish history, and for his construction projects in his capital of Babylon, including the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. Ruling for 43 years, Nebuchadnezzar was the longest-reigning king of the Babylonian dynasty. By the time of his death, he was among the most powerful rulers in the world. Possibly named after Nebuchadnezzar (governor of Uruk), his grandfather of the same name, or after Nebuchadnezzar I ( 1125–1104 BC), one of Babylon's greatest ancient warrior-kings, Nebuchadnezzar II had already secured renown for himself during his father's reign, leading armies in the Medo-Babylonian conquest of the Assyrian Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmyrene Empire
The Palmyrene Empire was a short-lived breakaway state from the Roman Empire resulting from the Crisis of the Third Century. Named after its capital city, Palmyra, it encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Arabia Petraea, and Egypt (Roman province), Egypt, as well as large parts of Anatolia, Asia Minor. The Palmyrene Empire was ruled by Queen Zenobia, officially as regent for her son Vaballathus, who inherited the throne in 267 at age ten. In 270, Zenobia rapidly conquered most of the Roman east, attempting to maintain relations with Rome as a legitimate power. In 271, she claimed the imperial title for both herself and her son, fighting a short war with the Roman emperor Aurelian, who conquered Palmyra and captured Zenobia. A year later the Palmyrenes rebelled, which led Aurelian to raze Palmyra. Despite its brief existence, the Palmyrene Empire is remembered for having been ruled by one of the most ambitious and powerful women in antiquity. It is also hailed in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amr Ibn Adi
Amr ibn Adi ibn Nasr ibn Rabi'a (), commonly known as Amr I, was the semi-legendary first king of the Lakhmid Kingdom. Biography Most of the details of his life are legendary and later inventions; according to Charles Pellat, "as the historical reality of this personage and of the events ..became blurred, legend made use of his name to fix the time of events displaced from their historical sequence, and of stories invented to explain proverbs which had become unintelligible". According to the medieval Arab historians, Amr's father Adi gained the hand of Raqash, the favourite sister of the Tanukhid king Jadhima al-Abrash, by a ruse. Amr is said to have been abducted as a child by a ''jinn'', before being returned to his uncle. He is then said to have been left behind as regent by Jadhima, who marched against al-Zabba (Zenobia), the Arab queen of Palmyra. When his uncle was killed in battle, Amr vowed to avenge his death; even after Zenobia denied him this chance by committing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |