|
Al-Fadl Ibn Rawh Ibn Hatim Al-Muhallabi
Al-Fadl ibn Rawh ibn Hatim al-Muhallabi () (d. 794) was a member of the Muhallabid family and a provincial governor for the Abbasid Caliphate. He was the last of the Muhallabid governors of Ifriqiya, serving there from 793 until his death. Career Al-Fadl was the son of Rawh ibn Hatim al-Muhallabi, who was governor of Ifriqiya from 787 until 791. Following Rawh's death, Nasr ibn Habib al-Muhallabi became governor of the province, but al-Fadl, who was then in charge of the Zab region, wanted the position for himself. He therefore left Ifriqiya and made his way to the court of the caliph Harun al-Rashid, who he convinced to give him the appointment instead. Nasr was then dismissed and al-Muhallab ibn Yazid was made interim governor, until al-Fadl returned to the province in the spring of 791 and took up his new position. Al-Fadl's governorship quickly became troubled due to his poor relations with the garrison troops ('' jund''), who he dealt with harshly as a result of their co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of science, culture, arts, and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. By housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th-century Arab People
The 8th century is the period from 701 (represented by the Roman numerals DCCI) through 800 (DCCC) in accordance with the Julian Calendar. In the historiography of Europe the phrase the long 8th century is sometimes used to refer to the period of circa AD 660–820. The coast of North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula quickly came under Islamic Arab domination. The westward expansion of the Umayyad Empire was famously halted at the siege of Constantinople by the Byzantine Empire and the Battle of Tours by the Franks. The tide of Arab conquest came to an end in the middle of the 8th century.Roberts, J., '' History of the World'', Penguin, 1994. In Europe, late in the century, the Vikings, seafaring peoples from Scandinavia, begin raiding the coasts of Europe and the Mediterranean, and go on to found several important kingdoms. In Asia, the Pala Empire is founded in Bengal. The Tang dynasty reaches its pinnacle under Chinese Emperor Xuanzong. The Nara period begins in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Governors Of Ifriqiya
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of science, culture, arts, and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. By housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
794 Deaths
Year 794 ( DCCXCIV) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 794th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 794th year of the 1st millennium, the 94th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 790s decade. The denomination 794 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Europe * King Charlemagne abandons his channel project (see 793), and attacks the Saxon rebels from the north, supported by a second Frankish army under his son Charles the Younger, which crosses the Rhine at Cologne from the west; threatened from two directions, the Saxons surrender near Paderborn (Westphalia). * August 10 – Queen Fastrada, third wife of Charlemagne, dies in Frankfurt after 11 years of marriage. Charlemagne consoles himself with Luitgard, an Alemannian noblewoman, whom he marries and moves into his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
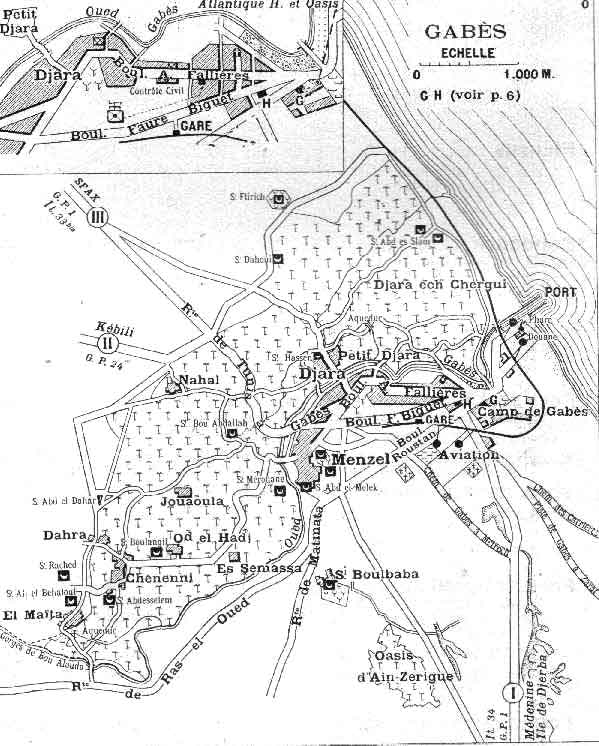
Gabès
Gabès (, ; ), also spelled Cabès, Cabes, and Kabes, is the capital of the Gabès Governorate in Tunisia. Situated on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès, the city has a population of 167,863, making it the 6th largest city in Tunisia. Located 327 km southeast of Tunis and 113 km from Sfax, Gabès lies at the delta of the Wadi Qabis, which originates 10 kilometers upstream at Ras El Oued, Algeria, Ras al-Oued and serves as its primary water source. Historically, the town was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian settlement known as Tacapae before falling under Roman Empire, Roman control. It was later ruined during the 7th-century Arab invasion but was recovered by Sidi Boulbaba, a revered companion of the Muhammad, Prophet Muhammad and a patron of the town. Although it experienced decline under the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, Gabès saw significant growth under French rule from 1881 to 1955, with the development of key infrastructure, including a railway, road network, and port. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
'Abdallah Ibn Al-Jarud
Abd Allah (), also spelled Abdullah, Abdhullah, Abdellah, Abdollah, Abdallah, Abdulla, Abdalla and many others, is an Arabic theophoric name meaning ''servant of God'' or "God's follower". It is built from the Arabic words '' abd'' () and ''Allāh'' (). Although the first letter "a" in ''Allāh'', as the first letter of the article ''al-'', is usually unstressed in Arabic, it is usually stressed in the pronunciation of this name. The variants ''Abdollah'' and ''Abdullah'' represent the elision of this "a" following the "u" of the Classical Arabic nominative case (pronounced in Persian). Humility before God is an essential value of Islam, hence ''Abdullah'' is a common name among Muslims. The name of the Islamic prophet Muhammad's father was Abdullah. As the prophet's father died before his birth, this indicates that the name was already in use in pre-Islamic Arabia. It is also common among Mizrahi Jews and Sephardic Jews, especially Iraqi Jews and Syrian Jews. Among the latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casablanca and Algiers) and the List of largest cities in the Arab world, eleventh-largest in the Arab world. Situated on the Gulf of Tunis, behind the Lake of Tunis and the port of La Goulette (Ḥalq il-Wād), the city extends along the coastal plain and the hills that surround it. At its core lies the Medina of Tunis, Medina, a World Heritage Site. East of the Medina, through the Sea Gate (also known as the ''Bab el Bhar'' and the ''Porte de France''), begins the modern part of the city called "Ville Nouvelle", traversed by the grand Avenue Habib Bourguiba (often referred to by media and travel guides as "the Tunisian Champs-Élysées"), where the colonial-era buildings provide a clear contrast to smaller, older structures. Further east by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biskra Province
Biskra (, Berber: ⴱⴻⵙⴽⵔⴰ) is a province (''wilaya'') of Algeria. Its capital is Biskra. It is located on the northern edge of the Algerian Sahara, south of the Atlas Mountains. Geographically, Biskra Province is arid, but oases and rivers can be found, such as the Djedi River which flows through the province. The mountainous Aurès region also extends into the province. Biskra Province is home to the district of Tolga, which is well-known internationally for its high-quality Deglet Nour dates. Other localities include Lichoua, Sidi Okba, Sidi Khaled, and El-Kantara. In 2019, several communes were removed from the province to form the new Ouled Djellal Province. History Berber tribes The Biskra area has been inhabited since at least the 3rd millennium BC, when the Gaetuli, an ancient Berber tribe, arrived in North Africa. They settled in the Aurès region, where they posed problems to Roman infiltration in the 3rd century BC as they were stellar horseme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the type of political region or polity, a ''governor'' may be either appointed or elected, and the governor's powers can vary significantly, depending on the public laws in place locally. The adjective pertaining to a governor is gubernatorial, from the Latin root ''gubernare''. In a federated state, the governor may serve as head of state and head of government for their regional polity, while still operating under the laws of the federation, which has its own head of state for the entire federation. Ancient empires Pre-Roman empires Though the legal and administrative framework of provinces, each administered by a governor, was created by the ancient Rome, Romans, the term ''governor'' has been a convenient term for historians to describe si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |