|
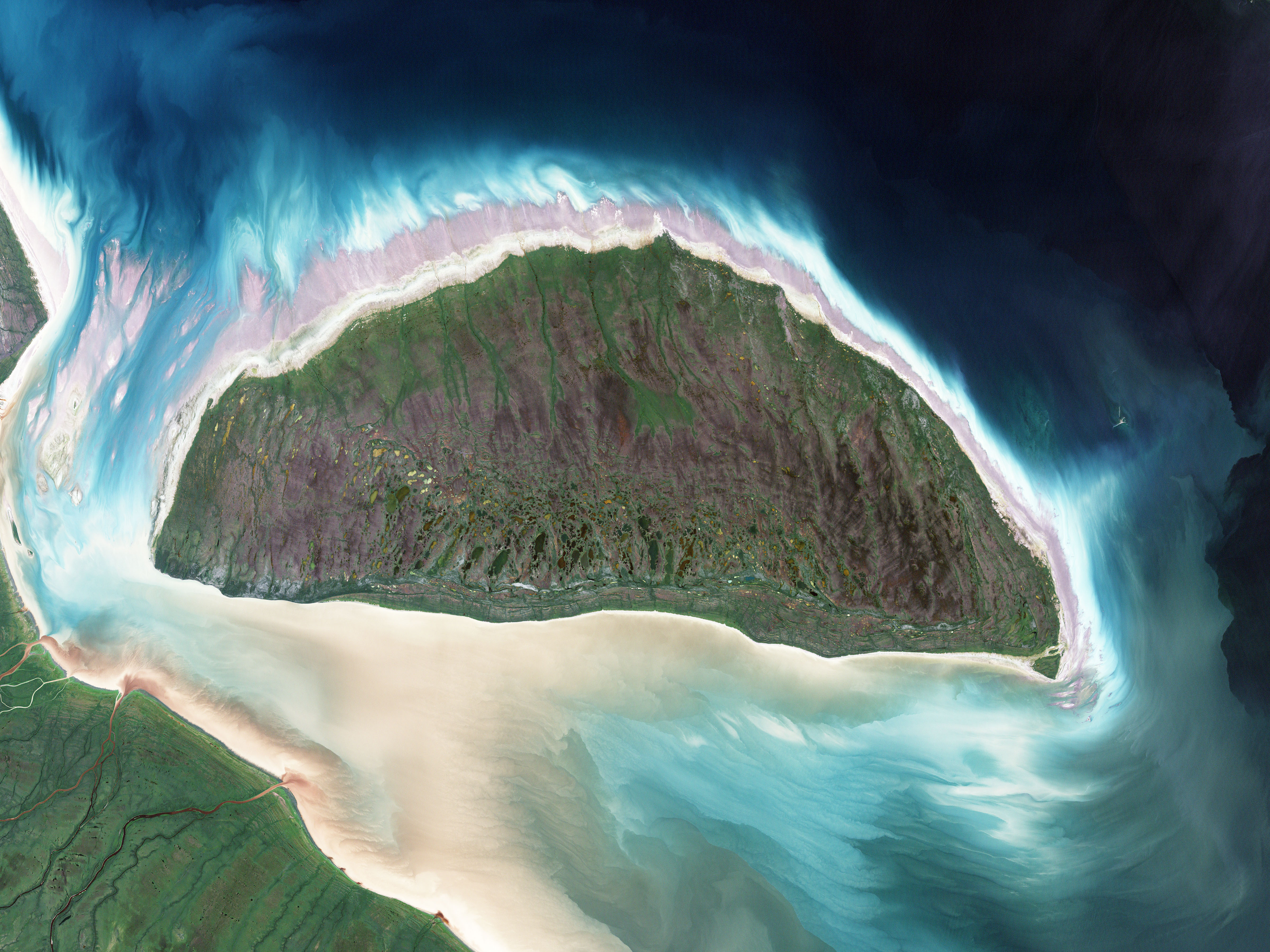
Akimiski Island
Akimiski Island is the largest island in James Bay (a southeasterly extension of Hudson Bay), Canada, which is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the territory of Nunavut. It has an area of , making it the 163rd largest island in the world, and Canada's 29th largest island. Akimiski Island is from the province of Ontario. From the western side of the island, the Ontario coastline is visible. The island's name is Swampy Cree for "land across the water". The island has no year-round human inhabitants. The surface of Akimiski is flat and slopes gradually to the north. Most of the vegetation that covers the island consists of lichen, moss, sedges, and dwarf black spruce. The island is a coastal wetland that includes mudflats, tidal marshes, and tidal mudflats. Freshwater streams that flow into southwestern James Bay carry sediments and abundant nutrients that help to sustain the productive waterfowl habitat around Akimiski Island. The Akimiski Island Group includes Akimiski, Gaske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swampy Cree
The Swampy Cree people, also known by their Exonym and endonym, autonyms ''Néhinaw'', ''Maskiki Wi Iniwak'', ''Mushkekowuk,'' ''Maškékowak, Maskegon'' or ''Maskekon'' (and therefore also ''Muskegon'' and ''Muskegoes'') or by exonyms including ''West Main Cree,'' ''Lowland Cree'', and ''Homeguard Cree'', are a division of the Cree Nation occupying lands located in northern Manitoba, along the Saskatchewan River in northeastern Saskatchewan, along the shores of Hudson Bay and adjoining interior lands south and west as well as territories along the shores of Hudson and James Bay in Ontario. They are geographically and to some extent culturally split into two main groupings, and therefore speak two dialects of the Swampy Cree language, which is an "n-dialect": * Western Swampy Cree called themselves: ''Mushkego'', ''Mushkegowuk'' (or ''Maškēkowak''), also called ''Lowland (Half-Homeguard) Cree'', speak the western dialect of the Swampy Cree language, while the ''s''/''š'' dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akimiski Island NASA
Akimiski Island is the largest island in James Bay (a southeasterly extension of Hudson Bay), Canada, which is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the territory of Nunavut. It has an area of , making it the 163rd largest island in the world, and Canada's 29th largest island. Akimiski Island is from the province of Ontario. From the western side of the island, the Ontario coastline is visible. The island's name is Swampy Cree for "land across the water". The island has no year-round human inhabitants. The surface of Akimiski is flat and slopes gradually to the north. Most of the vegetation that covers the island consists of lichen, moss, sedges, and dwarf black spruce. The island is a coastal wetland that includes mudflats, tidal marshes, and tidal mudflats. Freshwater streams that flow into southwestern James Bay carry sediments and abundant nutrients that help to sustain the productive waterfowl habitat around Akimiski Island. The Akimiski Island Group includes Akimiski, Gaske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden (Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lapland (Sweden), Lappland), northern Finland (North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lapland (Finland), Lappi), Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland (Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying cryosphere, snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semipalmated Sandpiper
The semipalmated sandpiper (''Calidris pusilla'') is a very small shorebird. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'', a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific ''pusilla'' is Latin for "very small". It is sometimes separated with other " stints" in ''Erolia,'' but, although these apparently form a monophyletic group, the present species' old genus ''Ereunetes'' had been proposed before ''Erolia''. Description It is a small sandpiper, long and weighing around . Wingspan ranges from . Adults have black legs and a short, stout, straight dark bill. The body is dark grey-brown on top and white underneath. The head and neck are tinged light grey-brown. This bird can be difficult to distinguish from other similar tiny shorebirds, in particular the western sandpiper; these are known collectively as "peeps" or " stints". Breeding and habitat Their breeding habitat is the southern tundra in Canada and Alaska near water. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marbled Godwit
The marbled godwit (''Limosa fedoa'') is a large migratory shorebird in the family Scolopacidae. On average, it is the largest of the four species of godwit. Taxonomy In 1750 the English naturalist George Edwards included an illustration and a description of the marbled godwit in the third volume of his ''A Natural History of Uncommon Birds''. He used the English name "The Greater American Godwit". Edwards based his hand-coloured etching on a preserved specimen that had been brought to London from the Hudson Bay area of Canada by James Isham. When in 1758 the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus updated his ''Systema Naturae'' for the tenth edition, he placed the marbled godwit with godwits and ibises in the genus '' Scolopax''. Linnaeus included a brief description, coined the binomial name ''Scolopax fedoa'' and cited Edwards' work. The marbled godwit is now placed in the genus '' Limosa'' that was introduced in 1760 by the French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson. The genus na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
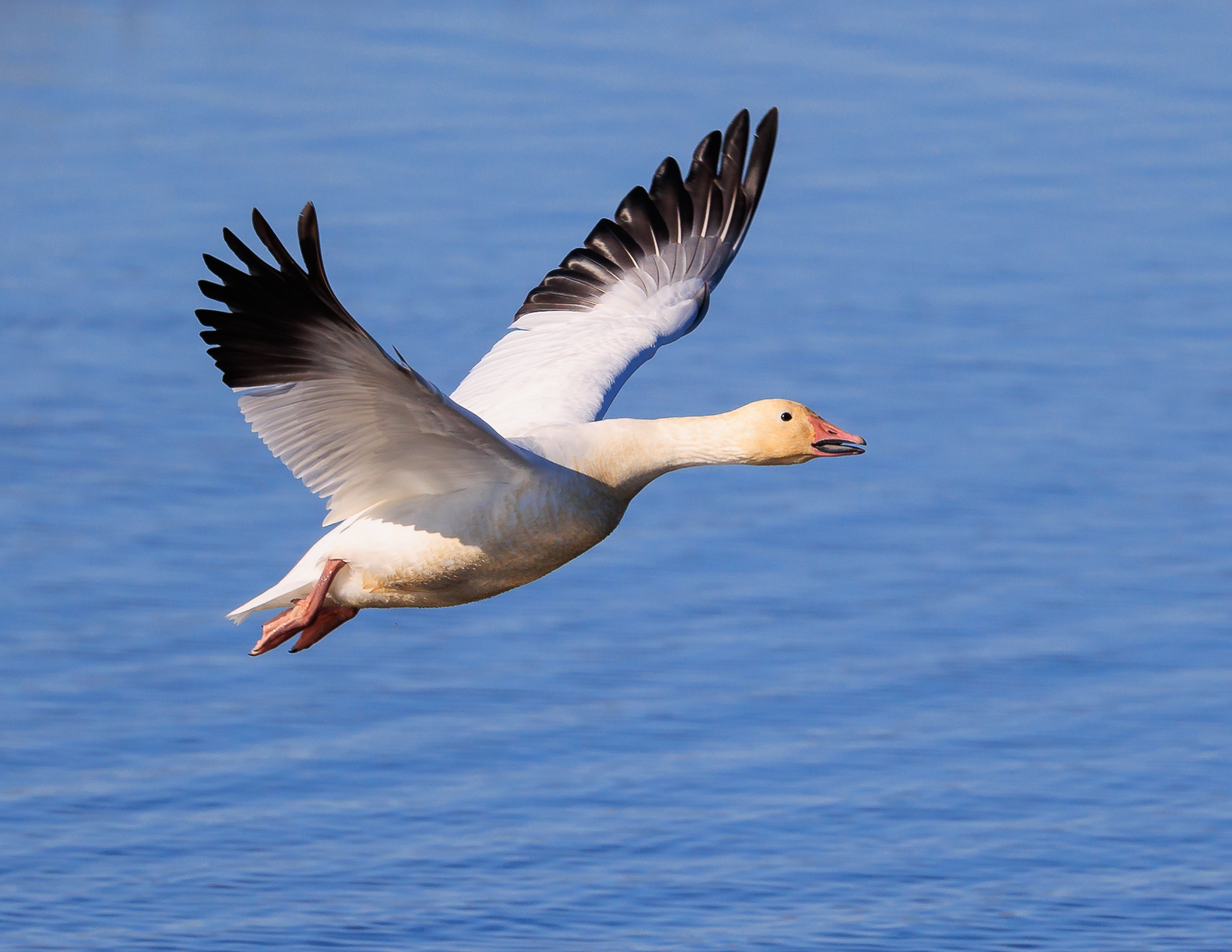
Snow Goose
The snow goose (''Anser caerulescens'') is a species of goose native to North America. Both white and dark morphs exist, the latter often known as blue goose. Its name derives from the typically white plumage. The species was previously placed in the Chen (genus), genus ''Chen'', but is now typically included in the "gray goose" genus ''Anser (genus), Anser''. Snow geese breed north of the tree line, timberline in Greenland, Canada, Alaska, and the northeastern tip of Siberia, and spend winters in warm parts of North America from southwestern British Columbia through parts of the United States to Mexico. Taxonomy In 1750 the English naturalist George Edwards (naturalist), George Edwards included an illustration and a description of the snow goose in the third volume of his ''A Natural History of Uncommon Birds''. He used the English name "The blue-winged goose". Edwards based his hand-coloured etching on a preserved specimen that had been brought to London from the Hudson Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada Goose
The Canada goose (''Branta canadensis''), sometimes called Canadian goose, is a large species of goose with a black head and neck, white cheeks, white under its chin, and a brown body. It is native to the arctic and temperate regions of North America, and it is occasionally found during bird migration, migration across the Atlantic in northern Europe. It has been introduced to France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Scandinavia, New Zealand, Japan, Chile, Argentina, and the Falkland Islands. Like most geese, the Canada goose is primarily herbivorous and normally migratory; often found on or close to fresh water, the Canada goose is also common in Brackish water, brackish marshes, estuaries, and lagoons. Extremely adept at urban wildlife, living in human-altered areas, Canada geese have established breeding colonies in urban and cultivated habitats, which provide food and few natural predators. The success of this common park species has led to it often being considered a pest (orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brant (goose)
The brant or brent goose (''Branta bernicla'') is a small goose of the genus ''Branta''. There are three subspecies, all of which winter along temperate-zone sea-coasts and breed on the high-Arctic tundra. The Brent oilfield was named after the species. Taxonomy The brant was Species description, formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial nomenclature, binomial name ''Anas bernicla''. Linnaeus specified the type locality (biology), type locality as Europe but in 1761 restricted it to Sweden. The brant is now one of six species placed in the genus ''Branta'' that was introduced in 1769 by the Austrian naturalist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli. The genus name ''Branta'' is a Latinised form of Old Norse ''brandgás'', "burnt (black) goose". The specific epithet ''bernicla'' is Medieval Latin for barnacle. The brant and the similar barnacle goose were previously c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Migration
Bird migration is a seasonal movement of birds between breeding and wintering grounds that occurs twice a year. It is typically from north to south or from south to north. Animal migration, Migration is inherently risky, due to predation and mortality. The Arctic tern holds the long-distance migration record for birds, travelling between Arctic breeding grounds and the Antarctic each year. Some species of Procellariiformes, tubenoses, such as albatrosses, circle the Earth, flying over the southern oceans, while others such as Manx shearwaters migrate between their northern breeding grounds and the southern ocean. Shorter migrations are common, while longer ones are not. The shorter migrations include altitudinal migrations on mountains, including the Andes and Himalayas. The timing of migration seems to be controlled primarily by changes in day length. Migrating birds navigate using celestial cues from the Sun and stars, the Earth's magnetic field, and mental maps. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Habitat Site
A Key Habitat Site is a Canadian Wildlife Service designation for an area that supports at least 1% of the country's population of any migratory bird species, or subspecies, at any time. There may be overlap with areas designated as a migratory bird sanctuary or National Wildlife Area A National Wildlife Area is a conservation designation for a geographical region in Canada that restricts most human activities on that region. However, land use permits may be issued "for activities that are compatible with conservation". Su .... References External links Key migratory bird terrestrial habitat sites in the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, March 2006 Canadian Wildlife Service Environment and Climate Change Canada Ornithology {{Canada-protected-area-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Migratory Bird Sanctuaries Of Canada
Migratory Bird Sanctuaries are created in Canada under the Migratory Birds Convention Act, Migratory Birds Convention Act, 1994. They are administered by the Canadian Wildlife Service. The first sanctuary in North America, Last Mountain Lake Bird Sanctuary, was created by federal order-in-council in 1887. Provinces Alberta There are four Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in Alberta. British Columbia There are seven Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in British Columbia. Manitoba Currently there are no Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in the province of Manitoba. New Brunswick There are three Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in New Brunswick. Newfoundland and Labrador There are three Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in Newfoundland and Labrador. Nova Scotia There are seven Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in Nova Scotia. Ontario There are nine Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in Ontario. Quebec There are twenty-eight Migratory Bird Sanctuaries in Quebec. Prince Edward Island There is one Migratory B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |