|
Akhmim
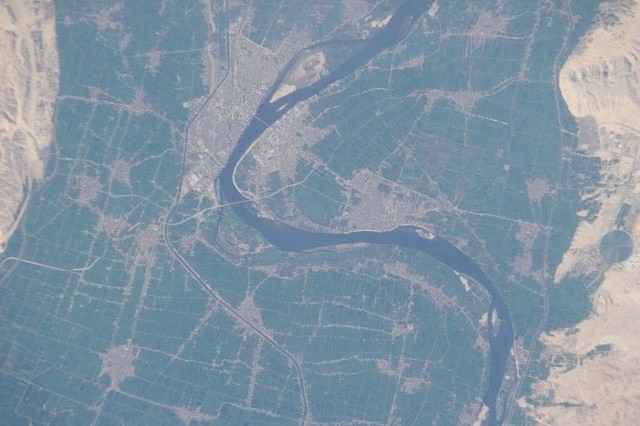
Akhmim (, ; Akhmimic , ; Sahidic/Bohairic ) is a city in the Sohag Governorate of Upper Egypt. Referred to by the ancient Greeks as Khemmis or Chemmis () and Panopolis (), it is located on the east bank of the Nile, to the northeast of Sohag. History Akhmim was known in Ancient Egypt as Ipu, Apu (according to Heinrich Brugsch, Brugsch the name is related to the nearby village of Kafr Abou) or Khent-min. It was the capital of the ninth (Chemmite) nome (Egypt), nome of Upper Egypt. The city is a suggested hometown for Yuya, the official of Tuthmosis IV and Amenhotep III. The ithyphallic Min (god), Min (whom the Greeks identified with Pan (mythology), Pan) was worshipped here as "the strong Horus." Herodotus mentions the temple dedicated to Perseus and asserts that Chemmis was remarkable for being the hero’s birthplace, wherein celebrations and games were held in his honour after the manner of the Greeks; at which prizes were given. As a matter of fact, some representation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohag
Sohag (, , ), also spelled as Suhag or Suhaj, is a city on the west bank of the Nile in Egypt. It has been the capital of Sohag Governorate since 1960, before which the capital was Girga and the name of the governorate was Girga Governorate. It also included Esna Governorate (nowadays Qena Governorate). History The modern city developed from the village of ''Suhay'' () (or ''Sumay''), the name of which eventually transformed into Suhaj, and is located on the site of several ancient settlements, the largest of which is ''Bompae'' (; or ). The others include ''Tmupaie'' (, ), ''Bay'' (, possibly an Arabisation of the aforementioned "Paha") and ''Sawaqi'' (). Geography Sohag lies on a fertile agricultural plain on the western bank of the Nile, approximately southwest of Akhmim. The city includes two islands; Karaman-ez-Zahur Island is larger and uninhabited, and ez-Zahur Island (جزيرة الزهور, Ǧazīrat az-Zuhur, "Flower Island") has some homes. Economy The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohag Governorate
Sohag () is one of the governorates of Egypt. It is located in the southern part of the country (Upper Egypt), and covers a stretch of the Nile Valley. Since 1960, its capital has been the city of Sohag. Prior to that, the capital was the city of Girga and the name of the governorate was Girga Governorate. Overview The rate of poverty is more than 60% in this governorate but recently some social safety networks have been provided in the form of financial assistance and job opportunities. The funding has been coordinated by the country's Ministry of Finance and with assistance from international organizations. In early 2019, some residents of the poorer villages of Sohag were able to move into their new homes built, in part, with aid from the National Bank of Kuwait. There was a celebration for the completion of 115 homes where residents also received cattle and other gifts. Archaeology In April 2019, the archaeological mission of the Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Min (god)
Min (), also called Menas, is an ancient Egyptian deities, ancient Egyptian god whose cult originated in the predynastic Egypt, predynastic period (4th millennium BCE). He was represented in many different forms, but was most often represented in male human form, shown with an erect penis which he holds in his left hand and an upheld right arm holding a Crook and flail, flail. Myths and function Min's cult began and was centered around Coptos (Koptos, modern day Qift) and Akhmim (Panopolis) of Upper Egypt, where in his honour great festivals were held celebrating his "coming forth" with a public procession and presentation of offerings. His other associations include the eastern desert and links to the god Horus. Flinders Petrie excavated two large statues of Min at Qift which are now in the Ashmolean Museum and it is thought by some that they are pre-dynastic. Although not mentioned by name, a reference to "he whose arm is raised in the East" in the Pyramid Texts is thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copt
Copts (; ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptian population, descended from the ancient Egyptians. Copts predominantly follow the Coptic Orthodox Church in Alexandria. They are the largest Christian denomination in Egypt and the Middle East, as well as in Sudan and Libya.Coptic Orthodox Church Listings for Libya, p. 136 account for roughly 5 to 15 percent of the population of Egypt. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorates Of Egypt
Egypt is administratively organized under a dual system that may consist of either two or three tiers, with further subdivisions occasionally resulting in an additional layer. It follows a centralized system of local government, officially termed local administration, as it functions as a part of the executive branch of the government. Overview Egyptian law delineates the units of local governance as governorates, centers, cities, districts, and villages, each possessing legal personality. The legal framework establishes a dual system of local administration that alternates between a two-tier and a three-tier structure, depending on the characteristics of the governorate. At the top of the hierarchy are 27 governorates (singular: ', plural: '). Each governorate has a capital, typically its largest city, and is headed by a governor, appointed by the President of Egypt, serving at the president’s discretion. Governors hold the civilian rank of minister and report directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Egypt
0-9 * 10th of Ramadan * 15th of May (city), 15th of May * 6th of October (city), 6th of October A * Abu El Matamir * Abu Hummus * Abu Tesht * Abu Tig * Akhmim * Al Khankah * Alexandria * Arish * Ashmoun * Aswan * Awsim * Ain Sokhna B * Badr, Egypt, Badr * Baltim * Banha * Basyoun * Biyala * Belqas * Beni Mazar * Beni Suef * Beni Ebeid * Biba, Egypt, Biba * Bilbeis * Birket El Sab * Borg El Arab * Borg El Burullus * Bush, Egypt, Bush C * Cairo D * Dahab * Dairut * Damanhur * Damietta * Dar El Salam * Daraw * Deir Mawas * Dekernes * Dendera * Desouk * Diarb Negm * Dishna, Egypt, Dishna E * Edfu * Edku * El Alamein * El Ayyat * El Badari, Egypt, El Badari * El Badrashein * El Bagour * El Balyana * El Basaliya * El Bayadiya * El Dabaa * El Delengat * El Fashn * El Gamaliya * El Ghanayem * El Hamool * El Hamam * El Hawamdeya * El Husseiniya * El Idwa * El Kanayat * El Mahalla El Kubra * El Mahmoudiyah * Ptolemais Hermiou, El Mansha * El Manzala * El Mara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuya
Yuya (sometimes Iouiya, or Yuaa, also known as Yaa, Ya, Yiya, Yayi, Yu, Yuyu, Yaya, Yiay, Yia, and Yuy) was a powerful ancient Egyptian courtier during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt ( 1390 BC). He was married to Thuya, an Egyptian noblewoman associated with the royal family, who held high offices in the governmental and religious hierarchies. Their daughter, Tiye, became the Great Royal Wife of Amenhotep III. Yuya and Thuya are known to have had a son named Anen, who carried the titles "Chancellor of Lower Egypt", "Second Prophet of Amun", "Sm-priest of Heliopolis", and "Divine Father". They may also have been the parents of Ay,Rice, p.222 an Egyptian courtier active during the reign of Akhenaten, who eventually became pharaoh as ''Kheperkheprure Ay''. There is no conclusive evidence, however, regarding the kinship of Yuya and Ay, although certainly both men came from the town of Akhmim. The tomb of Yuya and Thuya was, until the discovery of Tutankhamun's, one of the most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome (Egypt)
A nome (, from , ''nomós'', "district") was a territorial division in ancient Egypt. Each nome was ruled by a nomarch (, "Great Chief"). The number of nomes changed through the various periods of the history of ancient Egypt. Etymology The term ''nome'' comes from Ancient Greek νομός ''nomós'' meaning "pasture" extended to "dwelling" and "district"; the Ancient Egyptian term was ( /sɛpɑt/). Today's use of the Ancient Greek rather than the Ancient Egyptian term came about during the Ptolemaic period, when the use of Greek was widespread in Egypt. The availability of Greek records on Egypt influenced the adoption of Greek terms by later historians. History Dynastic Egypt The division of ancient Egypt into nomes can be traced back to prehistoric Egypt (before 3100 BC). These nomes originally existed as autonomous city-states, but later began to unify. According to ancient tradition, the ruler Menes completed the final unification. Not only did the division into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the southeast, and South Sudan to the south. Sudan has a population of 50 million people as of 2024 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's List of African countries by area, third-largest country by area and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum, secession of South Sudan in 2011; since then both titles have been held by Algeria. Sudan's capital and most populous city is Khartoum. The area that is now Sudan witnessed the Khormusan ( 40000–16000 BC), Halfan culture ( 20500–17000 BC), Sebilian ( 13000–10000 BC), Qadan culture ( 15000–5000 BC), the war of Jebel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake Nasser (formed by the Aswan High Dam). Name In ancient Egypt, Upper Egypt was known as ''tꜣ šmꜣw'', literally "the Land of Reeds" or "the Sedgeland", named for the sedges that grow there. In Biblical Hebrew it was known as and in Akkadian it was known as . Both names originate from the Egyptian '' pꜣ- tꜣ- rsj'', meaning "the southern land". In Arabic, the region is called Sa'id or Sahid, from صعيد meaning "uplands", from the root صعد meaning to go up, ascend, or rise. Inhabitants of Upper Egypt are known as Sa'idis and they generally speak Sa'idi Egyptian Arabic. Geography Upper Egypt is between the Cataracts of the Nile beyond modern-day Aswan, downriver (northward) to the area of El-Ayait, which places modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Of Punt
The Land of Punt (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pwnt#Egyptian, pwnt''; alternate Egyptian language#Egyptological pronunciation, Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') ) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold, aromatic resins, Dalbergia melanoxylon, blackwood, ebony, ivory trade, ivory and wild animals.Shaw & Nicholson, p. 231. Recent evidence locates it in northwestern Eritrea. It is possible that it includes or corresponds to Opone, as later known by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, while some Biblical criticism, biblical scholars have identified it with the biblical land of Phut, Put or Havilah. At times Punt is referred to as ''Ta netjer'' (''wikt:tꜣ-nṯr#Egyptian, tꜣ nṯr''), . The exact location of Punt is debated by historians. Various locations have been offered, southeast of Egypt, a coastal region south of it along the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean, in present day north-east Sudan, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caene
Qena ( ' , locally: ) is a city in Upper Egypt, and the capital of the Qena Governorate. Situated on the east bank of the Nile, it was known in antiquity as Kaine (Greek Καινή, meaning "new (city)"; Latinized transliteration: Caene) and Maximianopolis. Gauthier identifies Qena with ancient Shabt. Qena meaning in Arabic "very red" of fertile land. Overview This provincial capital is located about 95 km from El Balyana and 63 km north of Luxor. It is most famous for its proximity to the ruins of Dendara. It owes its modern prosperity to the opening of the Wadi Qena towards the Red Sea, which is a major traffic route between Upper Egypt and the Red Sea. Tourists traveling between Luxor and the Red Sea will assuredly pass through this city since there is only one good road connection. Qena is noted for its pottery. Qena is also known for its beautiful huge mountains and green nature. South Valley University has a campus in Qena. Qena is a large market town o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |