|
Ajrak Chadar
Ajrak ( sd, اجرڪ), also known as Ajrakh, is a unique form of blockprinting found mostly in Sindh, Pakistan and Ajrakhpur, Kutch district, India. These shawls display special designs and patterns made using block printing by stamps. Over the years, ajraks have become a symbol of the Sindhi culture and traditions. Ajrak print is also famous in neighbouring areas of India in the state of Gujarat due to their influence from Indus Valley civilization in Sindh, Pakistan. A later-on Saraiki version of Ajrak shawl was created called, Sajarak is found in South Punjab of Pakistan. Sajarak is mostly of cyan color while the simple Ajrak is of red and black. Etymology The Sindhi word ajrak (اجرڪ) comes from Persian language ajar or ajor (اجر) meaning brick and -ak (ک) meaning little. In Persian -ak is a suffix which forms the diminutive. History Early human settlements in the lower Indus Valley found a way of cultivating and using ''Gossypium arboreum'' commonly known as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
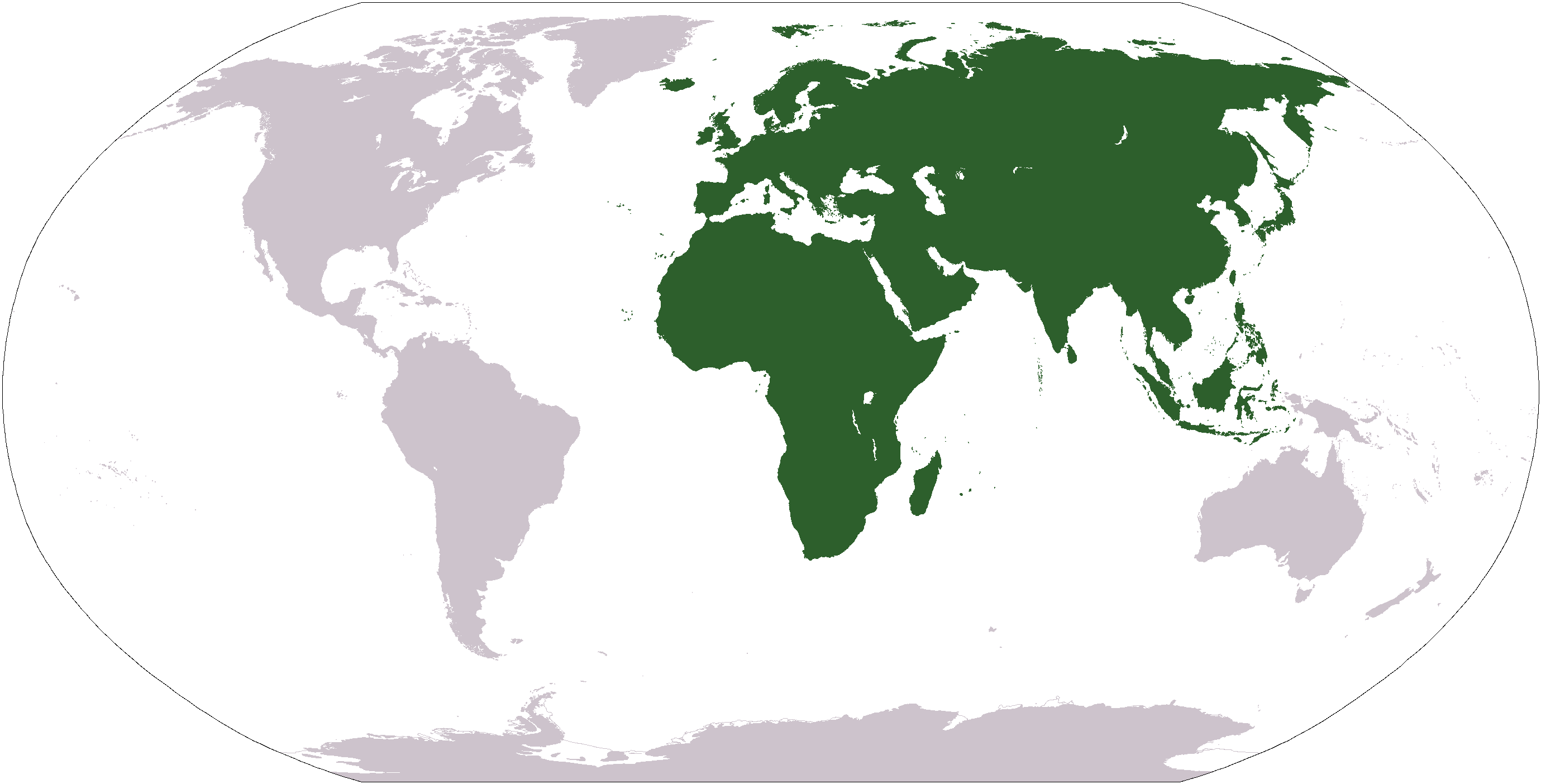
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyderabad, Sindh
Hyderabad ( Sindhi and ur, ; ) is a city and the capital of Hyderabad Division in the Sindh province of Pakistan. It is the second-largest city in Sindh, and the eighth largest in Pakistan. Founded in 1768 by Mian Ghulam Shah Kalhoro of the Kalhora Dynasty, Hyderabad served as a provincial capital until the British transferred the capital to Bombay presidency in 1840. It is about inland of Karachi, the largest city of Pakistan, to which it is connected by a direct railway and M-9 motorway. Toponymy The city was named in honour of Ali, the fourth caliph and cousin of the Prophet Muhammad. Hyderabad's name translates literally as "Lion City"—from ''haydar'', meaning "lion," and '' ābād'', which is a suffix indicating a settlement. "Lion" references Ali's valour in battle, and so he is often referred to as ''Ali Haydar'', roughly meaning "Ali the Lionheart," by South Asian Muslims. History Founding The River Indus was changing course around 1757, resulting i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukkur
Sukkur (; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh along the western bank of the Indus River, directly across from the historic city of Rohri. Sukkur is the third largest city in Sindh after Karachi and Hyderabad, and 14th largest city of Pakistan by population. New Sukkur was established during the British era alongside the village of Sukkur. Sukkur's hill, along with the hill on the river island of Bukkur, form what is sometimes considered the "Gate of Sindh". Etymology The name Sukkur may derive from the Arabic word for "sugar," ''shakkar'', in reference to the sugarcane fields that have historically been abundant in the region. This may be an allusion to the relative prosperity of the region at the time. Others have suggested the name may derive from the word ''Suukh'', derived from a Sindhi word for "comfort." History The region around Sukkur has been inhabited for millennia. The ruins of Lakhan-jo-daro, located near an industrial park on the outskirts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moro, Pakistan
Moro ( Sindhi:مورو, ur, ) is a city in the Naushahro Feroze District, of Sindh, Pakistan. The city is administratively subdivided into 12 Union councils. and is located on National highway (N5) in the centre of Sindh at an altitude of 28 m (95 ft) and is 12 km of the Indus River. It is the largest city in Naushahro Feroze District with a population of about 368,789 as per 2017 Census of Pakistan The 2017 Census of Pakistan was a detailed enumeration of the Pakistani population which began on 15 March 2017 and ended on 25 May 2017. It was the first census taken in the country in the 21st century, nineteen years after the previous one in .... Educational Institutes *Govt Mehran Degree College *Govt High School Moro Town campus *Govt Girl High School *Govt Girls Degree College *Bahria Foundation College *The Educators - A Project of BeaconhouseIQRAP.H.S School Moro *Intelligentsia Science College *Habibia School of Hope. A school for orphans started by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhit
Bhit or Bhit Shah ( sd, ڀٽ شاهه) is a small town located in Matiari District, Sindh, Pakistan. The town is best known as the location of the shrine to the Sindhi Sufi poet, Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai, who gave his name to the town (Bhttai sd, ڀٽائي). Passing along the road that leaves Haala for Hyderabad, beyond the shrubs there are a solitary group of large white mounds, which form hills known as Bhit in Sindhi. Shrine of Abdul Latif Bhittai The Shrine of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai, located in the centre of town, was built by Mian Ghulam Shah Kalhoro, who ruled over Sindh during the late 1700s. Kalhoro ordered the shrine to be built in 1772. It is a structure covered with traditional Sindhi ''Kashi'' tiles, glazed in the colours such as blue and turquoise. The final resting place of Shah Latif is under the main-dome of the building. His grave is enclosed by a carved wooden screen and lies under a fresco. Musicians are often seen serenading the constant trickle of devo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hala, Sindh
Hala ( sd, هـالا, ) is a city and taluka of Matiari district of Sindh, Pakistan. According to the Revenue record, Hala was given the status of Taluka of Hyderabad District in 1848. In 2005, it became part of Matiari District. Hala is located on the N-5 National Highway of Pakistan at a distance of about 62 kilometers from Hyderabad. Hala is also located on the Tando Adam - Mehrabpur Railway Line but railway line has been abandoned by Pakistan Railways. As of 2017 census, the Hala Municipal Corporation has a population of 65,731. Total population of Hala Taluka is 262,423 (2017) which includes Hala Municipal Corporation, Hala Old, Bhit Shah, Bhanote and surrounding areas. Hala is famous through the subcontinent for art, glazed colored pottery (Kaashi), woodwork (Jandi), cloth printing, woven cloth (Sussi) and khaddar made of handmade khaddi. Sufism Hala became a leading centre of the Suhrawardi sect of Sufism from the 16th century onwards. It contains the mausoleum o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matiari
Matyari or Matiari ( sd, مٽیاري, ur, ) is a city located in Sindh, Pakistan. It is north of Hyderabad on N-5 National Highway. Matiari is also the district headquarter of Matiari District. Matiari word is derived from two Sindhi words ''Mat'' and ''yari'', which means friendship with earthen water pots. The Dargah of Pir Pir or PIR may refer to: Places * Pir, Kerman, a village in Kerman Province, Iran * Pir, Satu Mare, commune in Satu Mare County, Romania Religion * Pir (Alevism), one of the 12 ranks of Imam in Alevism * Pir (Sufism), a Sufi teacher or spiritu ... Sayed sakhi Hashim Shah badshah is located in Matiari town. Matiari has three talukas, they are Matiari, Bhitshah and Saeedabad respectively. Matiari is known for its ice-Cream and Ajrak (a Sindhi dressing). References External links Populated places in Sindh Matiari District {{Sindh-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', meaning "Indian", as the dye was originally exported to Europe from India. It is traditionally regarded as a color in the visible spectrum, as well as one of the seven colors of the rainbow: the color between blue and violet; however, sources differ as to its actual position in the electromagnetic spectrum. The first known recorded use of indigo as a color name in English was in 1289. History '' Indigofera tinctoria'' and related species were cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, Bangladesh and Peru in antiquity. The earliest direct evidence for the use of indigo dates to around 4000 BC and comes from Huaca Prieta, in contemporary Peru. Pliny the Elder mentions India as the source of the dye after which it was named. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimson
Crimson is a rich, deep red color, inclining to purple. It originally meant the color of the kermes dye produced from a scale insect, '' Kermes vermilio'', but the name is now sometimes also used as a generic term for slightly bluish-red colors that are between red and rose. It is the national color of Nepal. History Crimson (NR4) is produced using the dried bodies of a scale insect, ''Kermes'', which were gathered commercially in Mediterranean countries, where they live on the kermes oak, and sold throughout Europe. Kermes dyes have been found in burial wrappings in Anglo-Scandinavian York. They fell out of use with the introduction of cochineal, also made from scale insects, because although the dyes were comparable in quality and color intensity, it needed ten to twelve times as much kermes to produce the same effect as cochineal. Carmine is the name given to the dye made from the dried bodies of the female cochineal, although the name crimson is sometimes applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dupatta
The dupattā is a Hindu shawl traditionally worn by women in Indian subcontinent to cover the head and shoulders. The dupatta is currently used most commonly as part of the women's shalwar kameez outfit, and worn over the kurta and the gharara. Etymology The Hindi-Urdu word ''dupattā'' (दुपट्टा, دوپٹہ), meaning "shawl of doubled cloth," derived from Middle Indic elements stemming from Sanskrit, is a combination of ''du-'' (meaning "two", from Sanskrit ''dvau'', "two" and ''dvi-'', combining form of dvau) and ''paṭṭā'' (meaning "strip of cloth," from ''paṭṭaḥ''), i. e., scarf usually doubled over the head. History Early evidence of the dupatta can be traced to the Indus valley civilization, where the sculpture of a priest-king whose left shoulder is covered with some kind of a chaddar suggests that the use of the dupatta dates back to this early Indic culture. Early Sanskrit literature has a wide vocabulary of terms for the veils and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cummerbund
A cummerbund is a broad waist sash, usually pleated, which is often worn with single-breasted dinner jackets (or ''tuxedos''). The cummerbund was adopted by British military officers in colonial India, where they saw it worn by sepoys (Indian soldiers) of the British Indian Army. It was adopted as an alternative to the waistcoat, and later spread to civilian use. The modern use of the cummerbund to Europeans and North Americans is as a component of traditional black tie events. Etymology The word ''cummerbund'' is the Anglicized form of Hindustani ''kamarband'' (Hindustani: कमरबंद; ), which is in turn from Persian (). It entered English vocabulary in 1616 from India. It is a combination of the words ''kamar'' meaning 'waist' and ''band'' meaning 'strap' or 'lacing'. The 'waist-band' was a sash accessory worn by Indian men for many occasions. The word ''cummerband'' (see below), and less commonly the German spelling (a Germanized spelling variation of the English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
