|
Air Suction Valve
An air suction valve (SAV) is a subsystem used to reduce emissions in the exhaust gases of internal combustion engines. Working principle When an engine exhaust valve is open, the pressure in the exhaust manifold is higher than atmospheric pressure. The exhaust manifold is configured in such a way that positive and negative pulses are produced during the operation of the cycle by designing it as a diffuser. The ASV has three openings: one is connected to the manifold vacuum, another is connected to the exhaust pipe and the third is open to the atmosphere. When a negative pulse is induced in the exhaust, air from the atmosphere enters the exhaust manifold through a one-way reed valve and serves to oxidize the carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons in the exhaust. Air cut valve system This system consists of a spring-loaded diaphragm, and a shaft which is attached to the bottom. A manifold vacuum is applied over the diaphragm where the shaft end is towards the opening of the atmospher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollutants
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidize
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Enfield Motors
Royal Enfield is an Indian multinational motorcycle manufacturing company headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. The Royal Enfield brand, including its original English heritage, is the oldest global motorcycle brand in continuous production.Can the oldest global motorcycle brand become sexy & cool to draw in a younger audience? Economic Times, 23 December 2017. The company operates manufacturing plants in in India. The first Royal Enfield motorcycle was built in 1901 by [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Enfield Bullet
The Royal Enfield Bullet was originally an overhead-valve single-cylinder four-stroke motorcycle made by Royal Enfield in Redditch, Worcestershire, now produced by Royal Enfield (India) at Chennai, Tamil Nadu, a company originally founded by Madras Motors to build Royal Enfield motorcycles under licence in India. The Royal Enfield Bullet has the longest unchanged production run of any motorcycle having remained continuously in production since 1948. The Bullet marque is even older, and has passed 75 years of continuous production. The Royal Enfield and Bullet names derive from the British company which had been a subcontractor to Royal Small Arms Factory in Enfield, London. Evolution The Bullet has evolved from a four-stroke engine with exposed valve-gear to the latest all-alloy unit construction engine with electronic fuel-injection. 1931–1939 Introduced in 1931 as a four-stroke single-cylinder motorcycle, this model was the first to feature the Bullet name. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Vacuum
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in an internal combustion engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere. Manifold vacuum is an effect of a piston's movement on the induction stroke and the choked flow through a throttle in the intake manifold of an engine. It is a measure of the amount of restriction of airflow through the engine, and hence of the unused power capacity in the engine. In some engines, the manifold vacuum is also used as an auxiliary power source to drive engine accessories and for the crankcase ventilation system. Manifold vacuums should not be confused with Venturi vacuums, which are an effect exploited in carburetors to establish a pressure difference roughly proportional to mass airflow and to maintain a somewhat constant air/fuel ratio. It is also used in light airplanes to provide airflow for pneumatic gyroscopic instruments. Overview The rate of airflow through an internal combustion engine is an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft ( Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm Valve
Diaphragm valves (or membrane valves) consists of a valve body with two or more ports, an elastomeric diaphragm, and a "weir or saddle" or seat upon which the diaphragm closes the valve. The valve body may be constructed from plastic, metal, wood or other materials depending on the intended use. Categories There are two main categories of diaphragm valves: one type seals over a "weir" (saddle) and the other (sometimes called a "full bore or straight-through" valve) seals over a seat. In general, straight-through diaphragm valves are used in on-off applications and weir-type diaphragm valves are used for control or throttling applications. While diaphragm valves usually come in two-port forms (2/2-way diaphragm valve), they can also come with three ports (3/2-way diaphragm valves also called T-valves) and more (so called block-valves). When more than three ports are included, they generally require more than one diaphragm seat; however, special dual actuators can handle more po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or exemplified by the odors of gasoline and lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to the naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, and to their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
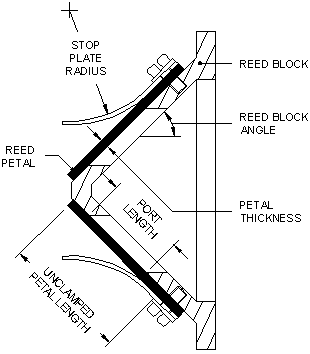
Reed Valve
Reed valves are a type of check valve which restrict the flow of fluids to a single direction, opening and closing under changing pressure on each face. Modern versions often consist of flexible metal or composite materials (fiberglass or carbon fiber). Applications Traditional Reed valves, normally a leather flap covering a hole, are amongst the earliest form of automatic flow control for liquids and gases. They have been used for thousands of years in water pumps and for hundreds of years in bellows for high-temperature forges and musical instruments such as church organs and accordions. In nature, heart valves operate in a somewhat similar fashion. Pumps Reed valves are used in some reciprocating compressor designs, and in the pumping element of some musical instruments, large and small. Two-stroke engines Reed valves are commonly used in high-performance versions of the two-stroke engine, where they control the fuel-air mixture admitted to the cylinder. As the pis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack, or propelling nozzle. It often disperses downwind in a pattern called an ''exhaust plume''. It is a major component of motor vehicle emissions (and from stationary internal combustion engines), which can also include crankcase blow-by and evaporation of unused gasoline. Motor vehicle emissions contribute to air pollution and are a major ingredient in the creation of smog in some large cities. A 2013 study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) indicates that 53,000 early deaths occur per year in the United States alone because of vehicle emissions. According to another study from the same university, traffic fumes alone cause the death of 5,000 people every year just in the United Kingdom. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Pipe
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of: *Cylinder head and exhaust manifold *A turbocharger to increase engine power. *A catalytic converter to reduce air pollution. *A muffler (North America) / silencer (UK/India), to reduce noise. Design criteria An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, if they are not properly vented to the outdoors. Also, the gases from most types of machines are very hot; the pipe must be heat-resistant, and it must not pass through or near anything that can burn or ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |