|
Ainu In Russia
The Ainu in Russia are an Small-numbered indigenous peoples of Russia, Indigenous people of Siberia located in Sakhalin Oblast, Khabarovsk Krai and Kamchatka Krai. The Russian Ainu people (''Aine''; ), also called ''Kurile'' (курилы, ''kurily''), ''Kamchatka's Kurile'' (камчатские курилы, ''kamchatskiye kurily'' / камчадальские айны, ''kamchadalskiye ayny'') or ''Eine'' (эйны, ''eyny''), can be subdivided into six groups. Although only around 100 people currently identify themselves as Ainu in Russia (according to the census of 2010), it is believed that at least 1,000 people are of significant Ainu ancestry. The low numbers identifying as Ainu are a result of the refusal by the government of the Russian Federation to recognise the Ainu as a "living" ethnic group. Most of the people who identify themselves as Ainu live in Kamchatka Krai, although the largest number of people who are of Ainu ancestry (without acknowledging it) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Russian Census
The 2021 Russian census () was the first census of the Russia, Russian Federation population since 2010 Russian census, 2010 and the third after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, dissolution of the Soviet Union. It took place between October 15 and November 14. However, for the remote and inaccessible areas of Russia, the census took place between April 1 and December 20.Постановление Правительства Российской Федерации «Об организации Всероссийской переписи населения 2020 года» от 08 октября 2018 года The preparations for the census started in 2017 with the adoption of the government decree "On the conduct of the Russian Population Census 2020". According to Pavel Malkov, head of Rosstat, the budget allocated for the 2020 census was 33 billion rubles. The motto of the census was "Create the future!". On June 25, 2020, Rosstat announced its intention to conduct the main st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu Chief
Ainu or Aynu may refer to: *Ainu people, an East Asian ethnic group of Japan and the Russian Far East **Ainu languages, a family of languages ***Ainu language of Hokkaido ***Kuril Ainu language, extinct language of the Kuril Islands ***Sakhalin Ainu language, extinct language from the island of Sakhalin **Ainu music **Ainu cuisine *Ainu (Middle-earth), spirit in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium *Ainu (insect), a beetle in the family Tenebrionidae *Äynu people, of Western China **Äynu language See also *Äynu (other) *Ainur (other) *Aino (other) Aino may refer to: * Aino (given name), a first name in Finland and Estonia * Ainu people (sometimes called ''Aino''), an ethnic group of northern Japan * Ainu language (also sometimes called ''Aino''), the language of the Ainu people * Aino, Naga ... * Aniu, character from ''Balto II'' {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ust-Bolsheretsky District
Ust-Bolsheretsky District () is an administrative Law #46 and municipalLaw #227 district (rayon) of Kamchatka Krai, Russia, one of the eleven in the krai. It is located in the southern and southwestern parts of the krai. The area of the district is . Its administrative center An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located. In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgiu ... is the rural locality (a '' selo'') of Ust-Bolsheretsk. Population: The population of Ust-Bolsheretsk accounts for 25.4% of the district's total population. References Notes Sources * * {{Use mdy dates, date=March 2013 Districts of Kamchatka Krai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander Islands
The Commander Islands, Komandorski Islands, or Komandorskie Islands (, ''Komandorskiye ostrova'') are a series of islands in the Russian Far East, a part of the Aleutian Islands, located about east of the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea. Treeless and sparsely populated, the islands consist of Bering Island, ; Medny Island, ; and fifteen islets and rocks. The largest of the latter are Tufted Puffin Rock ''(Kamen Toporkov'' or ''Ostrov Toporkov)'', , and Kamen Ariy, which are between west of the only settlement, Nikolskoye. Administratively, the Commanders compose the Aleutsky District of the Kamchatka Krai in Russia. In 2005, the Comandorsky State Nature Reserve was nominated for the List of World Heritage Sites in Russia of UNESCO. Geography The Commander Islands archipelago consists of 15 islands and is a part of a submarine volcanic ridge extending from Alaska to Kamchatka dated by the beginning of Paleogene (60-70 million years ago). The islands are the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (, ) is a city and the administrative center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. It is located in the Far East of the country and lies along the coast of Avacha Bay by the Pacific Ocean, nearby Khalaktyrskoye Lake. As of the 2021 census, it had a population of 164,900. The city is widely known simply as ''Petropavlovsk'' (literally "city of Peter and Paul"). The adjective ''Kamchatsky'' ("Kamchatkan") was added to the official name in 1924. History Origins Cossack units visited the area from 1697. The explorer and navigator Captain Vitus Bering (a Danish-born Russian) is considered to have founded the city in 1740, although navigator had laid the foundation a few months earlier. Bering reached Avacha Bay in late 1740 and in his capacity as the superior officer, named the new settlement "Petropavlovsk" (Peter and Paul) after his two ships, the ''Saint Peter'' and the '' Saint Paul'', which had been built in Okhotsk for his second expedition (1733–42). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
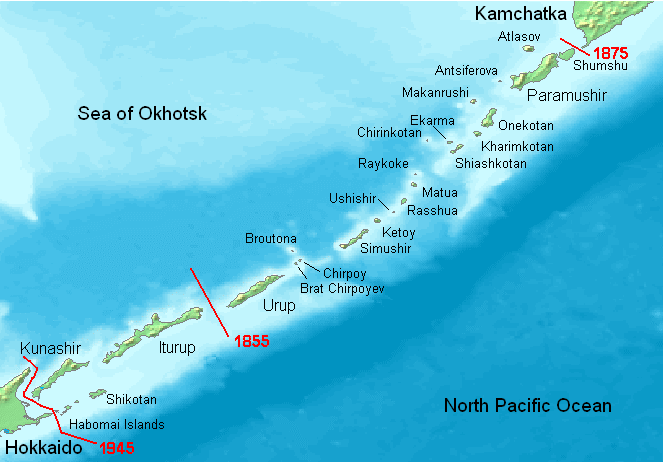
Treaty Of Saint Petersburg (1875)
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg (; ) between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire was signed on 7 May 1875, and its ratifications exchanged at Tokyo on 22 August 1875. The treaty itself went into effect in 1877. Its terms stipulated that Japan cedes to Russia the part of Sakhalin island it then owned in exchange for the group of the Kuril Islands owned by Russia (between Iturup island and the Kamchatka Peninsula). Consequently, Sakhalin island as a whole became Russian territory, and the entire Kuril archipelago Japanese territory. The authentic text of the treaty is written in French. Differences with its Japanese translation contributed to the controversy on what constitutes the Kuril islands, claims to which Japan renounced in 1951 by the Treaty of San Francisco. The Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875) is part of an ongoing, and long-standing, territorial dispute between Russia and Japan over the jurisdiction of the Kuril Islands. Background Golovnin Incident In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the Liaodong Peninsula and near Shenyang, Mukden in Southern Manchuria, with naval battles taking place in the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy in Siberia and the Russian Far East, Far East since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. At the end of the First Sino-Japanese War, the Treaty of Shimonoseki of 1895 had ceded the Liaodong Peninsula and Lüshun Port, Port Arthur to Japan before the Triple Intervention, in which Russia, Germany, and France forced Japan to relinquish its claim. Japan feared that Russia would impede its plans to establish a sphere of influence in mainland Asia, especially as Russia built the Trans-Siberian Railway, Trans-Siberian Railroad, began making inroads in K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland Islands, South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic fiber, synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by railway via the Seikan Tunnel. The largest city on Hokkaido is its capital, Sapporo, which is also its only cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin lies about to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands, which are administered by Russia, though the four most southerly are Kuril Islands dispute, claimed by Japan. The position of the island on the northern end of the archipelago results in a colder climate, with the island seeing significant snowfall each winter. Despite the harsher climate, it serves as an agricultural breadbasket for many crops. Hokkaido was formerly known as ''Ezo'', ''Yezo'', ''Yeso'', or ''Yes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amur River
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ''proper'' is long, and has a drainage basin of .Амур (река в Азии) If including its main stem , the Argun, the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and Karaginsky Island constitute Kamchatka Krai of the Russia, Russian Federation. The majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are ethnic Russians, with about 13,000 being Koryaks (2014). More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980). The Kamchatka Peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, that form part of the Ring of Fire. Geography Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. (Lopatka is Russian for spade.) The circular bay to the north of this on the Pacific side is Avac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivkh People
The Nivkh, or Gilyak (also Nivkhs or Nivkhi, or Gilyaks; ethnonym: Нивхгу, ''Nʼivxgu'' (Amur) or Ниғвңгун, ''Nʼiɣvŋgun'' (E. Sakhalin) "the people"), are an indigenous ethnic group inhabiting the northern half of Sakhalin Island and the lower Amur River and coast on the adjacent Russian mainland. Historically, they may have inhabited parts of Manchuria. Nivkh were traditionally fishermen, hunters, and dog breeders. They were semi-nomadic, living near the coasts in the summer and wintering inland along streams and rivers to catch salmon. The land the Nivkh inhabit is characterized as taiga forest with cold snow-laden winters and mild summers with sparse tree cover. The Nivkh are believed to be the original inhabitants of the region, and to derive from a proposed Neolithic people that migrated from the Transbaikal region during the Late Pleistocene.Fitzhugh, William, and Durbreui pp.39, 40 The Nivkh had long maintained trade and cultural relations with neigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |