|
Ahmose-Nebetta
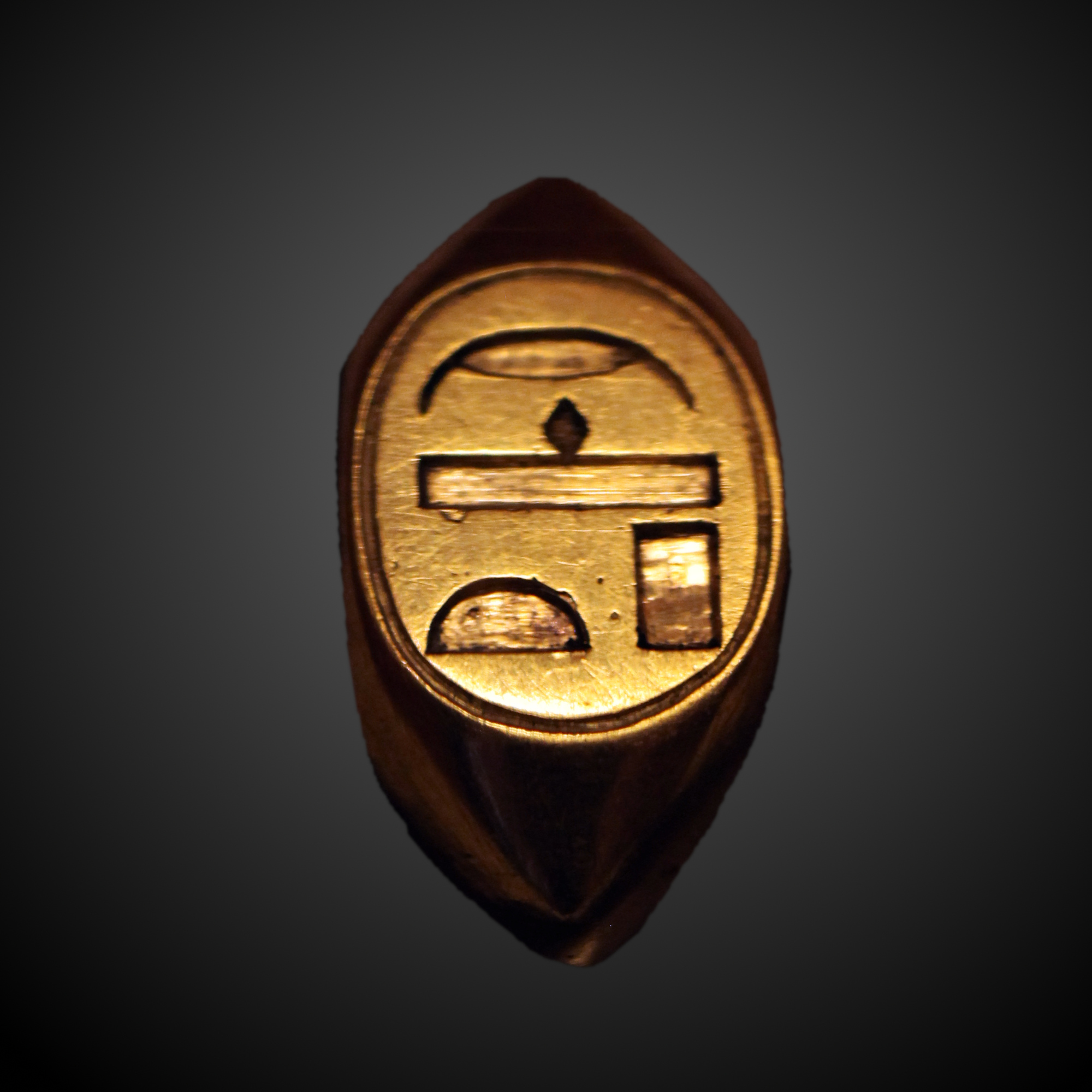
Ahmose-Nebetta (or Ahmose-Nebta) was an Egyptian princess during the late Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt in the late Second Intermediate Period. She was probably the daughter of Seqenenre Tao and Queen Ahhotep I. She was the sister of Pharaoh Ahmose I of who was the founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Life Ahmose-Nebetta ( “Child of Iah (the Moon) - Lady of the Land”) was likely a daughter of Seqenenre Tao. She may have married her brother Ahmose I, but her sister Ahmose-Nefertari was the Great Royal Wife.Tyldesley, Joyce. Chronicle of the Queens of Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2006. pp 88-90, Attestations Her titles include ''King's Daughter'' and ''King's Sister''. Her main attestation is an early Eighteenth Dynasty statue of a princess at the Louvre (N 496) which identifies her as a king's daughter, as a king's sister and as the daughter of Queen Ahhotep I. On this statue their names are written within a cartouche. Louvre E 15682 (weak) A statue of a young seated man identifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahhotep I
Ahhotep I (, alternatively Anglicized ''Ahhotpe'' or ''Aahhotep'', " Iah (the Moon) is satisfied") was an ancient Egyptian queen who lived , during the end of the Seventeenth Dynasty and beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her titles include King's Daughter, King's Sister, Great (Royal) Wife, She who is joined to the White Crown, and King's Mother. She was the daughter of Queen Tetisheri and Pharaoh Senakhtenre Ahmose, and was probably the sister, as well as the queen consort, of Pharaoh Seqenenre Tao. Ahhotep I had a long and influential life, and is believed to have governed as a regent for her young son, Ahmose I, until he was old enough to rule. A stela found at Karnak praises Ahhotep's abilities as a leader, and the cult of Amenhotep I continued to remember Ahhotep after her death, up until at least the Twenty-first Dynasty. While the 19th-century discovery of two separate coffins in Egypt set off debates about Ahhotep's identity and true burial place—w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seqenenre Tao
Seqenenre Tao (also Seqenera Djehuty-aa or Sekenenra Taa, called 'the Brave') was a pharaoh who ruled over the last of the local kingdoms of the Theban region of Egypt in the Seventeenth Dynasty during the Second Intermediate Period. Family Parentage He probably was the son and successor to Senakhtenre Ahmose and Queen Tetisheri. Wife and Children With his queen, Ahhotep I, Seqenenre Tao fathered two pharaohs: Kamose, his immediate successor who was the last pharaoh of the Seventeenth Dynasty, and Ahmose I, who, following a regency by his mother, was the first pharaoh of the Eighteenth. Seqenenre Tao is credited with starting the opening moves in a war of revanchism against Hyksos incursions into Egypt, which saw the country completely liberated during the reign of his son Ahmose I. Reign The dates of his reign are uncertain, but he may have risen to power in the decade ending in 1560 BC or in 1558 BC, based on the probable accession date of his son, Ahmose I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose-Nefertari
Ahmose-Nefertari (Ancient Egyptian: '' Jꜥḥ ms Nfr trj'') was the first Great Royal Wife of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. She was a daughter of Seqenenre Tao and Ahhotep I, and royal sister and wife to Ahmose I. Her son Amenhotep I became pharaoh and she may have served as his regent when he was young. Ahmose-Nefertari was deified after her death. Family Ahmose-Nefertari was a daughter of Seqenenre Tao and Ahhotep I and the granddaughter of Senakhtenre and queen Tetisheri. Ahmose-Nefertari was born in Thebes, likely during the reign of Senakhtenre Ahmose.Forbes, Dennis C. Imperial Lives: Illustrated Biographies of Significant New Kingdom Egyptians. KMT Communications, Inc. 1998. Ahmose-Nefertari had quite a few siblings and half-siblings, including her future husband Ahmose and King's Son Ahmose Sapair, and her many sisters: Ahmose-Henutemipet, Ahmose-Tumerisy, Ahmose-Nebetta, Ahmose-Meritamon, Ahmose-Henuttamehu, Ahmose, and Ahmose-Sitkamose. Ahmose-Neferta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT359
The Theban Tomb TT359, also referred to as the Tomb of Inherkhau, is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian workman Inherkhau, who was ''Foreman of the Lord of the Two Lands in the Place of Truth'' during the reigns of Ramesses III and Ramesses IV during the 20th Dynasty.Porter, Bertha and Moss, Rosalind, ''Topographical Bibliography of Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic Texts, Statues, Reliefs and Paintings Volume I: The Theban Necropolis, Part I. Private Tombs'', Griffith Institute. 1970, pp. 421–424 Inherkhau was also the owner of the Tomb TT299. He was the son of the similarly titled Foreman Huy, and Inherkhau's wife was named Wab.Porter and Moss, p. 380 Tomb The outer chamber of the tomb contains offering scenes with Inherkau, his wife and their son Kenna. Scenes include depictions of the Book of Gates, the Book of the Dead, and two rows of Kings, Queens and Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Language
The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian (; ), is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest known written languages, first recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4,000 years. Its classical form, known as " Middle Egyptian," served as the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity, the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era, diversified into various Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventeenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVII, alternatively 17th Dynasty or Dynasty 17) was a dynasty of Pharaoh, pharaohs that ruled in Upper Egypt during the late Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period, approximately from 1580 to 1550 BC. Its mainly Thebes, Egypt, Theban rulers are contemporary with the Hyksos of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifteenth Dynasty and succeed the Sixteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Sixteenth Dynasty, which was also based in Thebes.The chronology of the 17th dynasty is very uncertain and the king lists provide little help. In March 2012, French archeologists examining a limestone door in the Precinct of Amun-Re at Karnak discovered hieroglyphs with the name Senakhtenre Ahmose, Senakhtenre, the first evidence of this king dating to his lifetime. The last two kings of the dynasty opposed the Hyksos rule over Egypt and initiated a war that would rid Egypt of the Hyksos kings and began a period of unified rule, the New Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmoside Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose. Several of Egypt's most famous pharaohs were from the Eighteenth Dynasty, including Tutankhamun. Other famous pharaohs of the dynasty include Hatshepsut (c. 1479 BC–1458 BC), the longest-reigning woman pharaoh of an indigenous dynasty, and Akhenaten (c. 1353–1336 BC), the "heretic pharaoh", with his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti. The Eighteenth Dynasty is unique among Egyptian dynasties in that it had two Queen regnant, queens regnant, women who ruled as sole pharaoh: Hatshepsut and Neferneferuaten, usually identified as Nefertiti. History Early Dynasty XVIII Dynasty XVIII was founded by Ahmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Intermediate Period
The Second Intermediate Period dates from 1700 to 1550 BC. It marks a period when ancient Egypt was divided into smaller dynasties for a second time, between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the New Kingdom. The concept of a Second Intermediate Period generally includes the 13th through to the 17th dynasties, however there is no universal agreement in Egyptology about how to define the period. It is best known as the period when the Hyksos people of West Asia established the 15th Dynasty and ruled from Avaris, which, according to Manetho's '' Aegyptiaca'', was founded by a king by the name of Salitis. The settling of these people may have occurred peacefully, although later recounts of Manetho portray the Hyksos "as violent conquerors and oppressors of Egypt". The Turin King List from the time of Ramesses II remains the primary source for understanding the chronology and political history of the Second Intermediate Period, along with studying the typology of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty () until the Roman Egypt, annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, the equivalent Egyptian language, Egyptian word for "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs, regardless of gender, through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten (reigned –1336 BCE) or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III (–1425 BCE). In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as ancient Egyptian royal titulary, three titles: the Horus name, Horus, the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (wikt:nswt-bjtj, ''nswt-bjtj''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
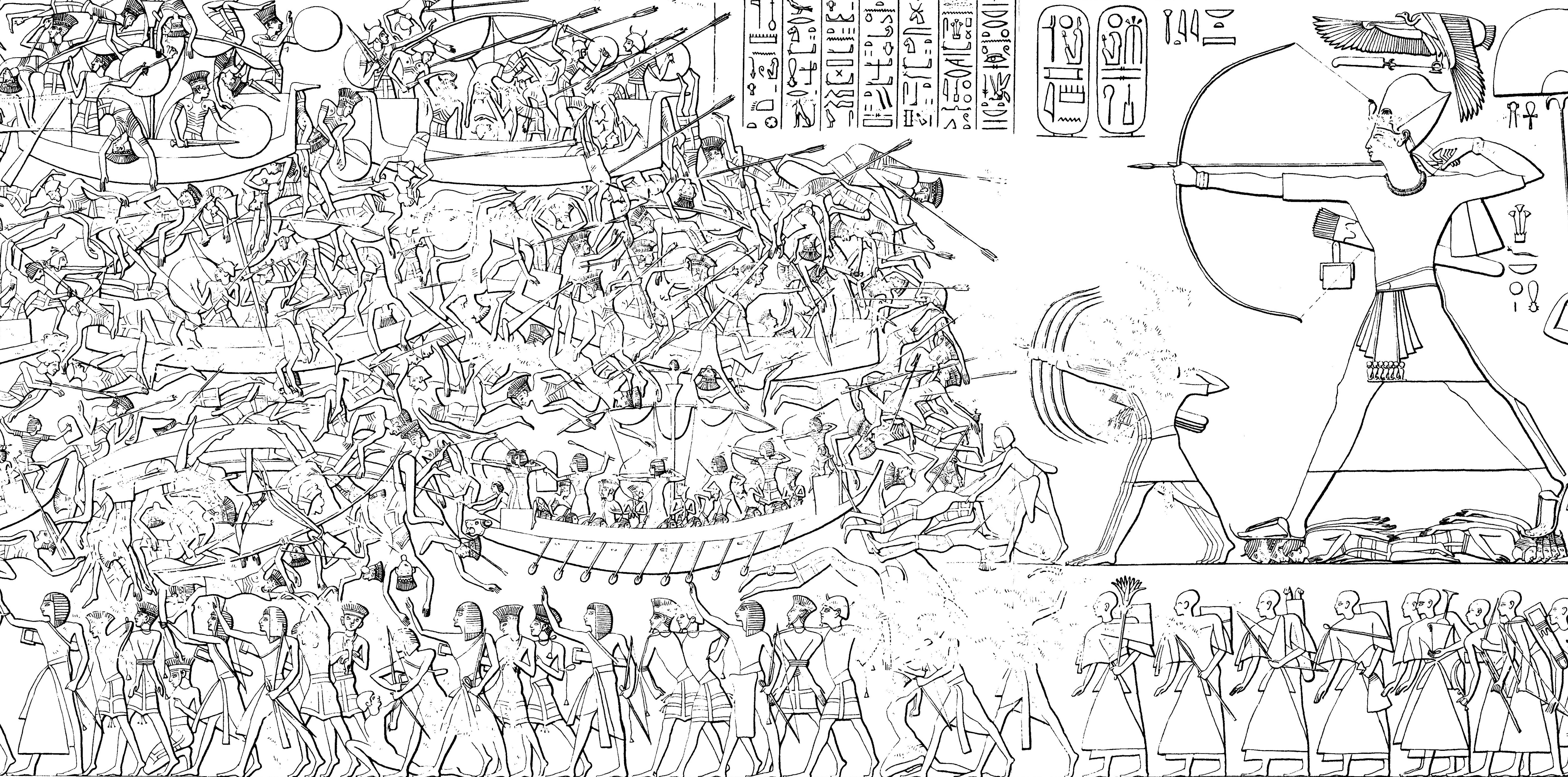
Ahmose I
Ahmose I (''Amosis'', ''Aahmes''; meaning "Iah (the Moon) is born") was a pharaoh and founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt in the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. His reign is usually dated to the mid-16th century BC at the beginning of the Late Bronze Age. During his reign, Ahmose completed the conquest and expulsion of the Hyksos, restored Theban rule over Lower- and Upper Egypt, and successfully reasserted Egyptian power in its formerly subject territories of Nubia and Canaan. He then reorganized the administration of the country, reopened quarry, quarries, mining, mines and trade routes and began massive construction projects of a type that had not been undertaken since the time of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom. This building program culminated in the construction of the last Egyptian pyramids, pyramid built by native Egyptian rulers. Ahmose's reign laid the foundations for the New Kingdom of Egypt, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Royal Wife
Great Royal Wife, or alternatively, Chief King's Wife () is the title that was used to refer to the Queen consort, principal wife of the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, who served many official functions. Description While most ancient Egyptians were monogamy, monogamous, a male pharaoh would have had other, lesser wives and concubines in addition to the Great Royal Wife. This arrangement would allow the pharaoh to enter into diplomatic marriages with the daughters of allies, as was the custom of ancient kings. In the past the order of succession in Ancient Egypt was thought to pass through the royal women. This theory, referred to as the Heiress Theory, has been rejected regarding the Eighteenth Dynasty ever since a 1980s study of its royalty.O'Connor and Cline (Editors), Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign, pg 6 The throne likely passed to the eldest living son of those pharaohs. The mother of the heir to the throne was not always the Great Royal Wife, but once a pharaoh was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period owing to the predominance of rulers with the given name "Ramesses". This dynasty is generally considered to mark the beginning of the decline of Ancient Egypt at the transition from the Late Bronze to Iron Age. During the period of the Twentieth Dynasty, Ancient Egypt faced the crisis of invasions by Sea Peoples. The dynasty successfully defended Egypt, while sustaining heavy damage. History After the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt entered into a period of civil war. Because of lost historical records, the cause of the civil war is unknown. The war was ended with the accession to the throne by Setnakhte, who founded the 20th Dynasty of Egypt. From the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |