|
Agusan Del Sur Provincial Board
The Agusan del Sur Provincial Board is the Sangguniang Panlalawigan (provincial legislature) of the Philippine province of Agusan del Sur. The members are elected via plurality-at-large voting: the province is divided into two districts, each sending five members to the provincial board; the electorate votes for five members, with the five candidates with the highest number of votes being elected. The vice governor is the ''ex officio'' presiding officer, and only votes to break ties. The vice governor is elected via the plurality voting system province-wide. District apportionment List of members An additional three ''ex officio'' members are the presidents of the provincial chapters of the Association of Barangay Captains, the Councilors' League, and the Sangguniang Kabataan. There is also a reserved seat for a representative of the indigenous peoples pursuant to the Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997 The Indigenous People's Rights Act of 1997 (IPRA), officially des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government Code Of The Philippines
Codification of laws is a common practice in the Philippines. Many general areas of substantive law, such as criminal law, civil law and labor law are governed by legal codes. Tradition of codification Codification is predominant in countries that adhere to the legal system of civil law. Spain, a civil law country, introduced the practice of codification in the Philippines, which it had colonized beginning in the late 16th century. Among the codes that Spain enforced in the Philippines were the Spanish Civil Code and the Penal Code. The practice of codification was retained during the period of American colonial period, even though the United States was a common law jurisdiction. However, during that same period, many common law principles found their way into the legal system by way of legislation and by judicial pronouncements. Judicial precedents of the Philippine Supreme Court were accepted as binding, a practice more attuned to common law jurisdictions. Eventually, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting Vote
A casting vote is a vote that someone may exercise to resolve a tied vote in a deliberative body. A casting vote is typically by the presiding officer of a council, legislative body, committee, etc., and may only be exercised to break a deadlock. Examples of presiding officers who hold casting votes are the Speaker of the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and the President of the United States Senate (an ex-officio role of the Vice President of the United States). In some legislatures, a casting vote may be exercised however the presiding officer wishes. For example, the Vice President of the United States may exercise their casting vote when the Senate is evenly divided according to their own personal beliefs; by virtue of the Vice President's political leanings and affiliations, the Vice President's political party is able to serve as the majority party in the Senate and elect one of their own to serve as Majority Leader. In some other legislatures, by contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakas Kampi CMD
{{disambiguation, surname ...
Lakas means ''strength'', ''power'' in Tagalog and may refer to: * Lakas ng Bayan (English: People's Power), a political party in the Philippines * Lakas–CMD, a political party in the Philippines founded in 2009 * Lakas–CMD (1991), a political party in the Philippines founded in 1991 * Demetrio B. Lakas (1925–1999), president of Panama * '' Lakas Tama'', studio album by comedian Vice Ganda See also * Laka (other) *Lakka (other) Lakka is a liqueur produced in Finland which derives its flavor from the cloudberry fruit. Lakka may also refer to: * Lakka, Greece * Lakka language, an Mbum language of Cameroon * Lakka, Sierra Leone * Lakka, a Linux distribution using RetroAr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakas–CMD (1991)
Lakas–Christian Muslim Democrats (), abbreviated as Lakas–CMD and popularly known as Lakas, was a political party in the Philippines. Its ideology and that of its successor is heavily influenced by Christian and Islamic democracy. The party's influence on Philippine society is very strong, especially after the People Power Revolution, which has led the country to elect two presidents from the party, namely Fidel V. Ramos, a United Methodist, and Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, a Roman Catholic. In May 2009, Lakas–CMD merged with Arroyo's Kabalikat ng Mamamayang Pilipino, thereby being known as Lakas Kampi CMD, a completely new entity. In May 2012, Lakas Kampi CMD renamed itself again as Lakas–CMD after the separation of KAMPI. History Early days and Ramos administration In late 1985, the Partido Demokratiko Pilipino (founded in February 1982), Lakas ng Bayan (LABAN), and Lakas ng Bansa parties united to form the United Nationalist Democratic Organization (UNIDO) coalition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 Philippine Barangay And Sangguniang Kabataan Elections
Barangay elections in the Philippines were held on May 14, 2018. The election shall elect the '' Punong Barangay'', more commonly known as barangay captains, and members of the ''Sangguniang Barangay'', or barangay council, in 41,948 barangays (villages) throughout the country whose terms start on June 30, 2018. Barangays are the smallest local government unit in the Philippines. Elections for the reformed Sangguniang Kabataan (SK; youth councils) will also be held at the same time. This shall be the first SK elections since 2010. Originally scheduled for October 2016, these elections supposedly concluded the 2016 election cycle that started in May with the election of the Philippine president, the members of Philippine Congress and provincial, city and municipal officials. It was then postponed to October 2017, then was postponed further to May 2018. There were attempts to postpone it further, but Congress ran out of time to pass a law to postpone the elections further. Upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2022 Philippine Local Elections
Local elections in the Philippines took place on May 9, 2022. These were conducted together with the 2022 general election for national positions. All elected positions above the barangay (village) level but below the regional level were disputed. The following 18,180 positions will be disputed: * 81 provincial governorships and vice-governorships * 782 Provincial Board ( Sangguniang Panlalawigan) members * 1,634 mayorships and vice-mayorships * 13,558 city and municipal councilors ( Sangguniang Panlungsod and Sangguniang Bayan) The elective positions in the Bangsamoro was originally scheduled to be held with these elections, but was postponed to 2025, concurrently with the 2025 elections. The elective positions in the barangays won't be decided on this day as well. These will be held on December 5, 2022. Provincial elections There are 81 provinces of the Philippines. Compostela Valley, which had a successful renaming plebiscite in 2019, will be known as "Davao de Oro" star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act Of 1997
The Indigenous People's Rights Act of 1997 (IPRA), officially designated as Republic Act No. 8371, is a Philippine law that recognizes and promotes the rights of indigenous cultural communities and indigenous peoples in the Philippines. History Early beginnings Year 1909, in the case oCariño vs. InsularGovernment, the court has recognized long occupancy of land by an indigenous member of the cultural communities as one of private ownership, which, in legal concept, is termed "native title". This case paved the way for the government to review the so-called "native title" or "private right." In the year 1919, the Second Public Land Act was enacted, recognizing the right of ownership of any native of the country who, since July 4, 1907, or prior thereto, has continuously occupied and cultivated, either by himself or through his predecessors-in-interest, a tract of agricultural public land. In 1936, Commonwealth Act No.141, amended by R.A. 3872 of 1964, was passed which provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
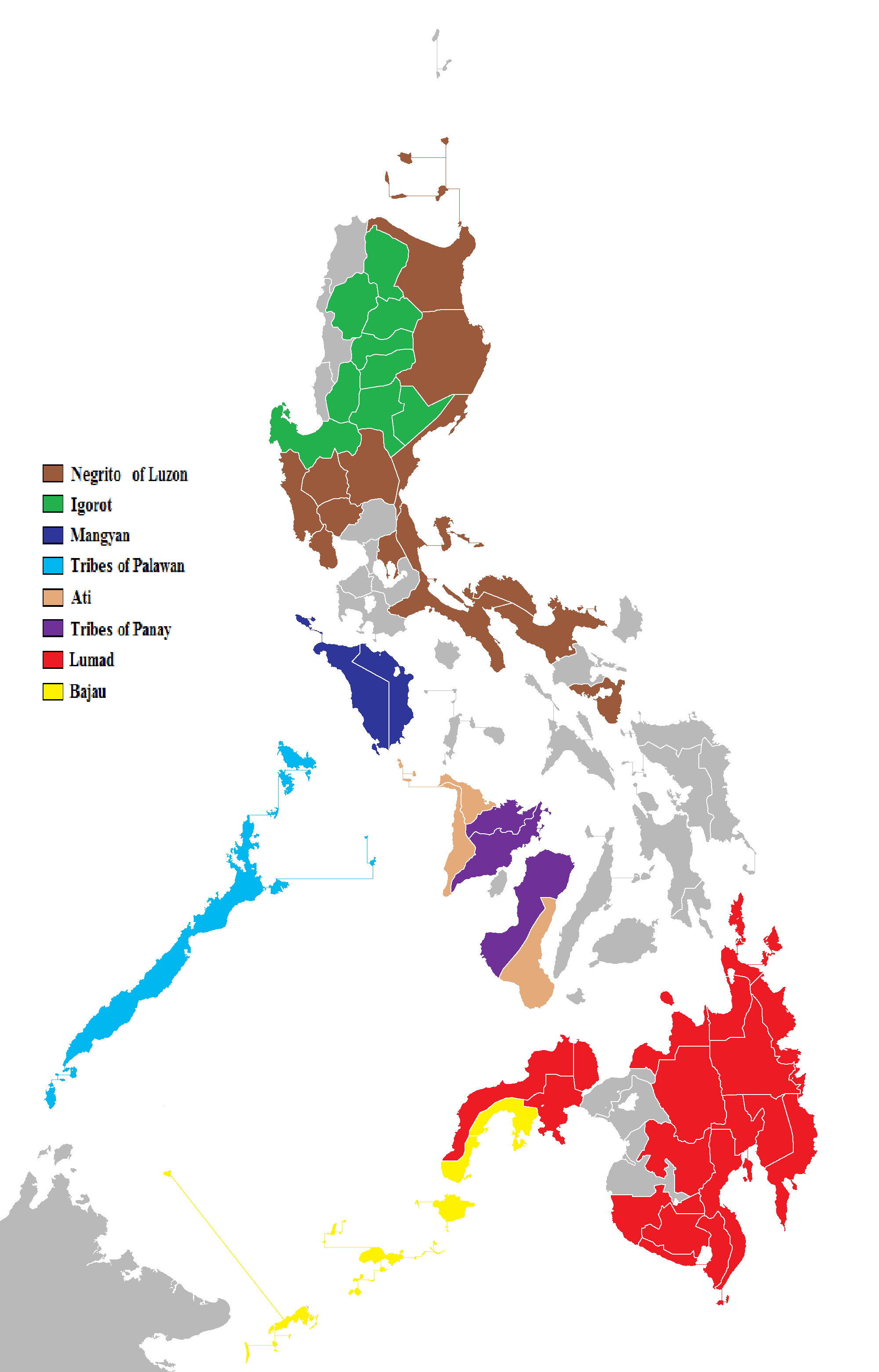
Indigenous Peoples Of The Philippines
The Philippines consist of numerous upland and lowland indigenous ethnolinguistic groups living in the country, with Austronesians making up the overwhelming majority, while full or partial Negritos scattered throughout the archipelago. The highland Austronesians and Negrito have co-existed with their lowland Austronesian kin and neighbor groups for thousands of years in the Philippine archipelago. The primary difference is that they were not absorbed by centuries of Spanish and United States colonization of the Philippines, and in the process have retained their customs and traditions. This is mainly due to the rugged inaccessibility of the mountains and established headhunting and warrior cultures, which discouraged Spanish and American colonizers from coming into contact with the highlanders. In the interest of clarity, the term ''indigenous'' as used in the Philippines refers to ethnolinguistic groups or subgroups that maintain lt of partial isolation, or independence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangguniang Kabataan
Sangguniang Kabataan (abbreviated as SK; ) is a council meant to represent the youth in each barangay in the Philippines. It was put "on hold", but not quite abolished, prior to the 2013 barangay elections. In January 2016, the Sangguniang Kabataan Reform Act was signed into law which made some significant changes to the SK and initially scheduled new elections for October 2016. In March 2017, the elections were postponed anew to May 2018. The SK Chairman leads the Sangguniang Kabataan. A Local Youth Development Council (LYDC) composed of representatives of different local youth groups supports the SK and its programs. The Sangguniang Kabataan is the successor of the Kabataang Barangay (KB; ) which was abolished by the Local Government Code of 1991. The author, Senator Aquilino Pimentel Jr. abolished KB because of allegations that this organization faced. Function and structure Each Barangay houses a Sangguniang Kabataan composed of a chairman, seven members, a secretar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Of Barangay Captains
The Liga ng mga Barangay sa Pilipinas (League of Barangays in the Philippines) and the Asosasyon ng mga Kapitan ng Barangay (Association of Barangay Captains) or ABC are formal organizations of all the barangays in the Philippines. Presently, almost 42,000 barangays are part of this organization, making it the association of Philippine local government units with the largest membership. The current association is just the latest form of an organization that has been known by various names in the past, such as the Barrio Lieutenants’ Association of the Philippines (BLAP), the Association of Barangay Councils (ABC), and the Pambansang Katipunan ng mga Barangay (PKB). Each barangay is represented in the League by their '' Punong Barangay'' (Barangay Chairman/Head/Captain). In case of his absence or incapacity, a ''sanggunian'' member of the barangay shall be its representative after being elected for this purpose by its members. History The Liga ng mga Barangay began with the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurality Voting System
Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in which a candidate, or candidates, who poll more than any other counterpart (that is, receive a plurality), are elected. In systems based on single-member districts, it elects just one member per district and may also be referred to as first-past-the-post (FPTP), single-member plurality (SMP/SMDP), single-choice voting (an imprecise term as non-plurality voting systems may also use a single choice), simple plurality or relative majority (as opposed to an ''absolute majorit''y, where more than half of votes is needed, this is called ''majority voting''). A system which elects multiple winners elected at once with the plurality rule, such as one based on multi-seat districts, is referred to as plurality block voting. Plurality voting is distinguished from ''majority voting'', in which a winning candidate must receive an absolute majority of votes: more than half of all votes (more than all other candidates combined if each voter has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chairman
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a Board of directors, board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the group, presides over meetings of the group, and conducts the group's business in an orderly fashion. In some organizations, the chairperson is also known as ''President (corporate title), president'' (or other title). In others, where a board appoints a president (or other title), the two terms are used for distinct positions. Also, the chairman term may be used in a neutral manner not directly implying the gender of the holder. Terminology Terms for the office and its holder include ''chair'', ''chairperson'', ''chairman'', ''chairwoman'', ''convenor'', ''facilitator'', ''moderator (town official), moderator'', ''president'', and ''presiding officer''. The chairperson of a parliamentary chamber is often called the ''Spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |