|
Agrostis Thurberiana
''Agrostis thurberiana'' is a species of Poaceae, grass that is native to northwest and southwest United States and Canada (the Aleutian Islands, Alaska, British Columbia, Colorado, Oregon, Washington (state), Washington and California). Description The species is perennial plant, perennial with short rhizomes and long culm (botany), culms. It has smooth leaf-sheaths with an eciliate membrane that is long and goes around the ligule. It is also lacerate, truncate and obtuse with the leaf blades being wide. The panicle is open, inflorescenced, lanceolate, and is long. The species' spikelets are long and are both elliptic and solitary with pedicel (botany), pedicelled fertile spikelets and one fertile floret which have a hairy callus. The chaff, glumes are long and are lanceolate, membranous and have one keel. They also have scaberulous vein (botany), veins and acute apexes. It have a hairy and long Rachilla (floral axis), rhachilla and elliptic long and keelless fertile lem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, including staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, oats, barley, and millet for people and as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials ( bamboo, thatch, and straw); oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedicel (botany)
In botany, a pedicel is a stem that attaches a single flower to the inflorescence. Such inflorescences are described as ''pedicellate''. The stalk at the base of a leaf is called a petiole. Description Pedicel refers to a structure connecting a single flower to its inflorescence. In the absence of a pedicel, the flowers are described as sessile. Pedicel is also applied to the stem of the infructescence. The word "pedicel" is derived from the Latin ''pediculus'', meaning "little foot". The stem or branch from the main stem of the inflorescence that holds a group of pedicels is called a peduncle. A pedicel may be associated with a bract or bracts. In cultivation In Halloween types of pumpkin A pumpkin is a cultivar, cultivated winter squash in the genus ''Cucurbita''. The term is most commonly applied to round, orange-colored squash varieties, but does not possess a scientific definition. It may be used in reference to many dif ... or squash plants, the shape o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilum (biology)
In botany, a hilum (pronounced ) is a scar or mark left on a seed coat by the former attachment to the ovary wall or to the funiculus (which in turn attaches to the ovary wall). On a bean seed, the hilum is called the "eye". For some species of fungus, the hilum is the microscopic indentation left on a spore when it separates from the sterigma of the basidium. A hilum can also be a nucleus of a starch grain; the point around which layers of starch are deposited. The adjectival form ''hilar'' denotes the presence of such a mark, and can be used as a distinguishing characteristic of a seed or spore In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo .... References {{Reflist Plant anatomy Fungal morphology and anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains sporangium, microsporangia. Most commonly, anthers are two-lobed (each lobe is termed a locule) and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile (i.e. nonreproductive) tissue between the lobes is called the Connective (botany), connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The size of anthers differs greatly, from a tiny fraction of a millimeter in ''Wolfia'' spp up to five inches (13 centimeters) in ''Canna iridiflora'' and ''Strelitzia nicolai''. The stamens in a flower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
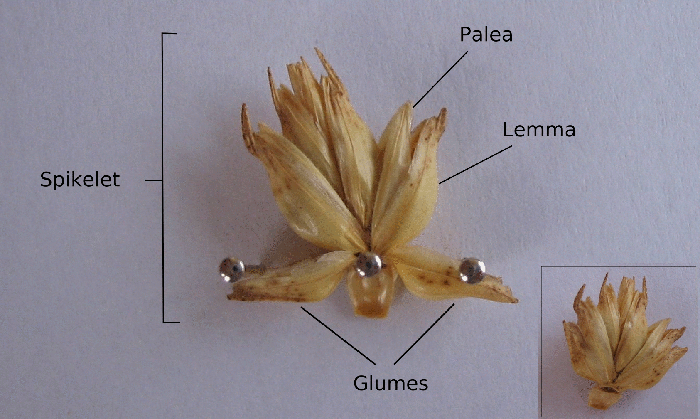
Lodicule
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, modified leaves; corolla, the petals; androecium, the male reproductive unit consisting of stamens and pollen; and gynoecium, the female part, containing style and stigma, which receives the pollen at the tip of the style, and ovary, which contains the ovules. When flowers are arranged in groups, they are known collectively as inflorescences. Floral growth originates at stem tips and is controlled by MADS-box genes. In most plant species flowers are heterosporous, and so can produce sex cells of both sexes. Pollination mediates the transport of pollen to the ovules in the ovaries, to facilitate sexual reproduction. It can occur between different plants, as in cross-pollination, or between flowers on the same plant or even the same f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemma (botany)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rachilla (floral Axis)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein (botany)
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the plant stem, stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the Shoot (botany), shoot system. In most leaves, the primary Photosynthesis, photosynthetic Tissue (biology), tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf, but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. The leaf is an integral part of the stem system, and most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (Glossary of botanical terms#adaxial, adaxial) and lower (Glossary of botanical terms#abaxial, abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, Trichome, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaff
Chaff (; ) is dry, scale-like plant material such as the protective seed casings of cereal grains, the scale-like parts of flowers, or finely chopped straw. Chaff cannot be digested by humans, but it may be fed to livestock, ploughed into soil, or burned. Etymology "Chaff" comes from Middle English , from Old English , related to Old High German ', "husk". Grain chaff In grasses (including cereals such as rice, barley, oats, and wheat), the ripe seed is surrounded by thin, dry, scaly bracts (called glumes, lemmas, and paleas), forming a dry husk (or hull) around the grain. Once it is removed, it is often referred to as chaff. In wild cereals and in the primitive domesticated einkorn,Potts, D. T. (1996) ''Mesopotamia Civilization: The Material Foundations'' Cornell University Press. p. 62. . emmer and spelt wheats, the husks enclose each seed tightly. Before the grain can be used, the husks must be removed. The process of loosening the chaff from the grain so as to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |