|
Agrarian Economy
An agrarian society, or agricultural society, is any community whose economy is based on producing and maintaining crops and farmland. Another way to define an agrarian society is by seeing how much of a nation's total production is in agriculture. In agrarian society, cultivating the land is the primary source of wealth. Such a society may acknowledge other means of livelihood and work habits but stresses the importance of agriculture and farming. Agrarian societies have existed in various parts of the world as far back as 10,000 years ago and continue to exist today. They have been the most common form of socio-economic organization for most of recorded human history. History Agrarian society were preceded by hunters and gatherers and horticultural societies and transition into industrial society. The transition to agriculture, called the Neolithic Revolution, has taken place independently multiple times. Horticulture and agriculture as types of subsistence developed among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesticated
Domestication is a multi-generational mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a steady supply of resources, such as meat, milk, or labor. The process is gradual and geographically diffuse, based on trial and error. Domestication affected genes for behavior in animals, making them less aggressive. In plants, domestication affected genes for morphology, such as increasing seed size and stopping the shattering of cereal seedheads. Such changes both make domesticated organisms easier to handle and reduce their ability to survive in the wild. The first animal to be domesticated by humans was the dog, as a commensal, at least 15,000 years ago. Other animals, including goats, sheep, and cows, were domesticated around 11,000 years ago. Among birds, the chicken was first domesticated in East Asia, seemingly for cockfighting, some 7,000 years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally related groups or sets of roles, with different functions, meanings, or purposes. Examples of social structure include family, religion, law, economy, and class. It contrasts with " social system", which refers to the parent structure in which these various structures are embedded. Thus, social structures significantly influence larger systems, such as economic systems, legal systems, political systems, cultural systems, etc. Social structure can also be said to be the framework upon which a society is established. It determines the norms and patterns of relations between the various institutions of the society. Since the 1920s, the term has been in general use in social science, especially as a variable whose sub-components needed to be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political science). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to one ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (other), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopulation Density Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011. Biological population densities Population density is population divided by total land area, sometimes including seas and oceans, as appropriate. Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and further reduce fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are: * Increased problems with locating sexual mates * Increased inbreeding Human densities Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually transcribed as "per square kilometre" or square mile, and which may include or exclude, for example, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Culture of Africa, African, Oceania, Oceanic, East Asian, Southeast Asian and South Asian cultures (similar to Yam (vegetable), yams). Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Common names The English term '':wikt:taro#English, taro'' was :wikt:taro#Maori, borrowed from the Māori language when James Cook, Captain Cook first observed ''Colocasia'' plantations in New Zealand in 1769. The form ''taro'' or ''talo'' is widespread among Polynesian languages:*''talo'': taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') – entry in the ''Polynesian Lexicon Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small-scale Agriculture
A smallholding or smallholder is a small farm operating under a small-scale agriculture model. Definitions vary widely for what constitutes a smallholder or small-scale farm, including factors such as size, food production technique or technology, involvement of family in labor and economic impact. There are an estimated 500 million smallholder farms in developing countries of the world alone, supporting almost two billion people. Smallholdings are usually farms supporting a single family with a mixture of cash crops and subsistence farming. As a country becomes more affluent, smallholdings may not be self-sufficient. Still, they may be valued for providing supplemental sustenance, recreation, and general rural lifestyle appreciation (often as hobby farms). As the sustainable food and local food movements grow in affluent countries, some of these smallholdings are gaining increased economic viability in the developed world as well. Small-scale agriculture is often in tension w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squash (vegetable)
is a genus of Herbaceous plant, herbaceous fruits in the gourd family (biology), family, Cucurbitaceae (also known as ''cucurbits'' or ''cucurbi''), native to the Andes and Mesoamerica. Five edible species are grown and consumed for their flesh and seeds. They are variously known as squash, pumpkin, or gourd, depending on species, Variety (botany), variety, and local parlance. Other kinds of gourd, also called bottle-gourds, are native to Africa and belong to the genus ''Lagenaria'', which is in the same family and subfamily as ''Cucurbita'', but in a different Tribe (biology), tribe; their young fruits are eaten much like those of the ''Cucurbita'' species. Most ''Cucurbita'' species are herbaceous vines that grow several meters in length and have tendrils, but non-vining "bush" cultivars of ''C. pepo'' and ''C. maxima'' have also been developed. The yellow or orange flowers on a ''Cucurbita'' plant are of two types: female and male. The female flowers produce the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
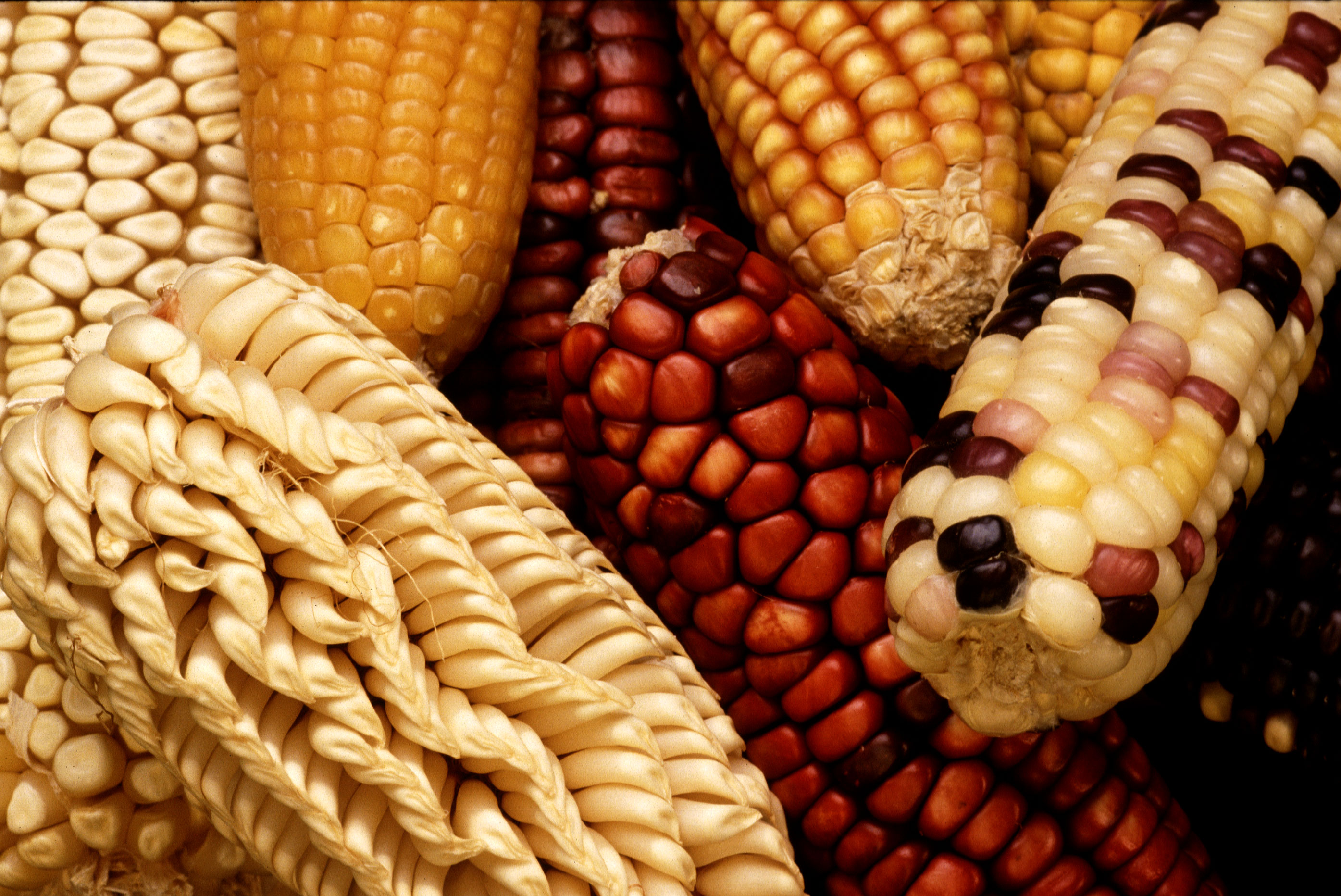
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much less commonly, ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). Asian rice was domesticated in China some 13,500 to 8,200 years ago; African rice was domesticated in Africa about 3,000 years ago. Rice has become commonplace in many cultures worldwide; in 2023, 800 million tons were produced, placing it third after sugarcane and maize. Only some 8% of rice is traded internationally. China, India, and Indonesia are the largest consumers of rice. A substantial amount of the rice produced in developing nations is lost after harvest through factors such as poor transport and storage. Rice yields can be reduced by pests including insects, rodents, and birds, as well as by weeds, and by List of rice diseases, diseases such as rice blast. Traditional rice polyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Japan, Japan, Economy of South Korea, South Korea, and Economy of Taiwan, Taiwan are among the world's largest and most prosperous. East Asia borders North Asia to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To its east is the Pacific Ocean. East Asia, especially History of China, Chinese civilization, is regarded as one of the earliest Cradle of civilization#China, cradles of civilization. Other ancient civilizations in East Asia that still exist as independent countries in the present day include the History of Japan, Japanese, History of Korea, Korean, and History of Mongolia, Mongolian civilizations. Various other civilizations existed as independent polities in East Asia in the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |