|
Agfacontour Professional
Agfacontour Professional was (as of 2002 not anymore produced) a special emulsion sheet film which, after exposure and development in the Agfacontour developer, produced direct equidensities. Agfacontour was introduced in 1970 by Agfa-Gevaert to produce equidensities by a direct, one-developing-step process. Until then equidensities had to be obtained using one of the following techniques: *The most popular method to obtain equidensities was the ''One-Film'' technique, better known as Sabattier effect (a.k.a. Pseudosolarization). *Another technique, making tonal extractions on high-contrast film, was called the ''Two-Film'' technique (negative-positive process): from a negative 3-5 different exposures were made on ultra high-contrast lith-films. These 3-5 positives were then copied again on ultra high-contrast lith-film to obtain negatives with virtually no grey tones. Then one positive and a negative from a different set were sandwiched together in register to obtain one sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equidensitometry
Equidensitometry is the technique of measuring ''equidensities'' in a photographic deposit or photographic layer, such as photographic films and photographic plates. *Equidensities are points, lines and areas having equal densities also called isodensities. * First order equidensities are points, lines and areas having isodensities obtained by applying one of the listed below techniques once, thus they exhibit one particular Density in the original *Second order equidentities are points and lines having isodensities obtained by applying one of the listed below techniques twice, thus they exhibit two particular Densities in the original. Second order equidensities do not normally show areas. * Equidensity series is a sandwich (in register) of a number of different equidensities. Usually each equidensity is coded by color or raster. Photographic and computerized image processing techniques Four techniques of obtaining equidensities are: * Tone separation process * Sabattier effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agfa-Gevaert
Agfa-Gevaert N.V. (Agfa) is a Belgian-German multinational corporation that develops, manufactures, and distributes analogue and digital imaging products, software, and systems. The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1867. In 1925, the company merged with several other German chemical companies to become chemicals giant IG Farben. IG Farben would go on to play major role in the economy of Nazi Germany. It extensively employed forced labour during the Nazi period, and produced Zyklon B poison gas used in the Holocaust. IG Farben was disestablished by the Allies in 1945. AGFA was reconstituted (as a subsidiary of Bayer) from the remnants of IG Farben in 1952. Agfa photographic film and cameras were once prominent consumer products. In 2004, the consumer imaging division was sold to a company founded via management buyout. AgfaPhoto GmbH, as the new company was called, filed for bankruptcy after a year, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabattier Effect
The Sabatier effect, also known as pseudo-solarization (or pseudo-solarisation) and erroneously referred to as the Sabattier effect, is a phenomenon in photography in which the image recorded on a negative or on a photographic print is wholly or partially reversed in tone. Dark areas appear light or light areas appear dark. Solarization and pseudo-solarization are quite distinct effects. Over time, the "pseudo" has been dropped in many photographic darkroom circles and discussions, but the effect that is meant is the Sabattier effect and not the solarization by extreme overexposure. Background Initially, the term " solarization" was used to describe the effect observed in cases of extreme overexposure of the photographic film or plate in the camera. The effect generated in the dark room was then called ''pseudo-solarization''. Spencer defines the Sabattier effect as: "Partial image reversal produced by brief exposure to white light of a partly developed silver halide image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lith Print
A lith print is an alternative photographic printing process that uses infectious development to achieve its distinct look. Lith print usually has harsh and gritty shadows. In lith print development, formaldehyde is added to the developer, in order to lock excess sulphite that is used to regulate development in "normal" B&W print. Process Lith print typically uses sometimes outdated Bromide papers such as Fomatone MG Classic, Fomabrom Variant III, Slavich Unibrom, and Moersch Easy Lith, see list of papers known to lith well (http://www.alternativephotography.com/lithprint-materials-update/) among many even rarer Bromide papers that have long since gone out of production black-and-white Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white to produce a range of achromatic brightnesses of grey. It is also known as greyscale in technical settings. Media The history of various visual media began with black and white, ... these often bromide formulated papers are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black And White
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white to produce a range of achromatic brightnesses of grey. It is also known as greyscale in technical settings. Media The history of various visual media began with black and white, and as technology improved, altered to color. However, there are exceptions to this rule, including black-and-white fine art photography, as well as many film motion pictures and art film(s). Early photographs in the late 19th and early to mid 20th centuries were often developed in black and white, as an alternative to sepia due to limitations in film available at the time. Black and white was also prevalent in early television broadcasts, which were displayed by changing the intensity of monochrome phosphurs on the inside of the screen, before the introduction of colour from the 1950s onwards. Black and white continues to be used in certain sections of the modern arts field, either stylistically or to invoke the perception of a hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halftone
Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous tone, continuous-tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size or in spacing, thus generating a gradient-like effect.Campbell, Alastair. ''The Designer's Lexicon''. ©2000 Chronicle, San Francisco. "Halftone" can also be used to refer specifically to the image that is produced by this process. Where continuous-tone imagery contains an infinite range of colors or greys, the halftone process reduces visual reproductions to an image that is printed with only one color of ink, in dots of differing size (pulse-width modulation) or spacing (frequency modulation) or both. This reproduction relies on a basic optical illusion: when the halftone dots are small, the human eye interprets the patterned areas as if they were smooth tones. At a microscopic level, developed black-and-white photographic film also consists of only two colors, and not an infinite range of continuous tones. For details, see film grain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a Nonlinearity, nonlinear operation used to encode and decode Relative luminance, luminance or CIE 1931 color space#Tristimulus values, tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following Power law, power-law expression: : V_\text = A V_\text^\gamma, where the non-negative real input value V_\text is raised to the power \gamma and multiplied by the constant ''A'' to get the output value V_\text. In the common case of , inputs and outputs are typically in the range 0–1. A gamma value \gamma 1 is called a ''decoding gamma'', and the application of the expansive power-law nonlinearity is called gamma expansion. Explanation Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. The human perception of brightness (lightness), un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Software
In computer graphics, graphics software refers to a program or collection of programs that enable a person to manipulate images or models visually on a computer. Computer graphics can be classified into two distinct categories: raster graphics and vector graphics, with further 2D and 3D variants. Many graphics programs focus exclusively on either vector or raster graphics, but there are a few that operate on both. It is simple to convert from vector graphics to raster graphics, but going the other way is harder. Some software attempts to do this. In addition to static graphics, there are animation and video editing software. Different types of software are often designed to edit different types of graphics such as video, photos, and vector-based drawings. The exact sources of graphics may vary for different tasks, but most can read and write files. Most graphics programs have the ability to import and export one or more graphics file formats, including those formats written fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
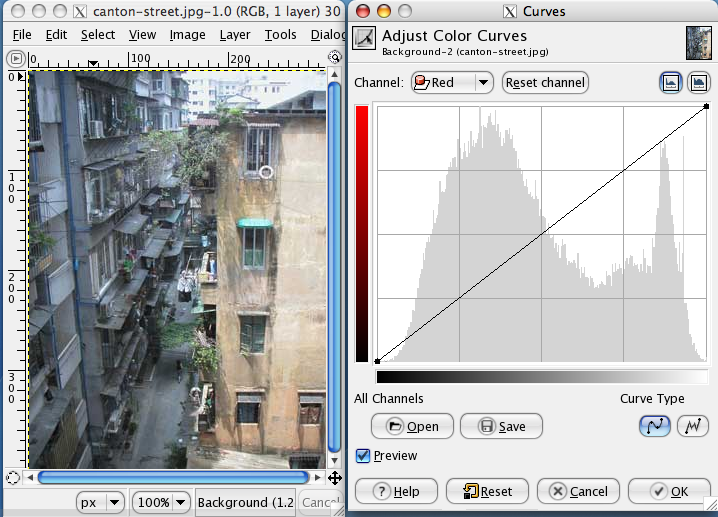
Curve (tonality)
In image editing, a curve is a remapping of image tonality, specified as a function from input level to output level, used as a way to emphasize colours or other elements in a picture. Curves can usually be applied to all channels together in an image, or to each channel individually. Applying a curve to all channels typically changes the brightness in part of the spectrum. Light parts of a picture can be easily made lighter and dark parts darker to increase contrast. Applying a curve to individual channels can be used to stress a colour. This is particularly efficient in the Lab color space, Lab colour space due to the separation of luminance and chromaticity, but it can also be used in RGB color model, RGB, CMYK color model, CMYK or whatever other color model, colour models the software supports. See also * Blend modes * Image histogram * Hurter–Driffield curve * Tone reproduction curve References {{reflist External links Defanging the Curves Vampire Dan Margulis, De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cow Agfacontour, Chromogenic Development Of Equidenities Serie
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are called cows and mature male cattle are bulls. Young female cattle are called heifers, young male cattle are oxen or bullocks, and castrated male cattle are known as steers. Cattle are commonly raised for meat, for dairy products, and for leather. As draft animals, they pull carts and farm implements. Cattle are considered sacred animals within Hinduism, and it is illegal to kill them in some Indian states. Small breeds such as the miniature Zebu are kept as pets. Taurine cattle are widely distributed across Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus are found mainly in India and tropical areas of Asia, America, and Australia. Sanga cattle are found primarily in sub-Saharan Africa. These types, sometimes classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Films
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication. A person who operates a camera to capture or take photographs is called a photographer, while the captured image, also known as a photograph, is the result produced by the camera. Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which is electronically processed and stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |