|
Agathla
Agathla Peak or Agathlan (, ) is a peak south of Monument Valley, Arizona, which rises over above the surrounding terrain. It is north of Kayenta and is visible from U.S. Route 163. The English designation ''Agathla'' is derived from the Navajo name ' meaning 'much wool', apparently for the fur of antelope and deer accumulating on the rock. The mountain is considered sacred by the Navajo. Agathla Peak is an eroded volcanic plug consisting of volcanic breccia cut by dikes of an unusual igneous rock called minette. It is one of many such volcanic diatremes that are found in Navajo country of northeast Arizona and northwest New Mexico. Agathla Peak and Shiprock in New Mexico are the most prominent. These rocks are part of the Navajo Volcanic Field, in the southern Colorado Plateau. Ages of these minettes and associated more unusual igneous rocks cluster near 25 million years. Climbing history Rock climbing is not currently allowed on Agathla Peak and surrounding Navaj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owl Rock
Owl Rock is a 6,547-foot (1,996 m) elevation sandstone summit located south of Monument Valley, in northeast Arizona. It is situated north of Kayenta on Navajo Nation land, and can be seen from Highway 163 perched on the east edge of Tyende Mesa, where it towers 1,000 feet (300 meters) above the surrounding terrain. Its nearest higher neighbor is Agathla Peak, to the east-northeast, on the opposite side of this highway. Precipitation runoff from this feature drains into El Capitan Wash, which is part of the San Juan River drainage basin. The first ascent of Owl Rock was made in April 1966 by Fred Beckey and Harvey Carter by climbing cracks on the west face, and then bolting up a smooth south nose to the summit. They employed 20 pitons and 14 bolts on this route called ''Warpath''. The descriptive name stems from its uncanny resemblance to an owl when viewed from the east. This feature is known as ''Bee 'Adizí'' in Navajo language meaning "spindle", and this sacred place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaistla Butte
Chaistla Butte is a elevation summit located south of Monument Valley, in Navajo County of northeast Arizona. It is situated northeast of the community of Kayenta, on Navajo Nation land, and can be seen from Highway 163. It is one of the eroded volcanic plugs, or diatremes, of the Navajo Volcanic Field, which is a volcanic field that includes intrusions and flows of minette and other unusual igneous rocks which formed around 30 million years ago during the Oligocene.Steven C. Semken, ''The Navajo Volcanic Field'', in ''Volcanology in New Mexico'', New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 18, p. 79, 2001. Chaistla Butte rises above the Little Capitan Valley, and the 1,000 by 700-foot base pokes up from the Chinle Formation. Its neighbors include Agathla Peak and Owl Rock, to the north-northwest. Precipitation runoff from this feature drains into the Laguña Creek drainage basin. The ''chaistla'' name, which means "beaver pocket" or "beaver corner" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan And Herb Conn
Jan H. Conn (April 22, 1924 – May 13, 2023) and Herbert William Conn (April 16, 1920 – February 1, 2012) were climbing and caving pioneers. They are credited with establishing many classic climbs in areas like Carderock in Maryland, Seneca Rocks in West Virginia, Cannon Cliff in New Hampshire and Black Hills of South Dakota. They are also well known as cave explorers who in the 1960s and 1970s discovered and mapped over 60 miles of Jewel Cave, making it the world’s third- longest cave system. Early life and education Both Herb and Jan were born and raised on the East Coast. Jan grew up in Maryland, just outside Washington, DC in a household with two older sisters. Jan loved music and played flute, classical guitar and several other instruments. Herb grew up in upstate New York, and graduated from the University of Colorado. Herb and Jan married in 1944. During World War II, Herb served as an electrical engineer for the Navy Department in Washington, DC. Jan and Herb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
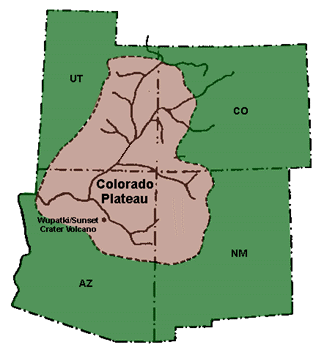
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. This plateau covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau, nicknamed High Country, lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored rock left bare to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiprock
Shiprock (, "rock with wings" or "winged rock") is a monadnock rising nearly above the high-desert plain of the Navajo Nation in San Juan County, New Mexico, United States. Its peak elevation is above sea level. It is southwest of the town of Shiprock, which is named for the peak. Governed by the Navajo Nation, the formation is in the Four Corners region and plays a significant role in Navajo religion, myth, and tradition. Shiprock is a point of interest for rock climbers and photographers and has been featured in several film productions and novels. It is the most prominent landmark in northwestern New Mexico. In 1975, Shiprock was designated a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service. Name The Navajo name for the peak, , "rock with wings" or "winged rock", refers to the legend of the great bird that brought the Navajo from the north to their present lands. The name "Shiprock" or Shiprock Peak or Ship Rock derives from the peak's resemblance to an enormous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navajo Nation
The Navajo Nation (), also known as Navajoland, is an Indian reservation of Navajo people in the United States. It occupies portions of northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southeastern Utah. The seat of government is located in Window Rock, Arizona. At roughly , the Navajo Nation is the largest Indian reservation in the United States, exceeding the size of List of U.S. states and territories by area, ten U.S. states. It is one of the few reservations whose lands overlap the nation's traditional homelands. In 2010, the reservation was home to 173,667 out of 332,129 Navajo tribal members; the remaining 158,462 tribal members lived outside the reservation, in urban areas (26%), border towns (10%), and elsewhere in the U.S. (17%). In 2020, the number of tribal members increased to 399,494, surpassing the Cherokee Nation as the largest tribal group by enrollment. The U.S. Mexican Cession, gained ownership of what is today Navajoland in 1848 following the Mexican–A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piton
A piton (; also called ''pin'' or ''peg'') in big wall climbing and in aid climbing is a metal spike (usually steel) that is driven into a crack or seam in the climbing surface using a Rock climbing hammer, climbing hammer, and which acts as an anchor for protection (climbing), protecting the climber from falling or to assist progress in aid climbing. Pitons are equipped with an eye hole or a ring to which a carabiner is attached; the carabiner can then be directly or indirectly connected to a climbing rope. Pitons were the original form of protection (climbing), protection and are still used where there is no alternative. Repeated hammering and extraction of pitons damage the rock, and climbers who subscribe to the clean climbing ethic avoid their use as much as possible. With the popularization of clean climbing in the 1970s, pitons were largely replaced by faster and easier-to-use clean protection, such as nut (climbing), nuts and spring-loaded camming device, camming devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Ascent
In mountaineering and climbing, a first ascent (abbreviated to FA in climbing guidebook, guide books), is the first successful documented climb to the top of a mountain or the top of a particular climbing route. Early 20th-century mountaineers and climbers focused on reaching the tops of iconic mountains (e.g. the eight-thousanders) and climbing routes (e.g. the great north faces of the Alps) by whatever means possible, often using considerable amounts of aid climbing, and/or with large expedition style support teams that laid "siege" to the climb. As all the key tops were summited, the manner in which each top was reached became important, particularly the ability to complete the ascent without artificial aid, which is called free climbing. In free climbing, the term first free ascent (abbreviated FFA) is used where a mountain or climbing route is ascended without any artificial aid (devices for climbing protection, protection in the event of a fall could be used as long as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona Highways
''Arizona Highways'' is a magazine that contains travelogues and artistic photographs related to the U.S. state of Arizona. It is published monthly in Phoenix by a unit of the Arizona Department of Transportation (ADOT). Background The magazine began in July 1921 by the Arizona Highway Department (now the Arizona Department of Transportation) as a 10-page pamphlet designed to promote "the development of good roads throughout the state." Publication of the pamphlet ended on December 30, 1922, after nine issues. The publication was relaunched on April 15, 1925, as a regular magazine. In addition to the engineering articles, cartoons and travelogues were also included in the early issues. Over the next two decades the magazine reduced, and then stopped, inclusion of the road engineering articles and dedicated itself to the present format of travel tales, historical stories, and humor about the state of Arizona (including stories about Arizona's contribution to the history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolt (climbing)
In rock climbing, a bolt is a permanent anchor fixed into a hole drilled in the rock as a form of climbing protection. Most bolts are either self-anchoring expansion bolts or fixed in place with liquid resin. Climbing routes that are bolted are known as sport climbs, and those that do not use (or allow) bolts, are known as traditional climbs. Description While bolts are commonplace in rock and gym climbing there is no universal vocabulary to describe them. Generally, a bolt hanger (or a fixed hanger) is a combination of a fixed bolt and a specialized stainless steel hanger designed to accept a carabiner, whereas in certain regions a bolt runner (or a carrot) describes a hangerless bolt (where the climber must provide their own hanger bracket such as a rivet hanger). A climbing rope is then clipped into the carabiner. Generally quickdraws or slings are employed between bolt hangers and the rope to reduce drag when ascending, belaying and rappelling. Types Variations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carabiner
A carabiner or karabiner (), often shortened to biner or to crab, colloquially known as a (climbing) clip, is a specialized type of shackle, a metal loop with a spring-loaded gate used to quickly and reversibly connect components, most notably in safety-critical systems. The word comes from the German language, German , short for , meaning "carbine hook," as the device was used by carabiniers to attach their carbines to their belts. Use Carabiners are widely used in rope-intensive activities such as climbing, fall arrest systems, arboriculture, caving, sailing, hot air ballooning, hot-air ballooning, rope rescue, construction, industrial rope access, industrial rope work, window cleaning, whitewater rescue, and acrobatics. They are predominantly made from both steel and aluminium. Those used in sports tend to be of a lighter weight than those used in commercial applications and rope rescue. Often referred to as carabiner-style or as mini-carabiners, carabiner keyrings and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |