 |
Agar Diffusion Test
The disk diffusion test (also known as the agar diffusion test, Kirby–Bauer test, disc-diffusion antibiotic susceptibility test, disc-diffusion antibiotic sensitivity test and KB test) is a culture-based microbiology assay used in diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. In diagnostic labs, the assay is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria isolated from a patient's infection to clinically approved antibiotics. This allows physicians to prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic treatment. In drug discovery labs, especially bioprospecting labs, the assay is used to screen biological material (e.g. plant extracts, bacterial fermentation broths) and drug candidates for antibacterial activity. When bioprospecting, the assay can be performed with paired strains of bacteria to achieve dereplication and provisionally identify antibacterial mechanism of action. In diagnostic laboratories, the test is performed by inoculating the surface of an agar plate with bacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Kleihauer–Betke Test
The Kleihauer–Betke ("KB") test, Kleihauer–Betke ("KB") stain, Kleihauer test or acid elution test is a blood test used to measure the amount of fetal hemoglobin transferred from a fetus to a mother's bloodstream. It is usually performed on Rhesus blood group system, Rh-negative mothers to determine the required dose of Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIg) to inhibit formation of Rh antibody, antibodies in the mother and prevent Rh disease in future Rh-positive children. It is named after Enno Kleihauer and Klaus Betke who described it in 1957. Test details The KB test is the standard method of quantitating Fetal-maternal haemorrhage, fetal–maternal hemorrhage (FMH). It takes advantage of the differential resistance of fetal hemoglobin to acid. A standard blood smear is prepared from the mother's blood and exposed to an acid bath. This removes adult hemoglobin, but not fetal hemoglobin, from the red blood cells. Subsequent staining, using Shepard's method, makes fetal cells (conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Biological Target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets are proteins and nucleic acids. The definition is context-dependent, and can refer to the biological target of a pharmacologically active drug compound, the receptor target of a hormone (like insulin), or some other target of an external stimulus. Biological targets are most commonly proteins such as enzymes, ion channels, and receptors. Mechanism The external stimulus (''i.e.'', the drug or ligand) physically binds to ("hits") the biological target. The interaction between the substance and the target may be: * noncovalent – A relatively weak interaction between the stimulus and the target where no chemical bond is formed between the two interacting partners and hence the interaction is completely reversible. * reversible c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
McFarland Standards
In microbiology, McFarland standards are used as a reference to adjust the turbidity of bacterial suspensions so that the number of bacteria will be within a given range to standardize microbial testing. An example of such testing is antibiotic susceptibility testing by measurement of minimum inhibitory concentration which is routinely used in medical microbiology and research. If a suspension used is too heavy or too dilute, an erroneous result (either falsely resistant or falsely susceptible) for any given antimicrobial agent could occur. Original McFarland standards were made by mixing specified amounts of barium chloride and sulfuric acid together. Mixing the two compounds forms a barium sulfate precipitate, which causes turbidity in the solution. A 0.5 McFarland standard is prepared by mixing 0.05 mL of 1.175% barium chloride dihydrate (BaCl2•2H2O), with 9.95 mL of 1% sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Now there are McFarland standards prepared from suspensions of latex Late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mueller–Hinton Agar
Mueller Hinton agar is a type of growth medium used in microbiology to culture bacterial isolates and test their susceptibility to antibiotics. This medium was first developed in 1941 by John Howard Mueller and Jane Hinton, who were microbiologists working at Harvard University. However, Mueller Hinton agar is made up of a couple of components, including beef extract, acid hydrolysate of casein, and starch, as well as agar to solidify the mixture. The composition of Mueller Hinton agar can vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use, but the medium is generally nutrient-rich and free of inhibitors that could interfere with bacterial growth. Mueller Hinton agar is commonly used in the disk diffusion method, which is a simple and widely used method for testing the susceptibility of bacterial isolates to antibiotics. In this method, small disks impregnated with different antibioti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
KB Test
KB test can refer to two different medical tests: * The Kirby–Bauer test ( agar diffusion test), a test of the antibiotic sensitivity of bacteria * The Kleihauer–Betke test ( acid elution test), a test of the amount of fetal hemoglobin transferred from a fetus to a mother's bloodstream {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
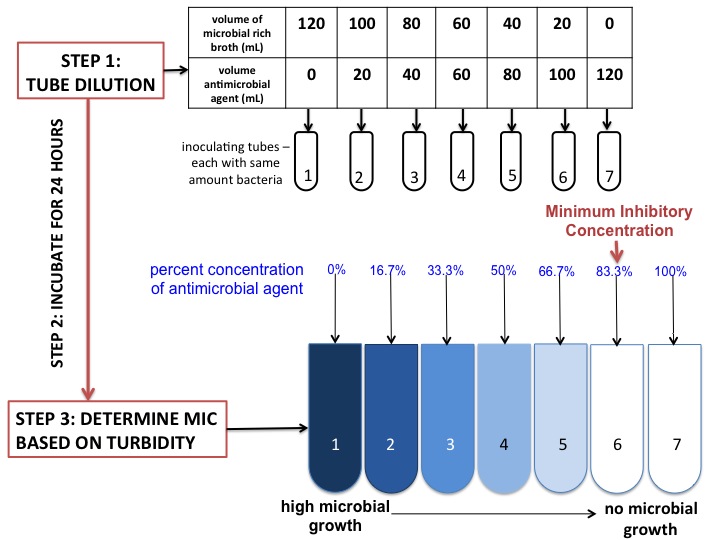 |
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible ''in vitro'' cell growth, growth of bacteria or Fungus, fungi. MIC testing is performed in both diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. The MIC is determined by preparing a Serial dilution, dilution series of the chemical, adding agar dilution, agar or broth microdilution, broth, then inoculating with bacteria or fungi, and incubating at a suitable temperature. The value obtained is largely dependent on the susceptibility of the microorganism and the antimicrobial potency of the chemical, but other variables can affect results too. The MIC is often expressed in micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). In diagnostic labs, MIC test results are used to grade the susceptibility of microbes. These grades are assigned based on agreed upon values called breakpoints. Breakpoints are published by standards organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
British Society For Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
The British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) is a UK-based multi-professional organisation committed to preventing infectious diseases and tackling the growing threat of drug-resistant infections – one of the top global public health and development threats. As one of the world’s largest networks of infection specialists, BSAC has thousands of members and works with a wide range of stakeholders, including researchers, scientists, health care providers, policymakers, and industry leaders to support their work and help them reach a global audience. On receiving BSAC's highest award, the Garrod Medal, in 2021, Dame Sally Davies, the UK's Special Envoy on Antimicrobial Resistance, commented: "For fifty years, BSAC have been at the forefront of the global fight against AMR...enabling communities globally to be more than the sum of their parts." Activities Current BSAC activities include: * Publishes the ''Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy'' and its sister pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Deutsches Institut Für Normung
' (DIN; in English language, English, the German Institute for Standardisation) is a Germany, German non-profit organization and acting as national organization for standardization. DIN is the German International Organization for Standardization, ISO member body. DIN is headquartered in Berlin. There are around thirty thousand DIN Technical standard, Standards, covering nearly every field of technology. History Founded in 1917 as the ' (NADI, "Standardisation Committee of German Industry"), the NADI was renamed ' (DNA, "German Standardisation Committee") in 1926 to reflect that the organization now dealt with standardization issues in many fields; viz., not just for industrial products. In 1975 it was renamed again to ', or 'DIN' and is recognised by the German government as the official national-standards body, representing German interests at the international and European levels. The acronym, 'DIN' is often incorrectly expanded as ' ("German Industry Standard"). This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Clinical And Laboratory Standards Institute
The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) is a volunteer-driven, membership-supported, not-for-profit, standards development organization. CLSI promotes the development and use of voluntary laboratory consensus standards and guidelines within the health care community. History In 1968, 31 clinicians and laboratory scientists representing 15 organizations convened to establish a formal consensus process for standardization. In 1977, CLSI received accreditation from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) as a voluntary consensus standards organization. Around the same time, CLSI became the home of the National Reference System for the Clinical Laboratory (NRSCL), a collection of reference systems intended to enhance the comparability of test results, consistent with medical practice needs. CLSI is a global association with over 1,500 member organizations and individual members, along with more than 2,000 volunteers. Until 2005, CLSI was known as the Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |