|
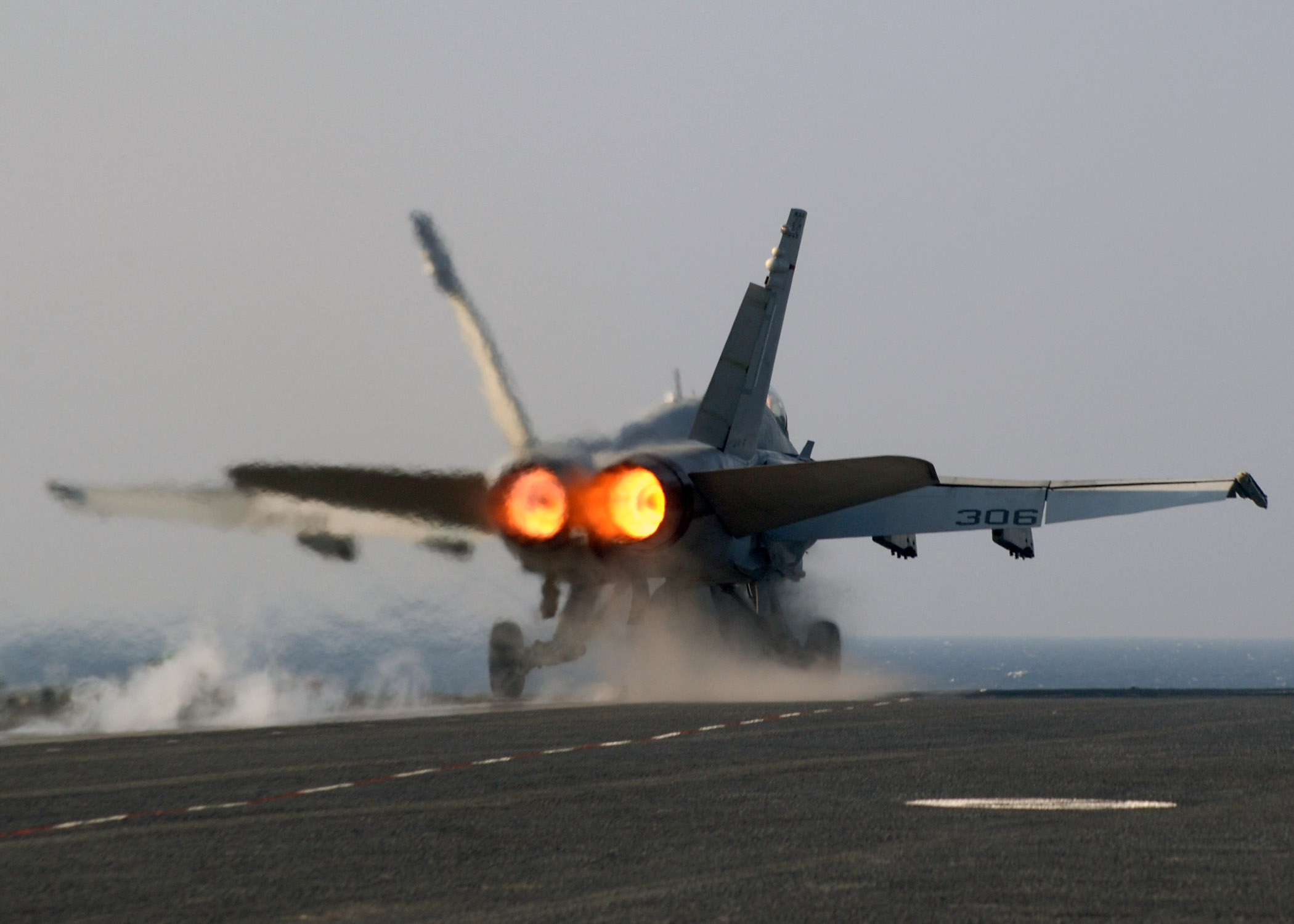
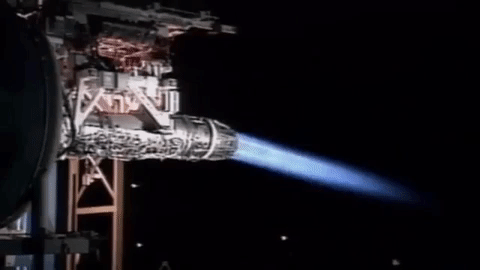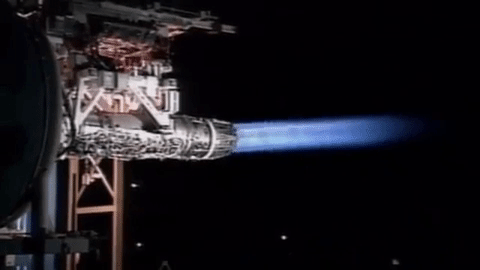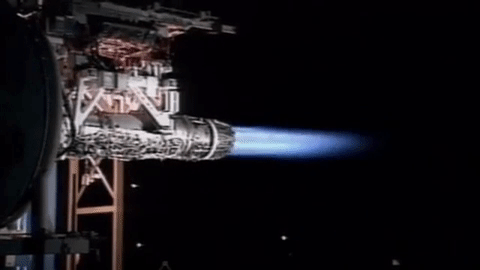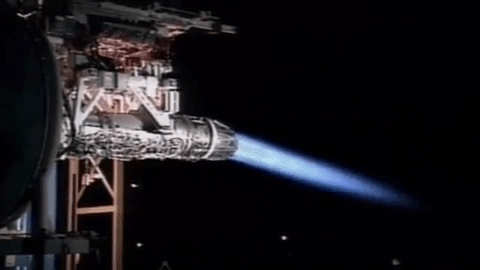
Afterburning
An afterburner (or reheat in British English) is an additional combustion component used on some jet engines, mostly those on military aircraft, military supersonic aircraft. Its purpose is to increase thrust, usually for supersonic flight, takeoff, and aerial combat, combat. The afterburning process injects additional Jet fuel, fuel into a combustor ("burner") in the jet pipe behind (i.e., "after") the turbine, "reheating" the exhaust gas. Afterburning significantly increases thrust as an alternative to using a bigger engine with its added weight penalty, but at the cost of increased fuel consumption (decreased fuel efficiency) which limits its use to short periods. This aircraft application of "reheat" contrasts with the meaning and implementation of "reheat" applicable to gas turbines driving electrical generators and which reduces fuel consumption. Jet engines are referred to as operating ''wet'' when afterburning and ''dry'' when not. An engine producing maximum thrust w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbofan
A turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft engine, aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a combination of references to the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet and the additional fan stage. It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to force air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust. The ratio of the mass-flow of air bypassing the engine core to the mass-flow of air passing through the core is referred to as the bypass ratio. The engine produces thrust through a combination of these two portions working together. Engines that use more Propel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine (that drives the compressor). The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s. Turbojets have poor efficiency at low vehicle speeds, which limits their usefulness in vehicles other than aircraft. Turbojet engines have been used in isolated cases to power vehicles other than aircraft, typically for attempts on land speed records. Where vehicles are "turbine-powere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Vectoring
Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to Aircraft flight control system, control the Spacecraft attitude control, attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle. In rocketry and ballistic missiles that fly outside the atmosphere, aerodynamic Flight control surfaces, control surfaces are ineffective, so thrust vectoring is the primary means of Flight dynamics (fixed-wing aircraft), attitude control. Exhaust vanes and Gimbaled thrust, gimbaled engines were used in the 1930s by Robert H. Goddard, Robert Goddard. For aircraft, the method was originally envisaged to provide upward vertical thrust as a means to give aircraft vertical (VTOL) or short (STOL) takeoff and landing ability. Subsequently, it was realized that using vectored thrust in combat situations enabled aircraft to perform various maneuvers not available to conventional-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney J57
The Pratt & Whitney J57 (company designation: JT3C) is an axial-flow turbojet engine developed by Pratt & Whitney in the early 1950s. The J57 (first run January 1950) was the first 10,000 lbf (45 kN) thrust class engine in the United States. It is a two spool engine. The J57/JT3C was developed into the J52 turbojet, the J75/JT4A turbojet, the JT3D/TF33 turbofan, and the XT57 turboprop (of which only one was built). The J57 and JT3C saw extensive use on fighter jets, jetliners, and bombers for many decades. Design and development The J57 was a development of the Pratt & Whitney XT45 (PT4) turboprop engine that was originally intended for the Boeing XB-52. As the B-52 power requirements grew, the design evolved into a turbojet, the JT3. Pratt & Whitney designed the J57 to have a relatively high overall pressure ratio to help improve both thrust-specific fuel consumption and specific thrust, but it was known that throttling a single high-pressure-ratio compressor w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Technical Information Center
The Defense Technical Information Center (DTIC, ) is the repository for research and engineering information for the United States Department of Defense (DoD). DTIC's services are available to DoD personnel, federal government personnel, federal contractors and selected academic institutions. The general public can access unclassified information through its public website. History The DTIC traces its history to the June 1945 formation of the Air Documents Research Center (ADRC), a joint effort of the US Army Air Force, US Navy and Royal Air Force to build a single collection of captured German aeronautical research, based in London. The ADRC was initially tasked with the sorting of the document collection into three broad groups; documents that would assist the war in the Pacific theater, documents of immediate intelligence interest to the United States or British forces and documents of interest for future research. With the ending of the war in 1945, the ADRC moved to Wrig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
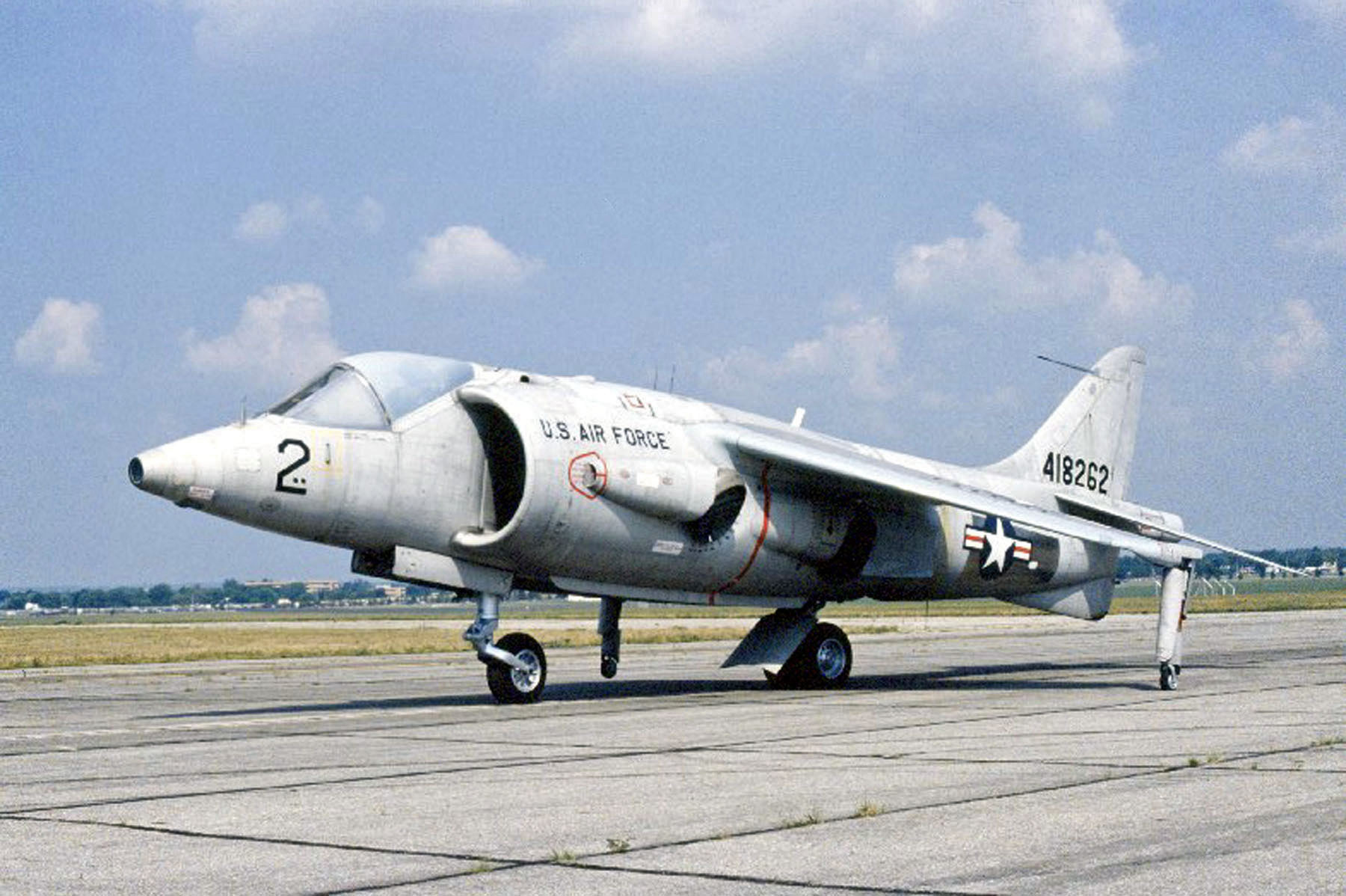
Hawker Siddeley Harrier
The Hawker Siddeley Harrier is a British jet-powered attack aircraft designed and produced by the British aerospace company Hawker Siddeley. It was the first operational ground attack and reconnaissance aircraft with vertical/short takeoff and landing (V/STOL) capabilities and the only truly successful V/STOL design of its era. It was the first of the Harrier series of aircraft, being developed directly from the Hawker Siddeley Kestrel prototype aircraft following the cancellation of a more advanced supersonic aircraft, the Hawker Siddeley P.1154. In the mid 1960s, the ''Harrier GR.1'' and ''GR.3'' variants were ordered by the British government for the Royal Air Force (RAF). The Harrier GR.1 made its first flight on 28 December 1967, and entered RAF service in April 1969. During the 1970s, the United States opted to procure the aircraft as the ''AV-8A''; it was operated by the US Marine Corps (USMC). Introduced to service amid the Cold War, the RAF positioned the bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Pegasus
The Rolls-Royce Pegasus is a British turbofan engine originally designed by Bristol Siddeley. It was manufactured by Rolls-Royce plc. The engine is not only able to power a jet aircraft forward, but also to direct thrust downwards via Thrust vectoring, swivelling nozzles. Lightly loaded aircraft equipped with this engine can manoeuvre like a helicopter. In particular, they can perform VTOL, vertical takeoffs and landings. In US service, the engine is designated F402. Originally the Bristol Siddeley Pegasus, the engine powers all versions of the Harrier jump jet, Harrier family of multi-role military aircraft. Rolls-Royce licensed Pratt & Whitney to build the Pegasus for US built versions. However Pratt & Whitney never completed any engines, with all new build being manufactured by Rolls-Royce in Bristol, England. The Pegasus was also the planned engine for a number of aircraft projects, among which were the prototypes of the German Dornier Do 31 VSTOL military transport project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Siddeley P
Hawker or Hawkers may refer to: Places *Hawker, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra *Hawker, South Australia, a town *Division of Hawker, an Electoral Division in South Australia *Hawker Island, Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica *Hawker Creek, Missouri, United States In business * Hawker (trade), a vendor of food or merchandise * Hawker Aircraft, a British aircraft manufacturer * Hawkers (company), a Spanish sunglasses company Other uses * Hawker (surname) * One who practices falconry Falconry is the hunting of wild animals in their natural state and habitat by means of a trained bird of prey. Small animals are hunted; squirrels and rabbits often fall prey to these birds. Two traditional terms are used to describe a person ..., hunting with hawks * Hawker College, a senior secondary college in the Australian Capital Territory * Hawker (dragonfly), a family of dragonflies in North America and Europe {{DEFAULTSORT:Hawker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Spey
The Rolls-Royce Spey (company designations RB.163 and RB.168 and RB.183) is a low-bypass turbofan engine originally designed and manufactured by Rolls-Royce that has been in widespread service for over 40 years. A co-development version of the Spey between Rolls-Royce and Allison in the 1960s is the Allison TF41. Intended for the smaller civilian jet airliner market when it was being designed in the late 1950s, the Spey concept was also used in various military engines, and later as a turboshaft engine for ships known as the Marine Spey, and even as the basis for a new civilian line, the Rolls-Royce RB.183 Tay. Aviation versions of the base model Spey have accumulated over 50 million hours of flight time. In keeping with Rolls-Royce naming practices, the engine is named after the River Spey. Design and development In 1954 Rolls-Royce introduced the first commercial bypass engine, the Rolls-Royce Conway, with 17,500 lbf (78 kN) of thrust aimed at what was then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney TF30
The Pratt & Whitney TF30 (company designation JTF10A) is a military low-bypass turbofan engine originally designed by Pratt & Whitney for the subsonic F6D Missileer fleet defense fighter, but this project was cancelled. It was later adapted with an afterburner for supersonic designs, and in this form it was the world's first production afterburning turbofan, going on to power the General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark, F-111 and the F-14 Tomcat, F-14A Tomcat, as well as being used in early versions of the A-7 Corsair II without an afterburner. First flight of the TF30 was in 1964 and production continued until 1986. Design and development In 1958, the Douglas Aircraft Company proposed a short-range, four-engined jet airliner to fill the gap below its new DC-8 intercontinental, known internally as the Douglas Model 2067, Model 2067. Intended to be marketed as DC-9, it was not directly related to the later twin-engined Douglas DC-9.Connors 2010, p. 341 Pratt & Whitney (P&W) had offered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Siddeley BS100
The Bristol Siddeley BS.100 is a British twin-spool, vectored thrust, turbofan aero engine that first ran in 1960. The engine was designed and built in limited numbers by Bristol Siddeley Engines Limited. The project was cancelled in early 1965. Design and development Based on the 300-series Olympus, the BS.100 was similar in general arrangement to that of the company's Pegasus design, but with the addition of plenum chamber burning (PCB), to enable the projected Hawker Siddeley P.1154 VSTOL fighter design to accelerate to supersonic speed and to allow the aircraft to hover. PCB is similar to reheat, but combustion is only applied to the bypass air (i.e. the front nozzles). PCB was quite difficult to develop since combustion had to occur on the bends between fan exit and entry to the two vectoring front nozzles and at much lower inlet pressure and temperature than a conventional afterburner. The PCB flame-holders were highly complex sheet metal fabrications which were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Waves
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium, but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distance. When a shock wave passes throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |