|
Affori
Affori is a ward of Milan, Italy, part of the Zone 9 administrative division of the city, located north of the city centre. It borders with the wards of Bruzzano, Comasina, Bovisasca, Dergano and Niguarda. Before being annexed to Milan in 1923, it was an autonomous ''comune''. History The rural settlement of Affori is referenced as early as 915, although in early references the name of the place is variously spelled Affoni,See Ripamonti (1995), pp. 19-23 Afoni, Afori or Avoni. This toponym is of uncertain origin; it might be from a Roman anthroponym "Afer", or from the Latin ''ad forum'' ("by the market", possibly a reference to a local market) or even from ''ad fontem'' ("by the spring", in reference to a local spring of water. It has also been suggested that the name might be from ''ad foris'', "outside", which was used to refer to the church of Affori (''Sanca Iustina a foris'') as the church was "outside" the walls of Milan. It has also been observed that "Affori" is also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zone 9 Of Milan
The Zone 9 of Milan, since 2016 officially Municipality 9 of Milan, (in Italian language, Italian: Zona 9 di Milano, Municipio 9 di Milano) is one of the 9 Administrative divisions of Milan, administrative divisions of Milan, Italy. It was officially created as an administrative subdivision during the 1980s. On 14 April 2016, in order to promote a reform on the municipal administrative decentralization, the City Council of Milan established the new Municipality 9, a new administrative body responsible for running most local services, such as schools, social services, waste collection, roads, parks, libraries and local commerce. On 5 March 1999 the new Zone 9, which corresponds to the northern part of the city, was made up by the union of the previous Zones 2 (Centro Direzionale di Milano, Centro Direzionale, Greco (district of Milan), Greco, Zara), 7 (Bovisa, Dergano), 8 (Affori, Bruzzano, Comasina) and 9 (Niguarda, Bicocca (district of Milan), Bicocca). Subdivision The borough i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruzzano
Bruzzano is a district (quartier) of Milan, Italy Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical .... It is an area located within Zone 9 of the city. Overview Its name comes from the Latin ''Bruttianum'', as the land owner of the agricultural ''fundus'' was a Roman citizen coming from ''Bruttium'' (today Calabria). In this region, in fact, there is now the namesake municipality of Bruzzano Zeffirio. The first written documents that testify the existence of an independent ''comune'' dates back to 1346, while the earliest proof of the existence of the church of Santa Maria Assunta dates back to 1011. Bruzzano formed a separate municipality until 1869, when it joined Affori, Bresso and Dergano to form the ''Comune di Affori e Uniti'' (named again just ''Affori'' since 1912), w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Milan
Milan is divided into nine municipalities ( it, municipi or ''zone''; known as , "decentralization zones" from 1999 until 2016). They are numbered from 1 to 9. The organization was established in 1997, implemented in 1999 and reformed in 2016; prior to that the city was divided into 20 administrative zones. Borough Councils Each Municipality has a local government called (Borough Council). Every Council is composed of a President and 40 members for boroughs exceeding 100,000 inhabitants or 30 members for smaller ones. While the 1997 plan was intended to ascribe several rights and functions to borough councils, this has been largely unattended, so that borough councils have, in practice, little power and few duties. Some of the actual functions of borough councils are: * expressing opinions on urbanistic and social issues such as public works, town planning, maintenance of green spaces, regulamentation of street markets. These opinions are not binding for the higher level city gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its Metropolitan City of Milan, metropolitan city has 3.26 million inhabitants. Its continuously built-up List of urban areas in the European Union, urban area (whose outer suburbs extend well beyond the boundaries of the administrative Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city and even stretch into the nearby country of Switzerland) is the fourth largest in the EU with 5.27 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan), is estimated between 8.2 million and 12.5 million making it by far the List of metropolitan areas of Italy, largest metropolitan area in Italy and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieve
In the Middle Ages, a pieve (, ; la, plebe, link=no; plural ''pievi'') was a rural church with a baptistery, upon which other churches without baptisteries depended. The Italian word ''pieve'' is descended from Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ... '' plebs'' which, after the expansion of Christianity in Italy, was applied to the community of baptized people. Many ''pievi'' began to appear in the 5th century, as Christianity expanded in the rural areas outside the main cities. In the 9th-10th centuries, they were often designed with bell towers. See also * List of pievi Church architecture Architecture in Italy Catholic Church in Italy {{Church-architecture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walls Of Milan
The city Milan, Italy, has had three different systems of defending walls. The oldest, Roman walls were developed in two stages, the first in the Republican and the second in the Imperial era. The second wall system was realized in the Middle Ages (12th Century), after the destruction of the city by Frederick I Barbarossa. Finally, the latest wall system was built by the Spanish rulers (16th Century). While very little remains of these walls, their structure is clearly reflected in the urbanistic layout of the city. In particular, modern Milan has two roughly circular rings of streets, namely the " Cerchia dei Navigli" and the "Cerchia dei Bastioni", which essentially correspond to the Medieval and Spanish walls, respectively. Note that a third ring of roads just beyond the Inner Ring Road (circonvallazione interna / "Cerchia dei Bastioni"), called the External Ring Road (circonvallazione esterna), does not owe itself to any old city walls; but was part of the 1884 Beruto Plan f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
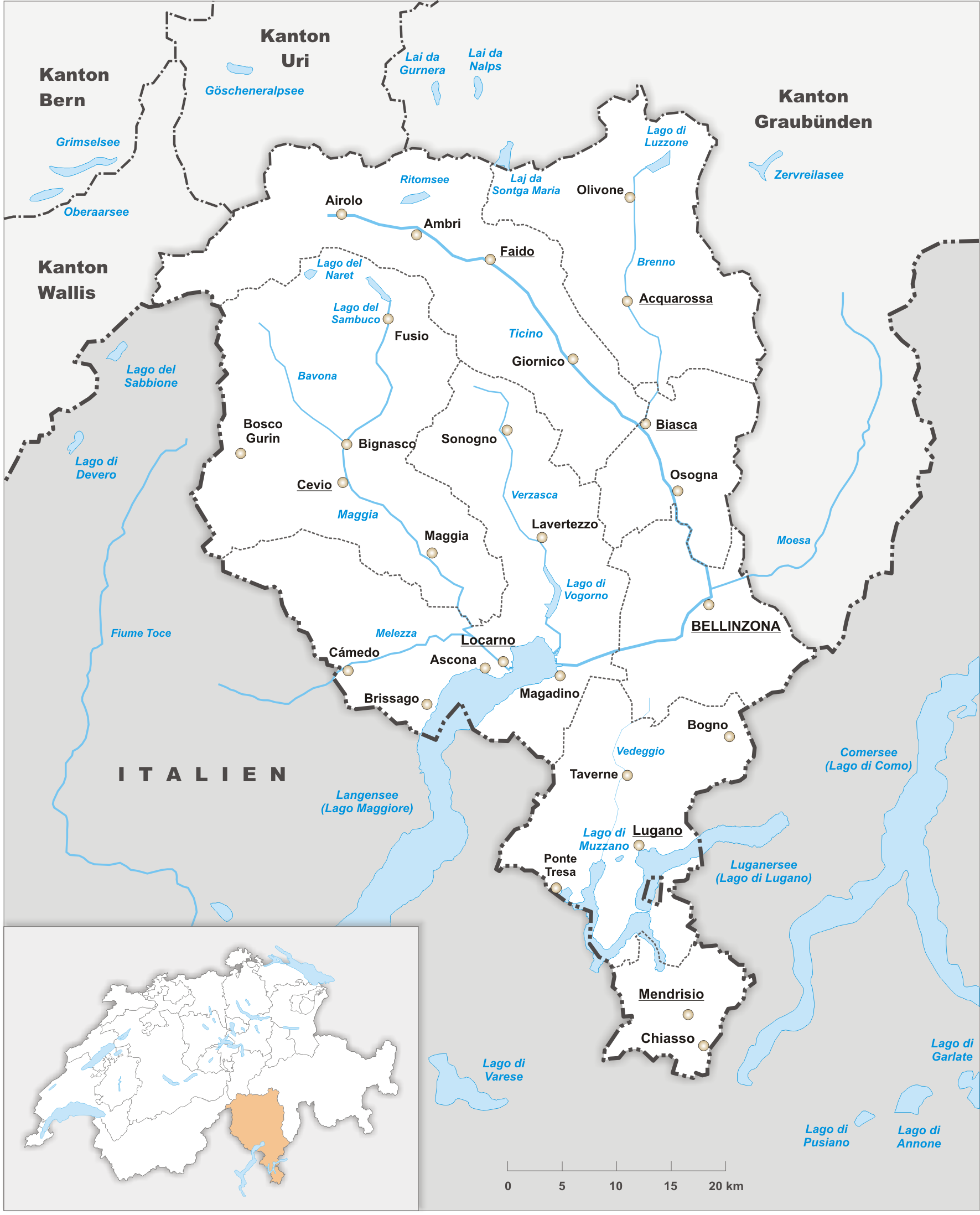
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag. Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps, and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Como
Como (, ; lmo, Còmm, label=Comasco , or ; lat, Novum Comum; rm, Com; french: Côme) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy. It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como. Its proximity to Lake Como and to the Alps has made Como a tourist destination, and the city contains numerous works of art, churches, gardens, museums, theatres, parks, and palaces: the ''Duomo'', seat of the Diocese of Como; the Basilica of Sant'Abbondio; the Villa Olmo; the public gardens with the Tempio Voltiano; the Teatro Sociale; the ''Broletto'' or the city's medieval town hall; and the 20th-century Casa del Fascio. With 215,320 overnight guests in 2013, Como was the fourth-most visited city in Lombardy after Milan, Bergamo, and Brescia. In 2018, Como surpassed Bergamo becoming the third most visited city in Lombardy with 1.4 million arrivals. Como was the birthplace of many historical figures, including the poet Caecilius mentioned by Catullus in the first century BCE, writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascina A Corte
In Italy, cascina a corte (; plural: cascine a corte) refers to a type of rural building traditional of the Po Valley, especially of Lombardy and of some areas of Piedmont and Emilia-Romagna. Also known as ''cascine lombarde'' or just ''cascine'', these buildings are reported in the Po Valley at least since the 16th century, even though they became common in the 18th and 19th centuries. In particular, during the Napoleonic era, a number of religious buildings were confiscated and transformed into ''cascine''. Etymology The term ''cascina'' is attested ever since the Middle Ages, when it was often spelt ''capsina'', ''caxina'' or ''cassina''. The noun seems to be a derivative of Vulgar Latin ''capsia'', meaning "corral", "stockyard" in English, but a common interpretation considers this word as a derivative of Old Italian ''cascio'' (Modern Italian ''cacio''), literally ''cheese'', a clear reference to cascine intended as dairy farms. The first records of farmhouses (then called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bollate
Bollate ( Milanese: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Milan in the Italian region Lombardy, located about northwest of Milan. As of 30 November 2017, it had a population of 36,488. Bollate borders the following municipalities: Paderno Dugnano, Senago, Garbagnate Milanese, Arese, Cormano, Novate Milanese, Baranzate, Milan Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 .... Bollate received the honorary title of city with a presidential decree on October 11, 1984. It is served by Bollate Centro railway station and Bollate Nord railway station. Sights include the historical Villa Arconati. References External links Official website {{Milan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthroponymy
Anthroponymy (also anthroponymics or anthroponomastics, from Ancient Greek ἄνθρωπος ''anthrōpos'' / 'human', and ὄνομα ''onoma'' / 'name') is the study of ''anthroponyms'', the proper names of human beings, both individual and collective. Anthroponymy is a branch of onomastics. Researchers in the field of anthroponymy are called ''anthroponymists''. Since the study of anthroponyms is relevant for several other disciplines within social sciences and humanities, experts from those disciplines engage in anthroponymic studies, including researchers from the fields of anthropology, history, human geography, sociology, prosopography, and genealogy. Anthroponymists are required to follow certain principles, rules and criteria when researching anthroponyms. The methods used for research are divided into two major categories: the collecting of anthroponymic information and the analysis and interpretation of anthroponyms. The collection of anthroponymic information include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
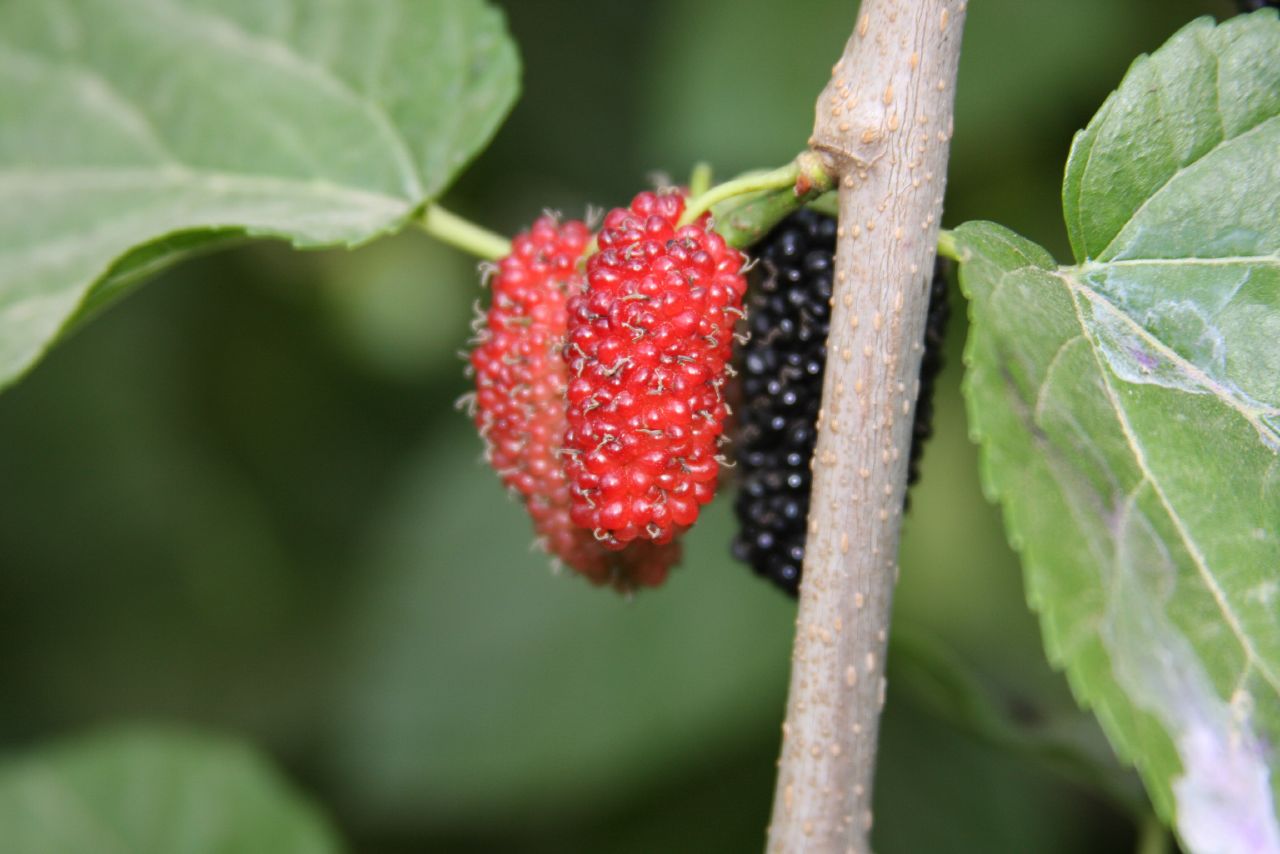
Mulberries
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 identified species, three of which are well-known and are ostensibly named for the fruit color of the best-known cultivar: white, red, and black mulberry (''Morus alba'', '' M. rubra'', and '' M. nigra'', respectively), with numerous cultivars. ''M. alba'' is native to South Asia, but is widely distributed across Europe, Southern Africa, South America, and North America. ''M. alba'' is also the species most preferred by the silkworm, and is regarded as an invasive species in Brazil and the United States. The closely related genus '' Broussonetia'' is also commonly known as mulberry, notably the paper mulberry (''Broussonetia papyrifera''). Description Mulberries are fast-growing when young, and can grow to tall. The leaves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |