|
Aerodynamic Center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magnitude varies with the choice of where the lift is chosen to be applied. The aerodynamic center is the point at which the pitching moment coefficient for the airfoil does not vary with lift coefficient (i.e. angle of attack), making analysis simpler. : =0 where C_L is the aircraft lift coefficient. The lift and drag forces can be applied at a single point, the center of pressure. However, the location of the center of pressure moves significantly with a change in angle of attack and is thus impractical for aerodynamic analysis. Instead the aerodynamic center is used and as a result the incremental lift and drag due to change in angle of attack acting at this point is sufficient to describe the aerodynamic forces acting on the given body. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfoils - Pressure Diagrams
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is a streamlined body that is capable of generating significantly more lift than drag. Wings, sails and propeller blades are examples of airfoils. Foils of similar function designed with water as the working fluid are called hydrofoils. When oriented at a suitable angle, a solid body moving through a fluid deflects the oncoming fluid (for fixed-wing aircraft, a downward force), resulting in a force on the airfoil in the direction opposite to the deflection. This force is known as aerodynamic force and can be resolved into two components: lift (perpendicular to the remote freestream velocity) and drag ( parallel to the freestream velocity). The lift on an airfoil is primarily the result of its angle of attack. Most foil shapes require a positive angle of attack to generate lift, but cambered airfoils can generate lift at zero angle of attack. Airfoils can be designed for use at different speeds by modifying their geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line segment joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil cross section parallel to the direction of the airflow. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the leading edge. L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the main chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil, the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering. "Aeronautical engineering" was the original term for the field. As flight technology advanced to include vehicles operating in outer space, the broader term "aerospace engineering" has come into use. Aerospace engineering, particularly the astronautics branch, is often colloquially referred to as "rocket science". Overview Flight vehicles are subjected to demanding conditions such as those caused by changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature, with structural loads applied upon vehicle components. Consequently, they are usually the products of various technological and engineering disciplines including aerodynamics, air propulsion, avionics, materials science, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joukowsky Transform
In applied mathematics, the Joukowsky transform (sometimes transliterated ''Joukovsky'', ''Joukowski'' or ''Zhukovsky'') is a conformal map historically used to understand some principles of airfoil design. It is named after Nikolai Zhukovsky, who published it in 1910. The transform is : z = \zeta + \frac, where z = x + iy is a complex variable in the new space and \zeta = \chi + i \eta is a complex variable in the original space. In aerodynamics, the transform is used to solve for the two-dimensional potential flow around a class of airfoils known as Joukowsky airfoils. A Joukowsky airfoil is generated in the complex plane (z-plane) by applying the Joukowsky transform to a circle in the \zeta-plane. The coordinates of the centre of the circle are variables, and varying them modifies the shape of the resulting airfoil. The circle encloses the point \zeta = -1 (where the derivative is zero) and intersects the point \zeta = 1. This can be achieved for any allowable centre p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin-airfoil Theory
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is a streamlined body that is capable of generating significantly more lift than drag. Wings, sails and propeller blades are examples of airfoils. Foils of similar function designed with water as the working fluid are called hydrofoils. When oriented at a suitable angle, a solid body moving through a fluid deflects the oncoming fluid (for fixed-wing aircraft, a downward force), resulting in a force on the airfoil in the direction opposite to the deflection. This force is known as aerodynamic force and can be resolved into two components: lift (perpendicular to the remote freestream velocity) and drag ( parallel to the freestream velocity). The lift on an airfoil is primarily the result of its angle of attack. Most foil shapes require a positive angle of attack to generate lift, but cambered airfoils can generate lift at zero angle of attack. Airfoils can be designed for use at different speeds by modifying their ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Static Stability
In flight dynamics, longitudinal stability is the stability of an aircraft in the longitudinal, or pitching, plane. This characteristic is important in determining whether an aircraft pilot will be able to control the aircraft in the pitching plane without requiring excessive attention or excessive strength. The longitudinal stability of an aircraft, also called pitch stability, refers to the aircraft's stability in its plane of symmetry about the lateral axis (the axis along the wingspan). It is an important aspect of the handling qualities of the aircraft, and one of the main factors determining the ease with which the pilot is able to maintain level flight. Longitudinal static stability refers to the aircraft's initial tendency on pitching. Dynamic stability refers to whether oscillations tend to increase, decrease or stay constant. Static stability If an aircraft is longitudinally statically stable, a small increase in angle of attack will create a nose-down pitchin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
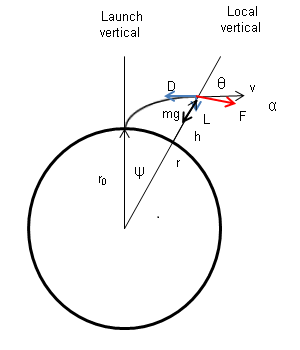
Flight Dynamics
Flight dynamics in aviation and spacecraft, is the study of the performance, stability, and control of vehicles flight, flying through the air or in outer space. It is concerned with how forces acting on the vehicle determine its velocity and attitude with respect to time. For a fixed-wing aircraft, its changing Orientation (geometry), orientation with respect to the local air flow is represented by two critical angles, the angle of attack of the wing ("alpha") and the angle of attack of the vertical tail, known as the slip (aerodynamics), sideslip angle ("beta"). A sideslip angle will arise if an aircraft yaws about its centre of gravity and if the aircraft sideslips bodily, i.e. the centre of gravity moves sideways.Flightwise - Volume 2 - Aircraft Stability And Control, Chris Carpenter 1997, Airlife Publishing Ltd., , p.145 These angles are important because they are the principal source of changes in the aerodynamic forces and moments applied to the aircraft. Spacecraft fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Flight Mechanics
Aircraft flight mechanics are relevant to fixed wing ( gliders, aeroplanes) and rotary wing (helicopters) aircraft. An aeroplane (''airplane'' in US usage), is defined in ICAO Document 9110 as, "a power-driven heavier than air aircraft, deriving its lift chiefly from aerodynamic reactions on surface which remain fixed under given conditions of flight". Note that this definition excludes both dirigibles (because they derive lift from buoyancy rather than from airflow over surfaces), and ballistic rockets (because their lifting force is typically derived directly and entirely from near-vertical thrust). Technically, both of these could be said to experience "flight mechanics" in the more general sense of physical forces acting on a body moving through air; but they operate very differently, and are normally outside the scope of this term. Take-off A heavier-than-air craft (aircraft) can only fly if a series of aerodynamic forces come to bear. In regard to fixed wing aircraft, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Pressure
In fluid dynamics, dynamic pressure (denoted by or and sometimes called velocity pressure) is the quantity defined by:Clancy, L.J., ''Aerodynamics'', Section 3.5 :q = \frac\rho\, u^2 where (in SI units): * is the dynamic pressure in pascals (i.e., N/ m2), * (Greek letter rho) is the fluid mass density (e.g. in kg/m3), and * is the flow speed in m/s. It can be thought of as the fluid's kinetic energy per unit volume. For incompressible flow, the dynamic pressure of a fluid is the difference between its total pressure and static pressure. From Bernoulli's law, dynamic pressure is given by : p_0 - p_\text = \frac\rho\, u^2 where and are the total and static pressures, respectively. Physical meaning Dynamic pressure is the kinetic energy per unit volume of a fluid. Dynamic pressure is one of the terms of Bernoulli's equation, which can be derived from the conservation of energy for a fluid in motion. At a stagnation point the dynamic pressure is equal to the difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Static Stability
In flight dynamics, longitudinal stability is the stability of an aircraft in the longitudinal, or pitching, plane. This characteristic is important in determining whether an aircraft pilot will be able to control the aircraft in the pitching plane without requiring excessive attention or excessive strength. The longitudinal stability of an aircraft, also called pitch stability, refers to the aircraft's stability in its plane of symmetry about the lateral axis (the axis along the wingspan). It is an important aspect of the handling qualities of the aircraft, and one of the main factors determining the ease with which the pilot is able to maintain level flight. Longitudinal static stability refers to the aircraft's initial tendency on pitching. Dynamic stability refers to whether oscillations tend to increase, decrease or stay constant. Static stability If an aircraft is longitudinally statically stable, a small increase in angle of attack will create a nose-down pitchin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aircraft)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line segment joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil cross section parallel to the direction of the airflow. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the leading edge. L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the main chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil, the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Pressure (fluid Mechanics)
In fluid mechanics, the center of pressure is the point on a body where a single force acting at that point can represent the total effect of the pressure field acting on the body. The total force vector acting at the center of pressure is the surface integral of the pressure vector field across the surface of the body. The resultant force and center of pressure location produce an equivalent force and moment on the body as the original pressure field. Pressure fields occur in both static and dynamic fluid mechanics. Specification of the center of pressure, the reference point from which the center of pressure is referenced, and the associated force vector allows the moment generated about any point to be computed by a translation from the reference point to the desired new point. It is common for the center of pressure to be located on the body, but in fluid flows it is possible for the pressure field to exert a moment on the body of such magnitude that the center of press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |