|
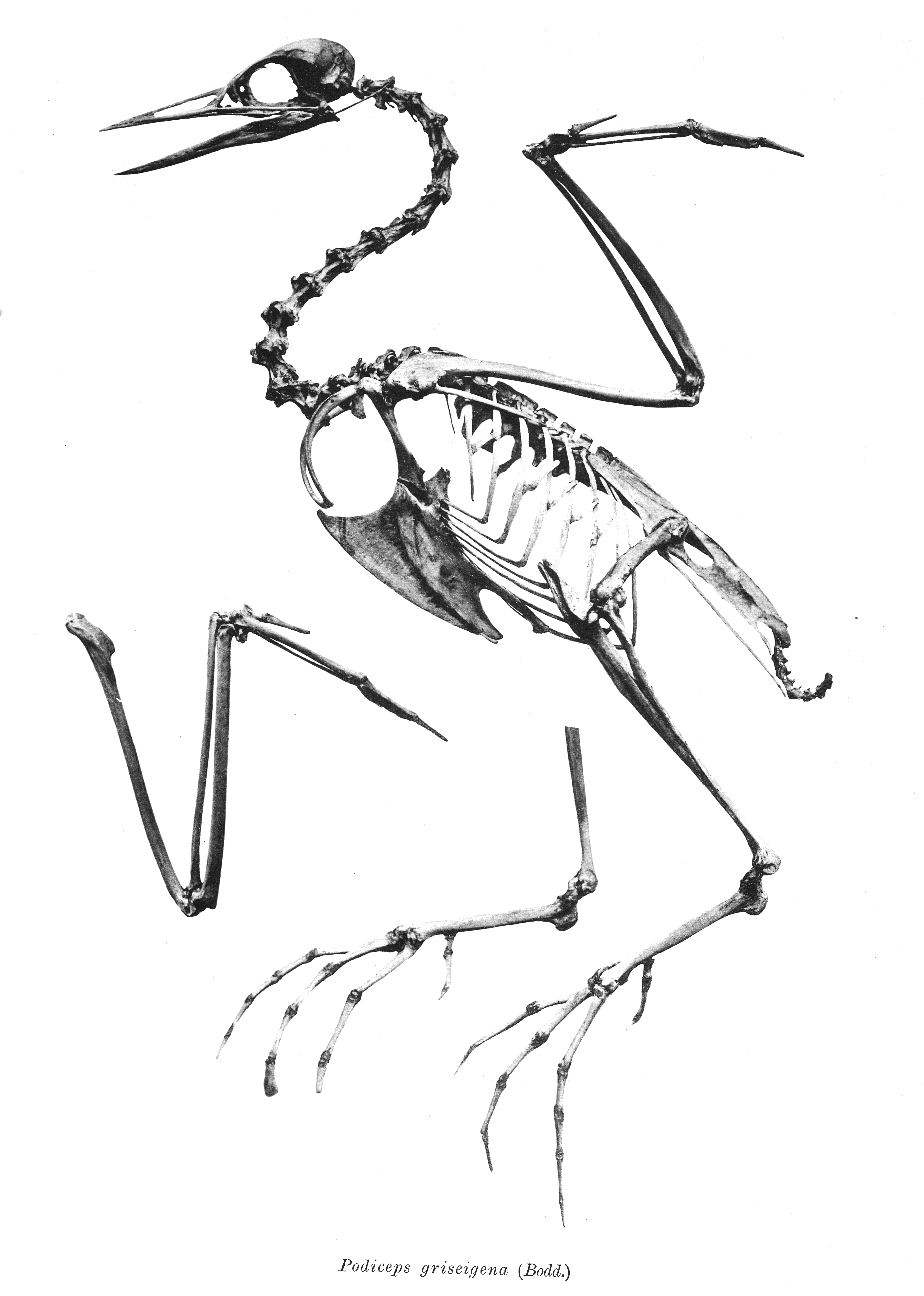
Aechmophorus Elasson
''Aechmophorus elasson'' is an extinct species of grebe recovered from the Piacenzian age of the United States. History The specimens were collected in the summer of 1962 from Idaho, United States by Claude W. Hibbard and the species was named in 1967 by Bertram G. Murray. Material was later described from California, United States by Robert M. Chandler (1990). Description The material overall resembles those of extant species of ''Aechmophorus'', although slightly smaller in dimensions. The holotype are the distal end of the humerus and a slightly worn left ulna. Other referred material from the Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument include several fragmentary remains of the humeri, ulnae and a proximal of a tarsometatarsus, as well as two complete and two distal portions of coracoids. Murrary (1967) did not provide a detailed osteological diagnosis on the Idaho material. Chandler (1990) would provide one for both the Idaho and California specimens. The California material in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order (biology), order Podicipediformes (). Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in sea, marine habitats during Bird migration, migration and winter. Most grebes fly, although some flightless species exist, most notably in stable lakes. The order contains a single family (biology), family, the Podicipedidae, which includes 22 species in six extant genus, genera. Although, superficially, they resemble other diving birds such as loons and coots, they are most closely related to flamingos, as supported by morphology (biology), morphological, molecular and paleontology, paleontological data. Many species are monogamy in animals, monogamous and are known for their courtship displays, with the pair performing synchronized dances across the water's surface. The birds build floating vegetative nests where they lay several eggs. About a third of the world's grebes are listed at various levels of conservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibiotarsus
The tibiotarsus is the large bone between the femur and the tarsometatarsus in the leg of a bird. It is the fusion of the proximal part of the tarsus with the tibia. A similar structure also occurred in the Mesozoic Heterodontosauridae. These small ornithischian dinosaurs were unrelated to birds and the similarity of their foot bones is best explained by convergent evolution. See also * Bird anatomy References * Proctor, Nobel S. ''Manual of Ornithology: Avian Structure and Function''. Yale University Press Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day and Clarence Day, grandsons of Benjamin Day, and became a department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and ope .... (1993) Bird anatomy Dinosaur anatomy {{ornithology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1967
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Diego Formation
The San Diego Formation is a geological formation in southwestern San Diego County, California, United States, and northwestern Baja California, Mexico. Geology It is a coastal transitional marine and non-marine pebble and cobble conglomerate deposit and marine sandstone rock with marine fossils, from a former bay, deposited during the Middle Pliocene to Late Pliocene ages (2–3 million years ago), of the Pliocene period during the Cenozoic Era. This formation is found from the south side of Mount Soledad in San Diego County to Rosarito Beach in northern Baja California, including Tijuana, Mexico, and the southwestern corner of San Diego County from San Ysidro to Pacific Beach. San Diego Formation deposits were formed in a large, open, crescent-shaped bay similar in size to Monterey Bay that existed on the coast in Pliocene times. Aquifer The formation contains the San Diego Formation Basin, a large aquifer under Imperial Beach, Chula Vista, National City, and souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenns Ferry Formation
The Glenns Ferry Formation is a Pliocene stratigraphic unit in the western United States. Outcrops of the formation in Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument preserve the remains of seven fish species, five of which are extinct. These include the teleosteans '' Mylopharodon hagermanensis'', '' Sigmopharyngodon idahoensis'', and '' Ptychocheilus oregonensis'', '' Ameirurus vespertinus'', and the sunfish '' Archoplites taylori''. A nearly complete skull of the catfish '' Ameirurus vespertinus'' was recovered in 2001 from the wall of the Smithsonian Horse Quarry. The formation was deposited by Lake Idaho. References References *Hunt, ReBecca K., Vincent L. Santucci and Jason Kenworthy. 2006. "A preliminary inventory of fossil fish from National Park Service units." in S.G. Lucas, J.A. Spielmann, P.M. Hester, J.P. Kenworthy, and V.L. Santucci (ed.s), Fossils from Federal Lands. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science The New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Grebe
The western grebe (''Aechmophorus occidentalis'') is a species in the grebe family of water birds. Folk names include "dabchick", "swan grebe" and "swan-necked grebe". Western grebe fossils from the Late Pleistocene of southwest North America were described as a distinct species, but later ranked as a paleosubspecies ''Aechmophorus occidentalis lucasi''. More recent study found them to fall within the variation now known to exist in today's birds. Description The western grebe is the largest North American grebe. It is long, weighs and measures across the wings.''CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses'' by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), .Burnie D and Wilson DE (Eds.), ''Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife''. DK Adult (2005), It is black-and-white, with a long, slender, swan-like neck and red eyes. It is easily confused with Clark's grebe, which shares similar features, body size, behavior and habitat, and hybrids are known. Western grebes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clark's Grebe
Clark's grebe (''Aechmophorus clarkii'') is a North American waterbird species in the grebe family. Until the 1980s, it was thought to be a pale morph of the western grebe, which it resembles in size, range, and behavior. Intermediates between the two species are known. This species nests on large inland lakes in western North America and migrates to the Pacific coast over the winter. It maintains local populations year-round in California, Nevada, and Arizona (the Lower Colorado River Valley), as well as in central Mexico. It feeds by diving for insects, polychaete worms, crustaceans, and salamanders. It performs the same elaborate courtship display as the western grebe. Etymology and common names The "Clark" of its common name—and its specific epithet ''clarkii''—honors John Henry Clark, a 19th-century American surveyor who was also a naturalist and collector. The genus name ''Aechmophorus'' comes from the Ancient Greek words αἰχμά (transliterated "aichme"), m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid
A coracoid is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is not homologous with the coracoid bone of most other vertebrates. In other tetrapods, it joins the scapula to the front end of the sternum and has a notch on the dorsal surface which, along with a similar notch on the ventral surface of the scapula, forms the socket in which the proximal end of the humerus (upper arm bone) is located. The acrocoracoid process is an expansion adjacent to this contact surface, to which the shoulderward end of the biceps brachii muscle attaches in these animals. In birds (and generally theropods and related animals), the entire unit is rigid and called scapulocoracoid. This plays a major role in bird flight. In other dinosaurs, the main bones of the pectoral girdle were the scapula (shoulder blade) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piacenzian
The Piacenzian is in the international geologic time scale the upper stage (stratigraphy), stage or latest age (geology), age of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 3.6 ± 0.005 year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma and 2.58 Ma (million years ago). The Piacenzian is after the Zanclean and is followed by the Gelasian (part of the Pleistocene). The Piacenzian is roughly coeval with the European land mammal age MN 16, overlaps the late Chapadmalalan and early Uquian South American land mammal age and falls inside the more extensive Blancan North American land mammal age. It also correlates with the Astian, Redonian, Reuverian and Romanian regional stages of Europe, and the Waipipian and Mangapanian stages of New Zealand geologic time scale, New Zealand. Some authorities describe the British Red Crag Formation and Waltonian Stage as late Piacenzian, while others regard them as early Pleistocene. Carbon dioxide levels during the Piacenzian were similar to those of today, making this age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bird bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and metatarsal bones (foot). Despite this, the tarsometatarsus of flying types is often referred to as just the shank, tarsus or metatarsus. Tarsometatarsal fusion occurred in several ways and extents throughout bird evolution. Paticularly, in Neornithes (modern birds), although the bones are joined along their entire length, the fusion is most thorough at the distal (metatarsal) end. In the Enantiornithes, a group of Mesozoic avialans, the fusion was complete at the proximal (tarsal) end, but the distal metatarsi were still partially distinct. While these fused bones are best known from birds and their relatives, avians are neither the only group nor the first to possess tarsometatarsi. In a remarkable case of parallel evolution, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument
Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument is a Pliocene-age site near Hagerman, Idaho, Hagerman, Idaho. The Monument is internationally significant because it protects one of the richest known fossil deposits from the Blancan North American Land Mammal Age. These fossils date from 3.07 million to at least 4 million years ago in age and represent at least 200 species. Hagerman is best known for having the largest known concentration of the fossil Hagerman horse, ''Equus simplicidens''. The fossil beds, including the historic Smithsonian Horse Quarry, were designated a National Natural Landmark in 1975 and was reclassified as a National monument (United States), National Monument in 1988. In 2014, Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument joined Sibiloi National Park in Kenya as "sister parks" through a memorandum of understanding between the National Park Service and Office of International Affairs, the National Museums of Kenya, and Kenya Wildlife Service. A fundraising campaign at Hag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |