|
Advanced Simulation Library
Advanced Simulation Library (ASL) is free and open-source hardware-accelerated multiphysics simulation platform. It enables users to write customized numerical solvers in C++ and deploy them on a variety of massively parallel architectures, ranging from inexpensive FPGAs, DSPs and GPUs up to heterogeneous clusters and supercomputers. Its internal computational engine is written in OpenCL and utilizes matrix-free solution techniques. ASL implements variety of modern numerical methods, i.a. level-set method, lattice Boltzmann, immersed Boundary. Mesh-free, immersed boundary approach allows users to move from CAD directly to simulation, reducing pre-processing efforts and number of potential errors. ASL can be used to model various coupled physical and chemical phenomena, especially in the field of computational fluid dynamics. It is distributed under the free GNU Affero General Public License with an optional commercial license (which is based on the permissive MIT License ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft ( Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE (HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the " Unix philosophy". According to this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiphysics
In computational modelling, multiphysics simulation (often shortened to simply "multiphysics") is defined as the simultaneous simulation of different aspects of a physical system or systems and the interactions among them. For example, simultaneous simulation of the physical stress on an object, the temperature distribution of the object and the thermal expansion which leads to the variation of the stress and temperature distributions would be considered a multiphysics simulation. Multiphysics simulation is related to multiscale simulation, which is the simultaneous simulation of a single process on either multiple time or distance scales. As an interdisciplinary field, multiphysics simulation can span many science and engineering disciplines. Simulation methods frequently include numerical analysis, partial differential equations and tensor analysis. Multiphysics simulation process The implementation of a multiphysics simulation follows a typical series of steps: * Identify th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Space Exploration
Design Space Exploration (DSE) refers to systematic analysis and pruning of unwanted design points based on parameters of interest. While the term DSE can apply to any kind of system, we refer to electronic and embedded system design in this article. Given the complex specification of electronic systems and the plethora of design choices ranging from the choice of components, number of components, operating modes of each of the components, connections between the components, choice of algorithm, etc.; design decisions need to be based on a systematic exploration process. However, the exploration process is complex because of a variety of ways in which the same functionality can be implemented. A tradeoff analysis between each of the implementation option based on a certain parameter of interest forms the basis of DSE. The parameter of interest could vary across systems, but the commonly used parameters are power, performance, and cost. Additional factors like size, shape, weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidisciplinary Design Optimization
Multi-disciplinary design optimization (MDO) is a field of engineering that uses optimization methods to solve design problems incorporating a number of disciplines. It is also known as multidisciplinary system design optimization (MSDO), and Multidisciplinary Design Analysis and Optimization (MDAO). MDO allows designers to incorporate all relevant disciplines simultaneously. The optimum of the simultaneous problem is superior to the design found by optimizing each discipline sequentially, since it can exploit the interactions between the disciplines. However, including all disciplines simultaneously significantly increases the complexity of the problem. These techniques have been used in a number of fields, including automobile design, naval architecture, electronics, architecture, computers, and electricity distribution. However, the largest number of applications have been in the field of aerospace engineering, such as aircraft and spacecraft design. For example, the propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Validation And Reconciliation
Industrial process data validation and reconciliation, or more briefly, process data reconciliation (PDR), is a technology that uses process information and mathematical methods in order to automatically ensure data validation and reconciliation by correcting measurements in industrial processes. The use of PDR allows for extracting accurate and reliable information about the state of industry processes from raw measurement data and produces a single consistent set of data representing the most likely process operation. Models, data and measurement errors Industrial processes, for example chemical or thermodynamic processes in chemical plants, refineries, oil or gas production sites, or power plants, are often represented by two fundamental means: # Models that express the general structure of the processes, # Data that reflects the state of the processes at a given point in time. Models can have different levels of detail, for example one can incorporate simple mass or compound con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Sensing
Virtual sensing techniques, also called soft sensing, proxy sensing, inferential sensing, or surrogate sensing, are used to provide feasible and economical alternatives to costly or impractical physical measurement instrument A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Establi .... A virtual sensing system uses information available from other measurements and process parameters to calculate an estimate of the quantity of interest. In the field of gas sensors, an array of virtual sensors Benefits of virtual sensors for air quality monitoring in humid conditions can substitute electronic noses. Virtual gas sensors can be obtained by using a single sensor working in dynamic mode, i.e., working in repeated cycles that include a customized range of temperature, voltage, or both, which is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-assisted Surgery
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for surgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions. CAS is also known as computer-aided surgery, computer-assisted intervention, image-guided surgery, digital surgery and surgical navigation, but these are terms that are more or less synonymous with CAS. CAS has been a leading factor in the development of robotic surgery. General principles Creating a virtual image of the patient The most important component for CAS is the development of an accurate model of the patient. This can be conducted through a number of medical imaging technologies including CT, MRI, x-rays, ultrasound plus many more. For the generation of this model, the anatomical region to be operated has to be scanned and uploaded into the computer system. It is possible to employ a number of scanning methods, with the datasets combined through data fusion techniques. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khronos Group
The Khronos Group, Inc. is an open, non-profit, member-driven consortium of 170 organizations developing, publishing and maintaining royalty-free interoperability standards for 3D graphics, virtual reality, augmented reality, parallel computation, vision acceleration and machine learning. The open standards and associated conformance tests enable software applications and middleware to effectively harness authoring and accelerated playback of dynamic media across a wide variety of platforms and devices. The group is based in Beaverton, Oregon. History The Khronos Group was founded in 2000 by companies including 3Dlabs, ATI, Discreet, Evans & Sutherland, Intel, SGI, and Sun Microsystems. Promoter members include AMD, Apple, Arm, Epic Games, Google, Huawei, Nokia, Imagination, intel, NVIDIA, Qualcomm, Samsung, Sony, Valve and Verisilcon. Its president is Neil Trevett. Exploratory groups Typically, Khronos first creates an exploratory group to gauge industry interest be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the free-stream flow of the fluid, and the interaction of the fluid ( liquids and gases) with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved, and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial validation of such software is typically performed using experimental apparatus such as wind tunnels. In addition, previously performed analytical or empirical analysis of a particular problem can be used for comparison. A final validation is often performed using full-scale testing, such as flight tests. CFD is appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meshfree Methods
In the field of numerical analysis, meshfree methods are those that do not require connection between nodes of the simulation domain, i.e. a mesh, but are rather based on interaction of each node with all its neighbors. As a consequence, original extensive properties such as mass or kinetic energy are no longer assigned to mesh elements but rather to the single nodes. Meshfree methods enable the simulation of some otherwise difficult types of problems, at the cost of extra computing time and programming effort. The absence of a mesh allows Lagrangian simulations, in which the nodes can move according to the velocity field. Motivation Numerical methods such as the finite difference method, finite-volume method, and finite element method were originally defined on meshes of data points. In such a mesh, each point has a fixed number of predefined neighbors, and this connectivity between neighbors can be used to define mathematical operators like the derivative. These operators are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immersed Boundary Method
In computational fluid dynamics, the immersed boundary method originally referred to an approach developed by Charles Peskin in 1972 to simulate fluid-structure (fiber) interactions. Treating the coupling of the structure deformations and the fluid flow poses a number of challenging problems for numerical simulations (the elastic boundary changes the flow of the fluid and the fluid moves the elastic boundary simultaneously). In the immersed boundary method the fluid is represented in an Eulerian coordinate system and the structure is represented in Lagrangian coordinates. For Newtonian fluids governed by the Navier–Stokes equations, the fluid equations are : \rho \left(\frac + \cdot\nabla\right) = -\nabla p + \mu\, \Delta u(x,t) + f(x,t) and if the flow is incompressible, we have the further condition that : \nabla \cdot u = 0. \, The immersed structures are typically represented as a collection of one-dimensional fibers, denoted by \Gamma . Each fiber can be viewed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
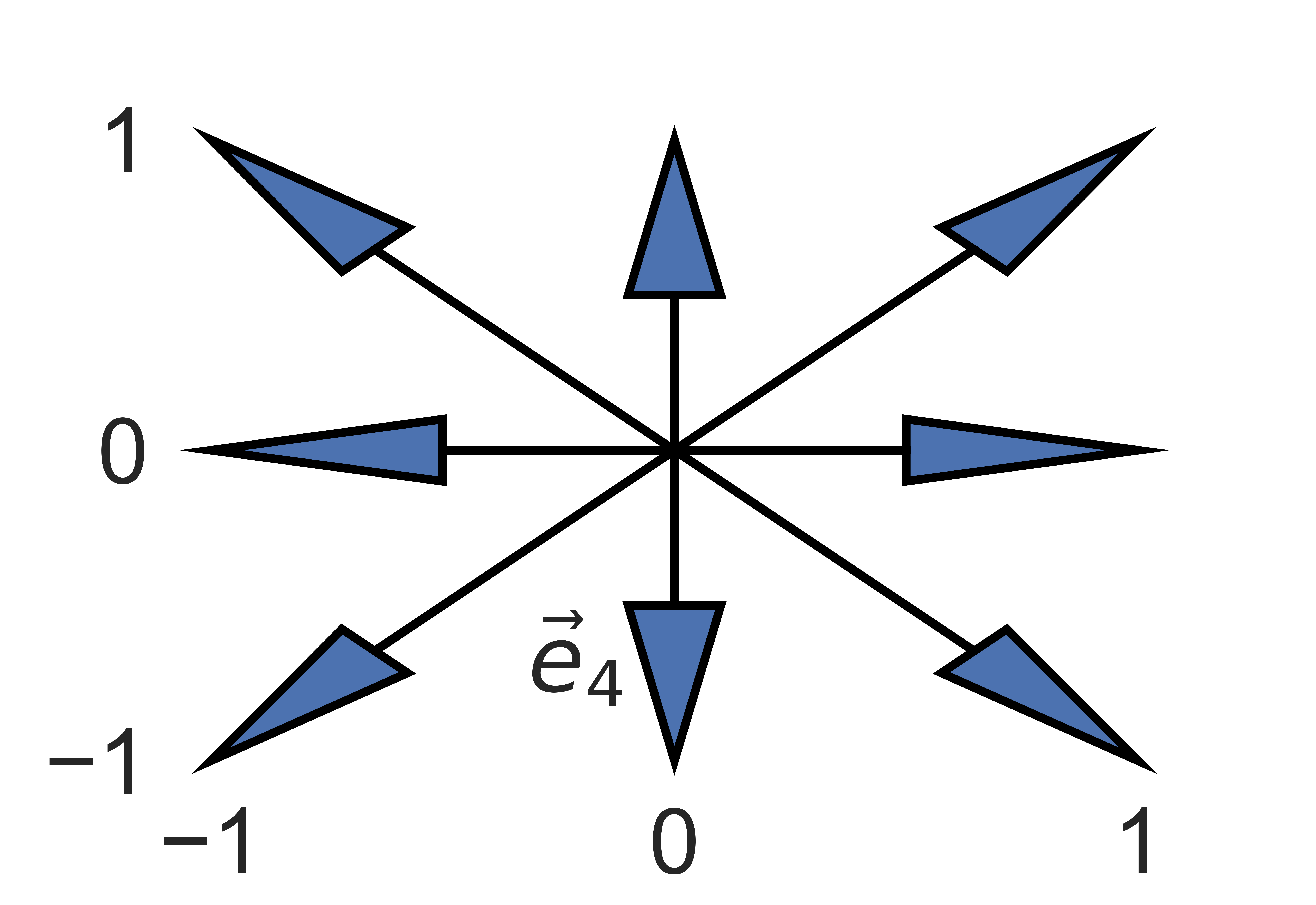
Lattice Boltzmann Methods
The lattice Boltzmann methods (LBM), originated from the lattice gas automata (LGA) method (Hardy- Pomeau-Pazzis and Frisch- Hasslacher- Pomeau models), is a class of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methods for fluid simulation. Instead of solving the Navier–Stokes equations directly, a fluid density on a lattice is simulated with streaming and collision (relaxation) processes. The method is versatile as the model fluid can straightforwardly be made to mimic common fluid behaviour like vapour/liquid coexistence, and so fluid systems such as liquid droplets can be simulated. Also, fluids in complex environments such as porous media can be straightforwardly simulated, whereas with complex boundaries other CFD methods can be hard to work with. Algorithm Unlike CFD methods that solve the conservation equations of macroscopic properties (i.e., mass, momentum, and energy) numerically, LBM models the fluid consisting of fictive particles, and such particles perform consecutive propag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |