|
Advanced Chemistry Development
Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., (ACD/Labs) specializes in the design of software, with a focus on the R&D and chemistry of molecules ('small molecules'). ACD/Labs provides solutions for the enterprise in varied areas, including analytical data handling and knowledge management; in addition, molecular property modelling and property-based design are relevant areas of expertise in ACD Labs. Location The company is headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada with direct sales offices in the UK, Germany, France, China, and India. The distribution channel extends throughout Europe to Australia, S. America, and Africa. History ACD/Labs was founded in 1994 as a private company. The intention was to monetize the experience of an international team of scientists specializing in quantitative structure-property relationships, such as NMR spectra and various physico-chemical properties, such as pKa, logP, logD, boiling point, vapor pressure. Early on the development focused on predictor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Private Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in the respective listed markets, but rather the company's stock is offered, owned, traded, exchanged privately, or over-the-counter. In the case of a closed corporation, there are a relatively small number of shareholders or company members. Related terms are closely-held corporation, unquoted company, and unlisted company. Though less visible than their publicly traded counterparts, private companies have major importance in the world's economy. In 2008, the 441 largest private companies in the United States accounted for ($1.8 trillion) in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In 2005, using a substantially smaller pool size (22.7%) for comparison, the 339 companies on '' Forbes'' survey of closely held U.S. businesses sold a trillion dollars' worth of goods and services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mass Spectra
A mass spectrum is a histogram plot of intensity vs. ''mass-to-charge ratio'' (''m/z'') in a chemical sample, usually acquired using an instrument called a ''mass spectrometer''. Not all mass spectra of a given substance are the same; for example, some mass spectrometers break the analyte molecules into '' fragments''; others observe the intact molecular masses with little fragmentation. A mass spectrum can represent many different types of information based on the type of mass spectrometer and the specific experiment applied. Common fragmentation processes for organic molecules are the '' McLafferty rearrangement'' and '' alpha cleavage''. Straight chain alkanes and alkyl groups produce a typical series of peaks: 29 (CH3CH2+), 43 (CH3CH2CH2+), 57 (CH3CH2CH2CH2+), 71 (CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2+) etc. X-axis: ''m/z'' (mass-to-charge ratio) The x-axis of a mass spectrum represents a relationship between the mass of a given ion and the number of elementary charges that it carries. This is writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemical methods and modern, instrumental methods. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as precipitation, extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Instrumental methods may be used to separate samples using chromatography, electrophoresis or field flow fractionation. Then qualitative and quantitative analysis can be performed, often with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Scientific Data Management System
Laboratory informatics is the specialized application of information technology aimed at optimizing and extending laboratory operations. It encompasses data acquisition (e.g. through sensors and hardware or voice), instrument interfacing, laboratory networking, data processing, specialized data management systems (such as a chromatography data system), a laboratory information management system, scientific data management (including data mining and data warehousing), and knowledge management (including the use of an electronic lab notebook). It has become more prevalent with the rise of other "informatics" disciplines such as bioinformatics, cheminformatics and health informatics. Several graduate programs are focused on some form of laboratory informatics, often with a clinical emphasis. A closely related - some consider subsuming - field is laboratory automation. Capability Areas In the context of Public Health Laboratories, the Association of Public Health Laboratories has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
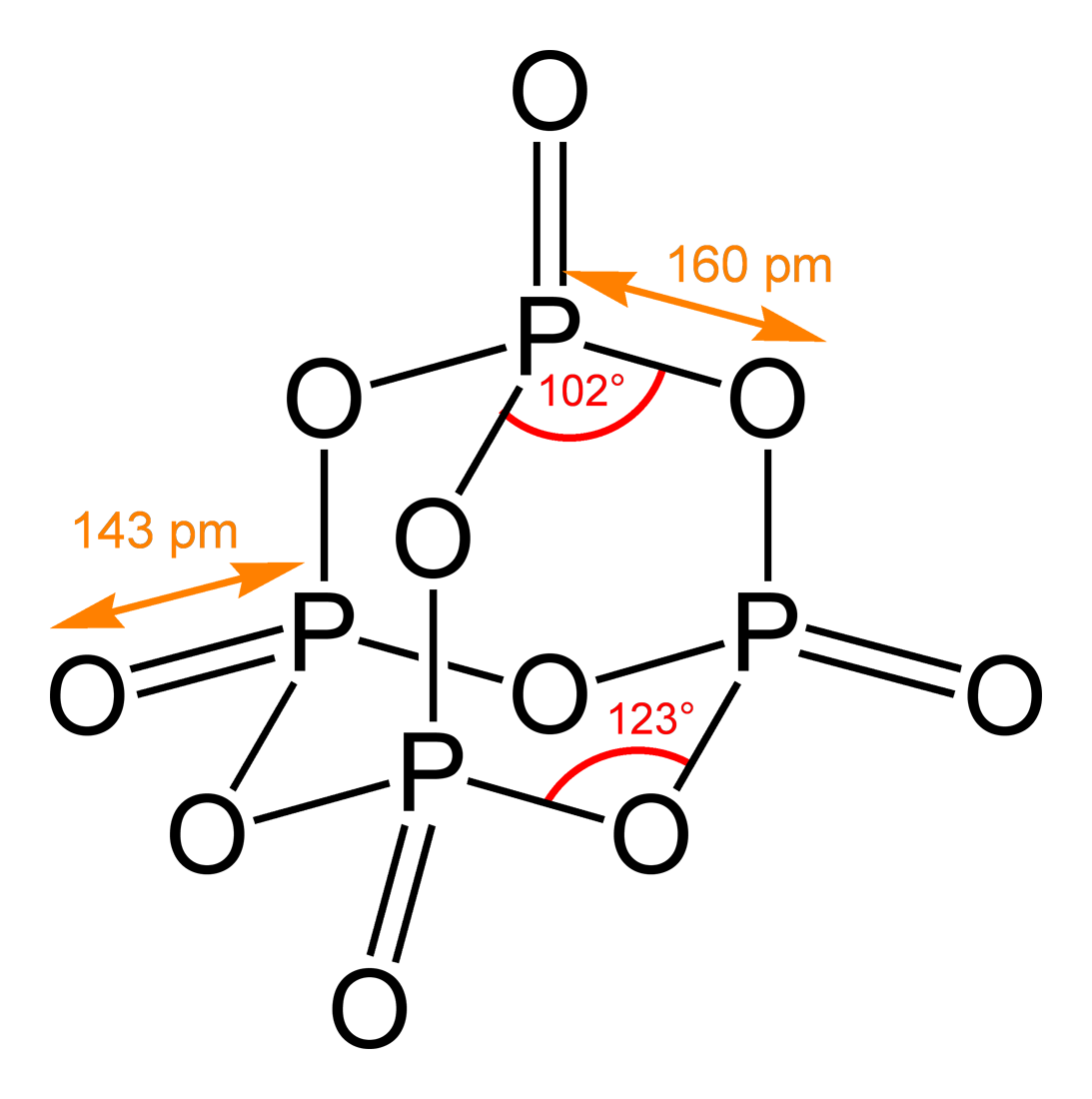 |
Structural Elucidation
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite order de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Drug Design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
ADME
ADME is an abbreviation in pharmacokinetics and pharmacology for " absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion", and describes the disposition of a pharmaceutical compound within an organism. The four criteria all influence the drug levels and kinetics of drug exposure to the tissues and hence influence the performance and pharmacological activity of the compound as a drug. Sometimes, liberation and/or toxicity are also considered, yielding LADME, ADMET, or LADMET. Components Absorption/administration For a compound to reach a tissue, it usually must be taken into the bloodstream – often via mucous surfaces like the digestive tract ( intestinal absorption) – before being taken up by the target cells. Factors such as poor compound solubility, gastric emptying time, intestinal transit time, chemical instability in the stomach, and inability to permeate the intestinal wall can all reduce the extent to which a drug is absorbed after oral administration. Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Optical Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada and the List of North American cities by population, fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multiculturalism, multicultural and cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with Toronto ravine system, rivers, deep ravines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Partition Coefficient
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (''P'') or distribution coefficient (''D'') is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a comparison of the solubilities of the solute in these two liquids. The partition coefficient generally refers to the concentration ratio of un-ionized species of compound, whereas the distribution coefficient refers to the concentration ratio of all species of the compound (ionized plus un-ionized). In the chemical and pharmaceutical sciences, both phases usually are solvents. Most commonly, one of the solvents is water, while the second is hydrophobic, such as 1-octanol. Hence the partition coefficient measures how hydrophilic ("water-loving") or hydrophobic ("water-fearing") a chemical substance is. Partition coefficients are useful in estimating the distribution of drugs within the body. Hydrophobic drugs with high octanol-water partition coefficients are ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Acid Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted ) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction :HA A^- + H^+ known as dissociation in the context of acid–base reactions. The chemical species HA is an acid that dissociates into , the conjugate base of the acid and a hydrogen ion, . The system is said to be in equilibrium when the concentrations of its components will not change over time, because both forward and backward reactions are occurring at the same rate. The dissociation constant is defined by :K_\text = \mathrm, or :\mathrmK_\ce = - \log_ K_\text = \log_\frac where quantities in square brackets represent the concentrations of the species at equilibrium. Theoretical background The acid dissociation constant for an acid is a direct consequence of the underlying thermodynamics of the dissociation reaction; the p'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |