|
Adolph Englemann
Adolph Engelmann (February 11, 1825 – October 5, 1890) was a farmer, lawyer, postmaster, Mexican–American War veteran, and Union Army colonel during the American Civil War. On May 18, 1866, the United States Senate confirmed his appointment as brevet brigadier general of volunteers. Biography Engelmann was born in Imsbach, then in the Kingdom of Bavaria, on February 11, 1825.Eicher, John H., and David J. Eicher, ''Civil War High Commands''. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 2001. . p. 227.Hunt, Roger D. and Brown, Jack R., ''Brevet Brigadier Generals in Blue''. Olde Soldier Books, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD, 1990. . p. 194. His family immigrated to the United States in 1831. He served as a second lieutenant in the 2nd Regiment of Illinois Volunteers (12 months) during the Mexican–American War.Elliott, Isaac H.; Illinois Adjutant General's Office ''Record of the Services of Illinois Soldiers in the Black Hawk War, 1831–32, and in the Mexican War, 1846-8'' Springfield, IL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imsbach
Imsbach is a municipality in the Donnersbergkreis district, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... References Municipalities in Rhineland-Palatinate Donnersbergkreis {{Donnersbergkreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Schleswig War
The First Schleswig War (), also known as the Schleswig-Holstein uprising () and the Three Years' War (), was a military conflict in southern Denmark and northern Germany rooted in the Schleswig–Holstein question: who should control the Duchies of Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg, which at the time were ruled by the king of Denmark in a personal union. Ultimately, the Danish side proved victorious with the diplomatic support of the great powers, especially Britain and Russia, since the duchies were close to an important Baltic seaway connecting both powers. While Schleswig had been predominantly Danish with a German elite concentrated in the cities and estates, modernization brought extensive German influence. German became the language of administration, education, and the church, creating an environment in which it was omnipresent and speaking Danish offered no advantages. Due to top-down pressure, many Danish South Schleswigers gradually adopted German in their dai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Vicksburg
The siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Major General Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Mississippi, led by Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton, into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading to the successful siege and Confederate surrender. Vicksburg was the last major Confederate stronghold on the Mississippi River; therefore, capturing it completed the second part of the Northern strategy, the Anaconda Plan. When two major assaults against the Confederate fortifications, on May 19 and 22, were repulsed with heavy casualties, Grant decided to besiege the city beginning on May 25. After holding out for more than 40 days, with their supplies nearly gone, the garrison surrendered on July 4. The Vicksburg campaign's successfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Raith
Julius Raith (March 29, 1819 – April 11, 1862) was a German-American military officer who served in the American Civil War and the Mexican–American War. He was mortally wounded at the Battle of Shiloh. Born in Göttingen, Hanover, Raith came to the United States in 1836 with his family, settling in St. Clair County, Illinois. During the Mexican–American War, he led a company of 2nd Illinois Volunteers. When the Civil War broke out, he helped Gustave Koerner organize a German regiment. During the Battle of Shiloh, he led a brigade in General McClernand's division composed of his own regiment, the 43rd Illinois along with the 17th Illinois, the 29th Illinois, and the 49th Illinois. The actual commanding officer was Colonel Leonard Fulton Ross, who was absent, leaving Colonel James S. Reardon in charge; however, Reardon was ill. Raith was wounded by a minie ball in the leg above the knee and laid on the battlefield for 24 hours. He died of tetanus from his injuries. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Shiloh
The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the American Civil War fought on April 6–7, 1862. The fighting took place in southwestern Tennessee, which was part of the war's Western Theater of the American Civil War, Western Theater. The battlefield is located between a small, undistinguished church named Shiloh, Hardin County, Tennessee, Shiloh and Pittsburg Landing, Tennessee, Pittsburg Landing on the Tennessee River. Two Union Army, Union armies combined to defeat the Confederate States Army, Confederate Army of Mississippi. Major general (United States), Major General Ulysses S. Grant was the Union commander, while General officers in the Confederate States Army#General, General Albert Sidney Johnston was the Confederate commander until his battlefield death, when he was replaced by his second-in-command, General P. G. T. Beauregard. The Confederate army hoped to defeat Grant's Army of the Tennessee before it could be reinforce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulysses S
Ulysses is the Latin Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ... name for Odysseus, a legendary Greek hero recognized for his intelligence and cunning. He is famous for his long, adventurous journey home to Ithaca after the Trojan War, as narrated in Homer's Odyssey. Ulysses may also refer to: People * Ulysses (given name), including a list of people with this name Places * 5254 Ulysses, an asteroid Places in the United States * Ulysses, Kansas * Ulysses, Kentucky * Ulysses, Nebraska * Ulysses Township, Butler County, Nebraska * Ulysses, New York * Ulysses, Pennsylvania * Ulysses Township, Pennsylvania Animals * Ulysses butterfly (''Papilio ulysses'') a butterfly endemic to Australasia * Ulysses (horse) (born 2013), a thoroughbred racehorse Arts and enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
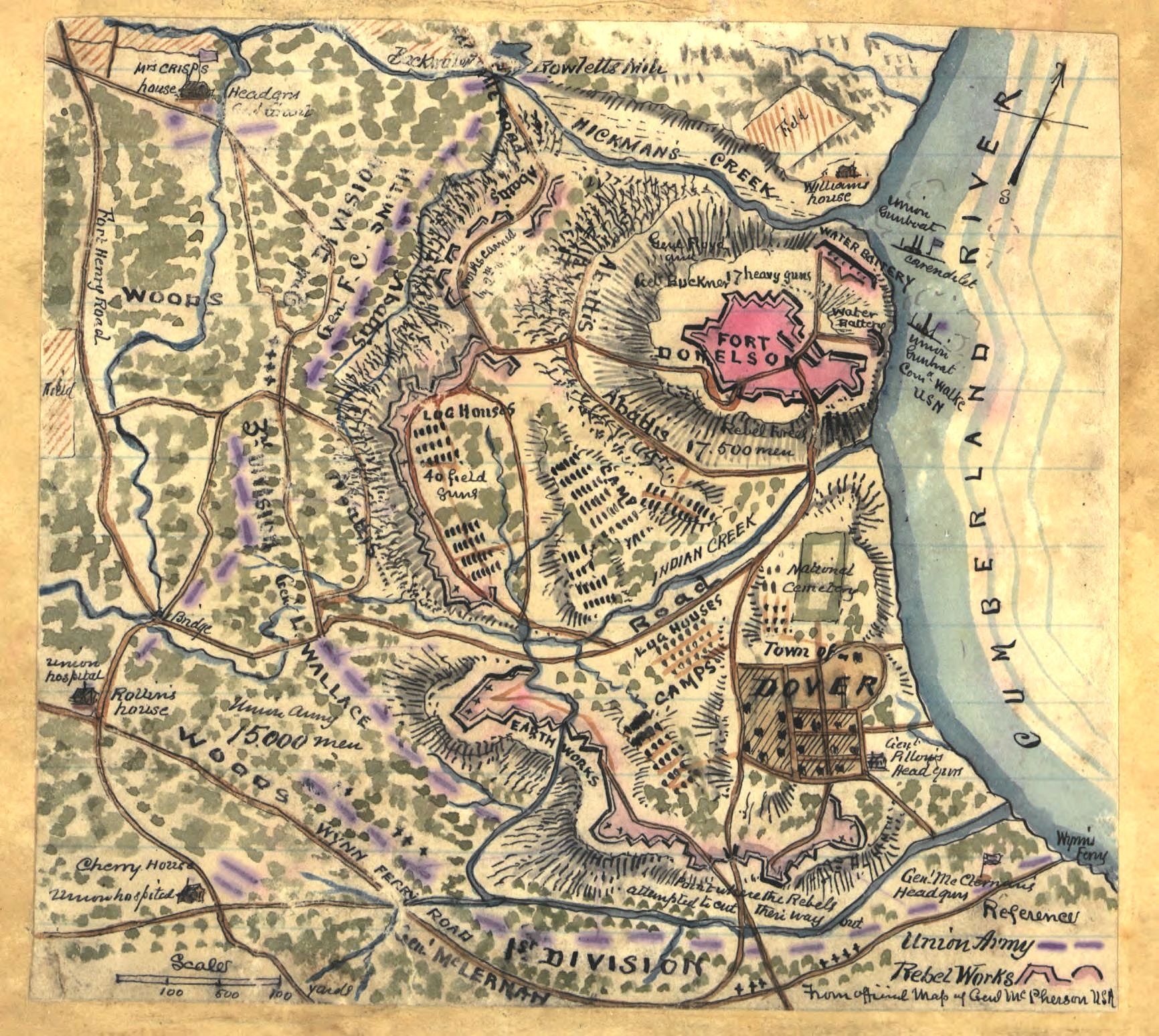
Fort Donelson
Fort Donelson was a fortress built early in 1862 by the Confederacy during the American Civil War to control the Cumberland River, which led to the heart of Tennessee, and thereby the Confederacy. The fort was named after Confederate general Daniel S. Donelson. The Union Army of the Tennessee, commanded by Brigadier General Ulysses S. Grant, who later became president, captured the fort in February 1862 from the Confederate Army in the Battle of Fort Donelson. This was a great strategic victory for the Union forces, and part of Grant's campaign to gain control of the Mississippi River. Union forces occupied the fort (and much of Tennessee) for the remainder of the war. A small detachment of Confederate troops made one unsuccessful attempt in 1863 to regain it. History Bushrod Johnson of the Confederate Corps of Engineers had approved the build site and supervised construction completed in early 1862. The site commanded a bend on the west side of the Cumberland River, It was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
43rd Illinois Volunteer Infantry Regiment
The 43rd Regiment Illinois Volunteer Infantry, known as the "Koerner Regiment" after Gustav Körner, was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Service The 43rd Illinois Infantry was organized at Camp Butler, Illinois and mustered into Federal service on October 12, 1861. The regiment was mustered out on November 30, 1865. Total strength and casualties The regiment suffered 8 officers and 75 enlisted men who were killed in action or mortally wounded and 2 officers and 161 enlisted men who died of disease, for a total of 246 fatalities. Commanders *Colonel Julius Raith - Mortally wounded at Shiloh, died on April 9, 1862. *Colonel Adolph Englemann - Mustered out on December 31, 1864. * Lieutenant Colonel Adolph Dengler - mustered out with the regiment.http://www.rootsweb.com/~ilcivilw/f&s/043-fs.htm Illinois in the Civil War website after Illinois Adjutant General's muster rolls See also *List of Illinois Civil War Units *Illinois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Colonel (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Air Force, Air Force and United States Space Force, Space Force, lieutenant colonel is a senior officer rank, just above the rank of Major (United States), major and just below the rank of Colonel (United States), colonel. It is equivalent to the naval rank of Commander (United States), commander in the other Uniformed services of the United States, uniformed services. The U.S. uniformed services pay grades, pay grade for the rank of lieutenant colonel is O-5. In the United States armed forces, the insignia for the rank is a silver oak leaf, with slight stylized differences between the version of the Army and the Air Force and that of the Navy and the Marine Corps. Promotion to lieutenant colonel is governed by Department of Defense policies derived from the Defense Officer Personnel Management Act (DOPMA) of 1980, for officers in the Active Component, and its companion Reserve Officer Personn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Buena Vista
The Battle of Buena Vista (February 22–23, 1847), known as the Battle of La Angostura in Mexico, and sometimes as Battle of Buena Vista/La Angostura, was a battle of the Mexican–American War. It was fought between U.S. forces, largely volunteers, under General Zachary Taylor, and the much larger Mexican Army under General Antonio López de Santa Anna. It took place near Buena Vista, a village in the state of Coahuila, about south of Saltillo, Mexico. ''La Angostura'' ("the narrow place") was the local name for the site. The outcome of the battle was ambiguous, with both sides claiming victory. Santa Anna's forces withdrew with war trophies of cannons and flags and left the field to the surprised U.S. forces, who had expected there to be another day of hard fighting. Background U.S. president James K. Polk had decided that an invasion into central Mexico via the Gulf Coast port of Veracruz would make the Mexicans come to the negotiating table. He told Major General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |