|
Administrative Scrivener
is a legal profession in Japan which files government licenses and permits, drafts documents, and provides legal advice around such interactions. They are also known as Immigration Lawyers, Gyosei-shoshi Lawyers or Certified Administrative Procedures Legal Specialists, although they are not allowed by the law to represent their clients in the judicial procedures in and outside of the court of law. Occupation Administrative Scriveners prepare legal documents such as filings with the national and local government, which do not include the court of law. Administrative Scrivener are found in a variety of roles. Many specialize in immigration matters, wills, inheritances, motor vehicle registrations, Development approvals, articles of incorporation, company minutes, etc. Under the Administrative Scrivener Law, the types of documents that such professionals are authorised to prepare extends into the thousands, involving the aforementioned as well as attachments to administrative applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immigration
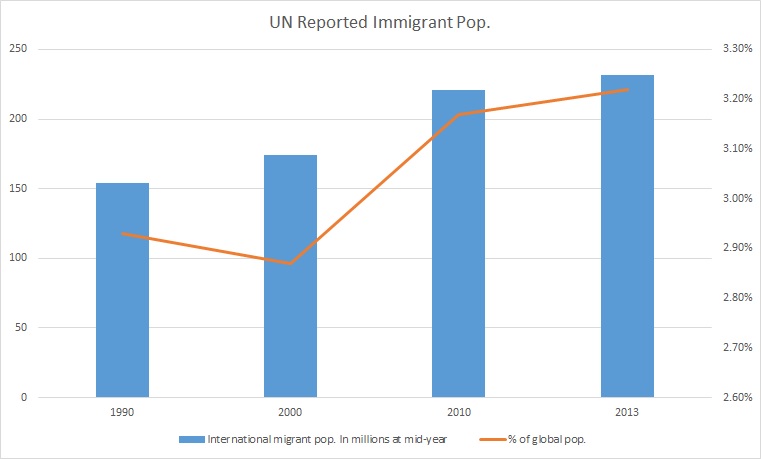
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuters, Tourism, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; Seasonal industry, seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Will (law)
A will and testament is a legal document that expresses a person's (testator) wishes as to how their property ( estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person ( executor) is to manage the property until its final distribution. For the distribution (devolution) of property not determined by a will, see inheritance and intestacy. Though it has been thought a "will" historically applied only to real property, while "testament" applied only to personal property (thus giving rise to the popular title of the document as "last will and testament"), records show the terms have been used interchangeably. Thus, the word "will" validly applies to both personal and real property. A will may also create a testamentary trust that is effective only after the death of the testator. History Throughout most of the world, the disposition of a dead person's estate has been a matter of social custom. According to Plutarch, the written will was invented by Solon. Originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officially bequeathing private property and/or debts can be performed by a testator via will, as attested by a notary or by other lawful means. Terminology In law, an "heir" ( heiress) is a person who is entitled to receive a share of property from a decedent (a person who died), subject to the rules of inheritance in the jurisdiction where the decedent was a citizen, or where the decedent died or owned property at the time of death. The inheritance may be either under the terms of a will or by intestate laws if the deceased had no will. However, the will must comply with the laws of the jurisdiction at the time it was created or it will be declared invalid (for example, some states do not recognise handwritten wills as valid, or only in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attorney At Law (Japan)
In Japan, form the base of the country's legal community. History Pre-Meiji restoration Historically, Japanese customs instituted an avoidance of legal involvement, based upon Confucian doctrines, and Japanese principles of harmony; anyone brought before a court for a criminal or civil matter suffered public and private humiliation, since they disrupted harmony. Nevertheless, by the 18th century, innkeepers in Edo began offering simple legal services for guests. They were known as '' Kujishi''. By the 19th century, references began to appear in Japanese literature on the role of "European-style" lawyers. Officially recognized legal representatives in civil trials, known as ''daigennin'', began to appear by the mid-19th century. No legal training was required to be a ''daigennin''. Meiji restoration Regulation of legal professionals began during the Meiji Restoration. In 1890, the Criminal Code was amended, which recognized the right to legal representation during a criminal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certified Public Accountant
Certified Public Accountant (CPA) is the title of qualified accountants in numerous countries in the English-speaking world. It is generally equivalent to the title of chartered accountant in other English-speaking countries. In the United States, the CPA is a license to provide accounting services to the public. It is awarded by each of the 50 states for practice in that state. Additionally, all states except Hawaii have passed mobility laws to allow CPAs from other states to practice in their state. State licensing requirements vary, but the minimum standard requirements include passing the Uniform Certified Public Accountant Examination, 150 semester units of college education, and one year of accounting-related experience. Continuing professional education (CPE) is also required to maintain licensure. Individuals who have been awarded the CPA but have lapsed in the fulfillment of the required CPE or who have requested conversion to inactive status are in many states permitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent Attorney
A patent attorney is an attorney who has the specialized qualifications necessary for representing clients in obtaining patents and acting in all matters and procedures relating to patent law and practice, such as filing patent applications and oppositions to granted patents. Terminology The term "patent attorney" is used differently in different countries and thus may or may not require the same legal qualifications as a general legal practitioner. The titles patent agent and patent lawyer are also used in some jurisdictions. In some jurisdictions, the terms are interchangeable; in others, the latter is used only if the person is qualified as a lawyer. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and the International Federation of Intellectual Property Attorneys (FICPI) propose since 2022 a Patent Drafting Training Program to enhance the knowledge and skills of professionals, such as patent agents, who wish to strengthen their patent drafting skills. Role A study ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Attorney
Tax law or revenue law is an area of legal study in which public or sanctioned authorities, such as federal, state and municipal governments (as in the case of the US) use a body of rules and procedures (laws) to assess and collect taxes in a legal context. The rates and merits of the various taxes, imposed by the authorities, are attained via the political process inherent in these bodies of power, and not directly attributable to the actual domain of tax law itself. Tax law is part of public law. It covers the application of existing tax laws on individuals, entities and corporations, in areas where tax revenue is derived or levied, e.g. income tax, estate tax, business tax, employment/payroll tax, property tax, gift tax and exports/imports tax. There have been some arguments that consumer law is a better way to engage in large-scale redistribution than tax law because it does not necessitate legislation and can be more efficient, given the complexities of tax law. Major iss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrivener
A scrivener (or scribe) was a person who, before the advent of compulsory education, could literacy, read and write or who wrote letters as well as court and legal documents. Scriveners were people who made their living by writing or copying written material. This usually indicated secretary, secretarial and Administration (government), administrative duties such as Dictation (exercise), dictation and keeping business, judicial, and history, historical records for monarch, kings, nobility, nobles, temples, and municipality, cities. Scriveners later developed into notaries, court reporters, and in England and Wales, scrivener notaries. They were and are generally distinguished from scribes, who in the European Middle Ages mostly copied books; with the spread of printing this role largely disappeared, but scriveners were still required. Styles of handwriting used by scriveners included secretary hand, book hand and court hand. Current role Scriveners remain common mainly in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Document Assistant
A legal document assistant (LDA, also known as "document technician", "legal document preparer", "legal technician", "online legal document provider" or "legal document clerk") in the United States is a person who is a non-lawyer but authorized to assist with the preparation of legal instruments. Unlike a paralegal, legal document assistants do not work under the supervision of an attorney. The existence of LDAs is a phenomenon in US due to the strict licensing laws for attorneys compared to elsewhere in the world. The job was created by using the doctrine of ''pro se'' to enable someone to help another to prepare a legal document. In all America's states except for Louisiana and Puerto Rico, only an attorney can advise and draft a legal document for someone. With the self-help ''pro se'' concept and stock legal forms, the Legal Document Preparer profession was arise. The role of a Legal Document Assistant varies significantly across legal jurisdictions. The job performed by Legal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Scrivener
"Judicial scrivener" is a term used to refer to similar legal professions in Japan, South Korea and Taiwan. Judicial scriveners assist clients in commercial and real estate registration procedures and in the preparation of documents for litigation. Japan In Japan, are authorized to represent their clients in real estate registrations, commercial registrations (e.g. the incorporation of companies), preparation of court documents and filings with legal affairs bureaus. Judicial scriveners may also represent clients in summary courts, arbitration and mediation proceedings, but are not allowed to represent clients in district courts or more advanced stages of litigation. The more familiar term "solicitor" is also sometimes used to refer to them, although the division of responsibilities is not the same as between solicitors and barristers in the English legal system. The term "judicial scrivener", while somewhat archaic in tone, is a fairly accurate literal translation of the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial System Of Japan
In the judicial system of Japan, the Constitution of Japan guarantees that "all judges shall be independent in the exercise of their conscience and shall be bound only by this constitution and the Laws" (Article 76). They cannot be removed from the bench "unless judicially declared mentally or physically incompetent to perform official duties", and they cannot be disciplined by executive agencies (Article 78). Supreme Court of Japan, Supreme Court judges, however, may be removed by a majority of voters in a referendum that occurs at the first general election following the judge's appointment and every ten years thereafter. The judiciary was far more constrained under the Meiji Constitution than it is under the present Constitution and had no authority over administrative or constitutional law cases. Moreover, the Ministry of Justice (Japan), Ministry of Justice had complete and direct control over the courts' administrative affairs. Nonetheless, Professor John Haley argues that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |