|
Administrative Police (France)
The Administrative police in France is the corps of French police whose goal is the prevention of disturbances to the public order. Administrative policing is an activity whose goal is to ensure the maintenance of public order, prevent crime, and are under local or national administrative authorities, not in the search for, or arrest of the perpetrator of a particular offense. This includes the French Border Police, traffic police, and others. They have certain rights to stop and ask for identification, but are not involved in criminal proceedings. The goals of the Administrative police are distinct from those of the Judicial police which, according to article 14 of the is concerned with the prosecution and punishment for offenses committed. The separation of administrative and judicial policing functions dates to the 1795 Code of Offences and Penalties, and is still in force today. It is a functional distinction, which does not necessarily imply an organizational separation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Police
Law enforcement in France has a long history dating back to AD 570 when night watch systems were commonplace.Dammer, H. R. and Albanese, J. S. (2014). ''Comparative Criminal Justice Systems'' (5th ed.). Wadesworth Cengage learning: Belmont, CA. Policing is centralized at the national level. Recently, legislation has allowed local governments to hire their own police officers which are called the "''police municipale''. There are two national police forces called "'' Police nationale'' and "'' Gendarmerie nationale''. The Prefecture of Police of Paris provides policing services directly to Paris as a subdivision of France's Ministry of the Interior. Within these national forces, only certain designated police officers have the power to conduct criminal investigations which are supervised by investigative magistrates. Organizations National agencies France has two national police forces: * The '' Police nationale'', formerly called the "'' Sûreté''", is considered a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
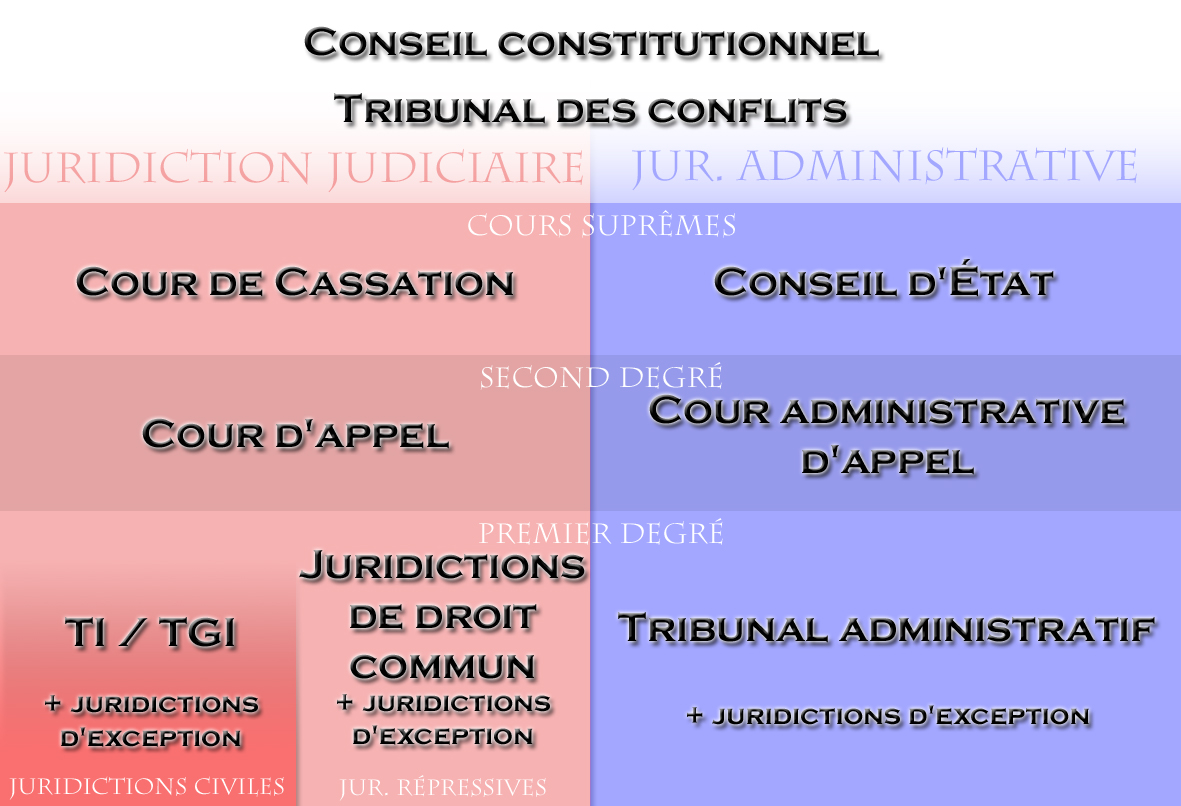
Court Of Cassation
A court of cassation is a high-instance court that exists in some judicial systems. Courts of cassation do not re-examine the facts of a case, they only interpret the relevant law. In this they are appellate courts of the highest instance. In this way they differ from systems which have a supreme court which can rule on both the facts of a case and the relevant law. The term derives from the Latin , "to reverse or overturn". The European Court of Justice answers questions of European Union law following a referral from a court of a member state. In exercising this function it is not a court of cassation: it issues binding advice to the national courts on how EU law ought to be interpreted, it does not overturn decisions of those courts. However, the Court of Justice can act as a court of cassation when it hears appeals from the General Court of the European Union. Many common-law supreme courts, like the United States Supreme Court, use a similar system, whereby the court vaca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Legality In French Criminal Law
The principle of legality in French criminal law holds that no one may be convicted of a criminal offense unless a previously published legal text sets out in clear and precise wording out the constituent elements of the offense and the penalty which applies to it. (Latin:, in other words, "no crime, no penalty, without a law"). The principle of legality (french: link=no, principe de légalité) is one of the most fundamental principles of French criminal law, and goes back to the Penal Code of 1791 adopted during the French Revolution, and before that, was developed by Italian criminologist Cesare Beccaria and by Montesquieu. The principle has its origins in the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which endows it with constitutional force and limits the conditions in which citizens may be punished for infractions. History The principle of legality of punishment and crime was identified and conceptualized in the Enlightenment. It is generally attribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nulla Poena Sine Lege
''Nulla poena sine lege'' (Latin for "no penalty without law", Anglicized pronunciation: ) is a legal principle which states that one cannot be punished for doing something that is not prohibited by law. This principle is accepted and codified in modern democratic states as a basic requirement of the rule of law. It has been described as "one of the most 'widely held value-judgement in the entire history of human thought. Requirements In modern European criminal law, e.g. of the Constitutional Court of Germany, the principle of ''nulla poena sine lege'' has been found to consist of four separate requirements: ;''Nulla poena sine lege praevia'': There is to be no penalty without ''previous'' law. This prohibits ex post facto laws, and the retroactive application of criminal law. It is a basic maxim in mainland European legal thinking. It was written by Paul Johann Anselm Ritter von Feuerbach as part of the Bavarian Criminal Code in 1813. ;''Nulla poena sine lege scripta'': There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of France
The Law of France refers to the legal system in the French Republic, which is a civil law legal system primarily based on legal codes and statutes, with case law also playing an important role. The most influential of the French legal codes is the Napoleonic Civil Code, which inspired the civil codes of Europe and later across the world. The Constitution of France adopted in 1958 is the supreme law in France. European Union law is becoming increasingly important in France, as in other EU member states. In academic terms, French law can be divided into two main categories: private law (''Droit privé'') and public law (''droit public''). This differs from the traditional common law concepts in which the main distinction is between criminal law and civil law. Private law governs relationships between individuals. It includes, in particular: * Civil law ('). This branch refers to the field of private law in common law systems. This branch encompasses the fields of inheritanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Penal Code French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which |