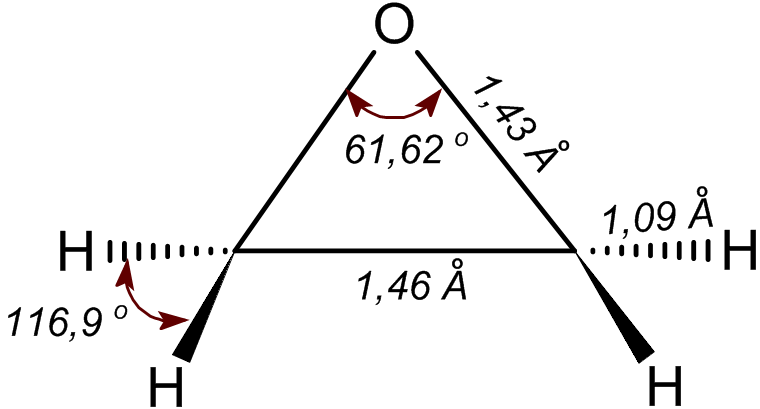
|
Addition Polymer
In polymer chemistry, an addition polymer is a polymer that forms by simple linking of monomers ''without'' the co-generation of other products. Addition polymerization differs from condensation polymerization, which ''does'' co-generate a product, usually water. Addition polymers can be formed by chain polymerization, when the polymer is formed by the sequential addition of monomer units to an active site in a chain reaction, or by polyaddition, when the polymer is formed by addition reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of some simple monomer units repeatedly. Generally polymers are unsaturated compounds like alkenes, alkalines etc. The addition polymerization mainly takes place in free radical mechanism. The free radical mechanism of addition polymerization completed by three steps i.e. Initiation of free radical, Chain propagation, Termination of chain. Polyolefins Many common addition polymers are formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer Chemistry
Polymer chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. The principles and methods used within polymer chemistry are also applicable through a wide range of other chemistry sub-disciplines like organic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and physical chemistry. Many materials have polymeric structures, from fully inorganic metals and ceramics to DNA and other biological molecules. However, polymer chemistry is typically related to synthetic and organic compositions. Synthetic polymers are ubiquitous in commercial materials and products in everyday use, such as plastics, and rubbers, and are major components of composite materials. Polymer chemistry can also be included in the broader fields of polymer science or even nanotechnology, both of which can be described as encompassing polymer physics and polymer engineering.Hans-Heinrich Moretto, Manfred Schulz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bottles, cups, jars, etc.). , over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market. Many kinds of polyethylene are known, with most having the chemical formula (C2H4)''n''. PE is usually a mixture of similar polymers of ethylene, with various values of ''n''. It can be ''low-density'' or ''high-density'' and many variations thereof. Its properties can be modified further by crosslinking or copolymerization. All forms are nontoxic as well as chemically resilient, contributing to polyethylene's popularity as a multi-use plastic. However, polyethylene's chemical resilience also makes it a long-lived and decomposition-resistant pollutant when disposed of improperly. Being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nylon 6
Nylon 6 or polycaprolactam is a polymer, in particular semicrystalline polyamide. Unlike most other nylons, nylon 6 is not a condensation polymer, but instead is formed by ring-opening polymerization; this makes it a special case in the comparison between condensation and addition polymers. Its competition with nylon 66 and the example it set have also shaped the economics of the synthetic fibre industry. It is sold under numerous trade names including Perlon (Germany), Dederon (former East Germany), Nylatron, Capron, Ultramid, Akulon, Kapron (former Soviet Union and satellite states), Rugopa (Turkey) and Durethan. History Polycaprolactam was developed by Paul Schlack at IG Farben in late 1930s (first synthesized in 1938) to reproduce the properties of Nylon 66 without violating the patent on its production. (Around the same time, Kohei Hoshino at Toray also succeeded in synthesizing nylon 6.) It was marketed as Perlon, and industrial production with a capacity of 3,500 tons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene Glycol
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH. PEG is commonly incorporated into hydrogels which present a functional form for further use. Uses Medical uses * Pharmaceutical-grade PEG is used as an excipient in many pharmaceutical products, in oral, topical, and parenteral dosage forms. * PEG is the basis of a number of laxatives (as ''MiraLax, RestoraLAX, MoviPrep, etc.''). Whole bowel irrigation with polyethylene glycol and added electrolytes is used for bowel preparation before surgery or colonoscopy or for children with constipation. Macrogol (with brand names such as Laxido, Movicol and Miralax) is the generic name for polyethylene glycol used as a laxative. The name may be followed by a number th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
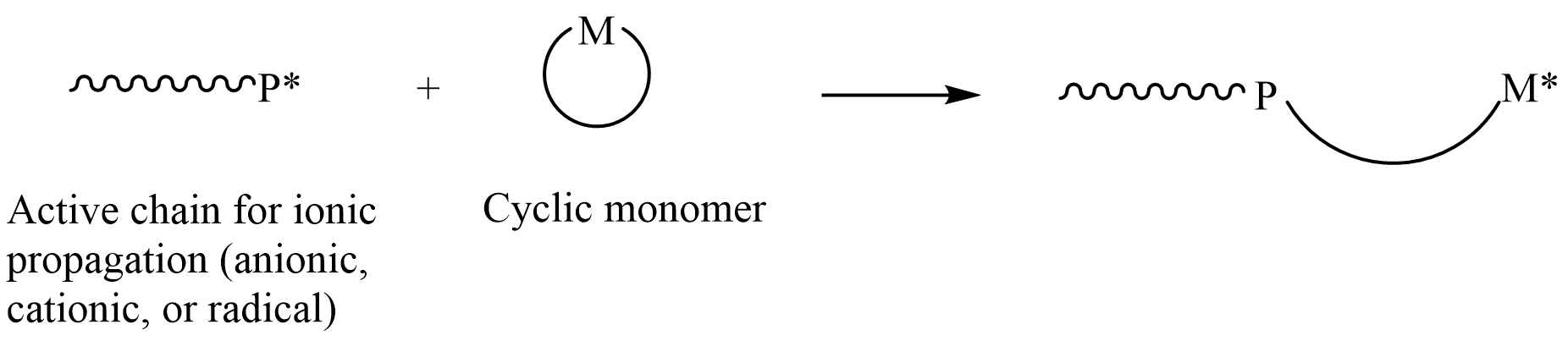
Ring-opening Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) is a form of chain-growth polymerization in which the terminus of a polymer chain attacks cyclic monomers to form a longer polymer (see figure). The reactive center can be radical, anionic or cationic. Ring-opening of cyclic monomers is often driven by the relief of bond-angle strain. Thus, as is the case for other types of polymerization, the enthalpy change in ring-opening is negative. Many rings undergo ROP. Monomers Many cyclic monomers are amenable to ROP. These include epoxides, cyclic trisiloxanes, some lactones and lactides, cyclic anhydrides, cyclic carbonates, and amino acid ''N''-carboxyanhydrides. Many strained cycloalkenes, e.g norbornene, are suitable monomers via ring-opening metathesis polymerization. Even highly strained cycloalkane rings, such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane derivatives, can undergo ROP. History Ring-opening polymerization has been used since the beginning of the 1900s to produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinylidene Chloride
1,1-Dichloroethylene, commonly called vinylidene chloride or 1,1-DCE, is an organochloride with the molecular formula . It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. Like most chlorocarbons, it is poorly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. 1,1-DCE was the precursor to the original clingwrap, Saran, for food, but this application has been phased out. Production 1,1-DCE is produced by dehydrochlorination of 1,1,2-trichloroethane, a relatively unwanted byproduct in the production of 1,1,1-trichloroethane and 1,2-dichloroethane. The conversion is a base-catalyzed reaction which uses either NaOH or Ca(OH) with temperature ca. 100 °C. :ClCHCHCl + NaOH → ClC=CH + NaCl + HO The gas phase reaction, without the base, would be more desirable but is less selective. Applications 1,1-DCE is mainly used as a comonomer in the polymerization of vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile, and acrylates. It is also used in semiconductor device fabrication for growing high pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinyl Chloride
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C =CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. It is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Vinyl chloride is a colourless flammable gas that has a sweet odor and is carcinogenic. Vinyl chloride monomer is among the top twenty largest petrochemicals (petroleum-derived chemicals) in world production. The United States remains the largest vinyl chloride manufacturing region because of its low-production-cost position in chlorine and ethylene raw materials. China is also a large manufacturer and one of the largest consumers of vinyl chloride. It can be formed in the environment when soil organisms break down chlorinated solvents. Vinyl chloride that is released by industries or formed by the breakdown of other chlorinated chemicals can enter the air and drinking water supplies. Vinyl chloride is a common contaminant found near landfills. Before the 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saran Wrap
Plastic wrap, cling film, Saran wrap, cling wrap, Glad wrap or food wrap is a thin plastic film typically used for sealing food items in containers to keep them fresh over a longer period of time. Plastic wrap, typically sold on rolls in boxes with a cutting edge, clings to many smooth surfaces and can thus remain tight over the opening of a container without adhesive. Common plastic wrap is roughly 0.0005 inches (12.7 μm) thick. The trend has been to produce thinner plastic wrap, particularly for household use (where very little stretch is needed), so now the majority of brands on shelves around the world are 8, 9 or 10 μm thick. Materials used Plastic wrap was initially created from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which remains the most common component globally. PVC has an acceptably-low permeability to water vapor and oxygen, helping to preserve the freshness of food. There are concerns about the transfer of plasticizers from PVC into food. Pliofilm was made of various kinds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCTFE
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) is a thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer with the molecular formula , where ''n'' is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is similar to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except that it is a homopolymer of the monomer chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) instead of tetrafluoroethene. It has the lowest water vapor transmission rate of any plastic. History It was discovered in 1934 by Fritz Schloffer and Otto Scherer who worked at IG Farben Company, Germany. Trade names After World War II, PCTFE was commercialized under the trade name of Kel-F 81 by M. W. Kellogg Company in early 1950s. The name "Kel-F" was derived from "Kellogg" and "fluoropolymer", which also represents other fluoropolymers like the copolymer poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene-co-vinylidene fluoride) (Kel-F 800). These were acquired by 3M Company in 1957. 3M discontinued manufacturing of Kel-F by 1996. PCTFE resin is now manufactured under different trade name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
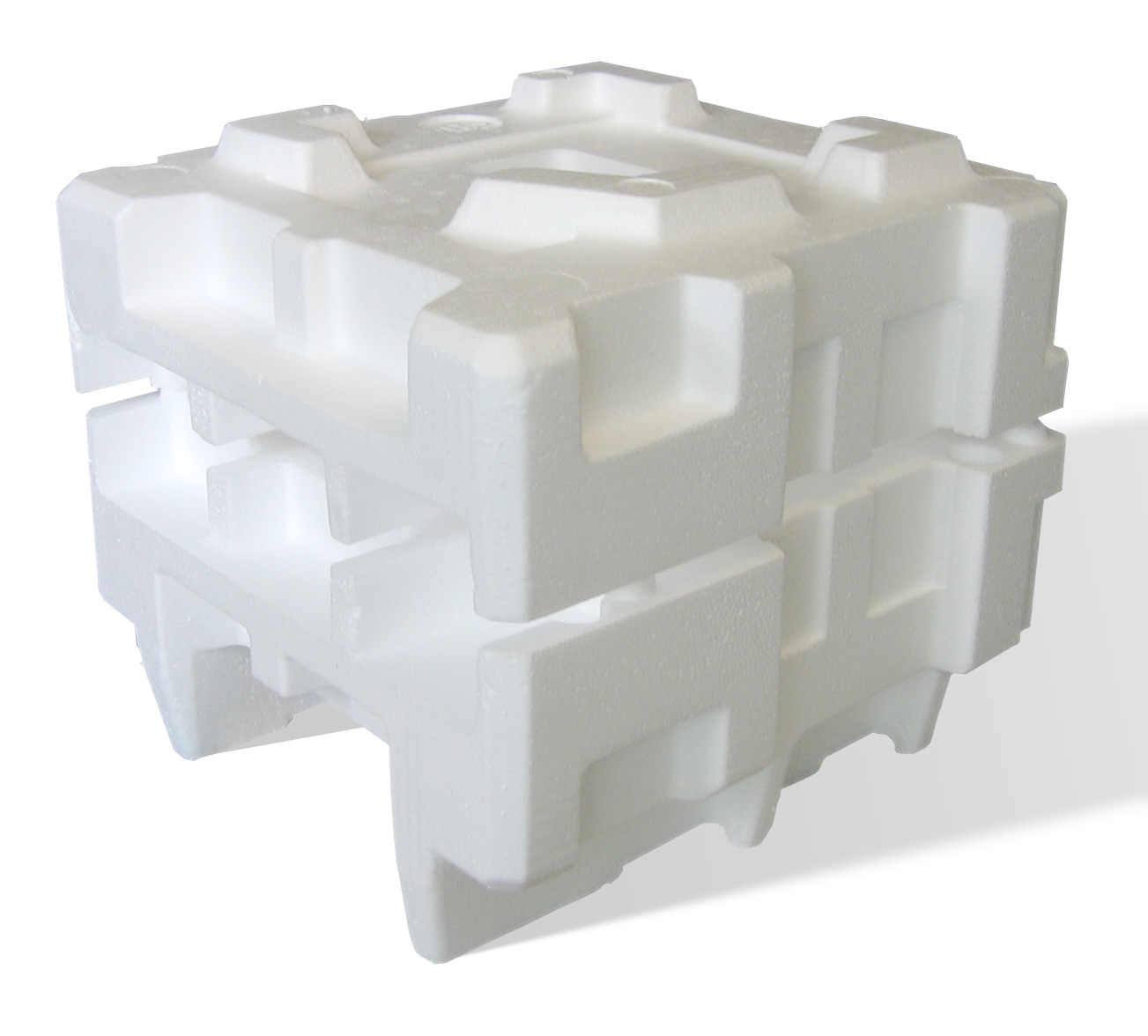
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to air and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, with the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene is naturally transparent to visible light, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging (such as packing peanuts and optical disc jewel cases), containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room temperature but flows if heated above about 100 °C, its glass transition temperature. It becomes rigid again when cooled. This te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylate
An acrylate polymer (also known as acrylic or polyacrylate) is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity. Acrylate polymer is commonly used in cosmetics, such as nail polish, as an adhesive. History The first synthesis of acrylic polymer was reported by G. W. A. Kahlbaum in 1880. Acrylic elastomers Acrylic elastomer is a general term for a type of synthetic rubber whose primary component is acrylic acid alkylester ( ethyl or butyl ester). Acrylic elastomer possesses characteristics of heat and oil resistance, with the ability to withstand temperatures of 170–180 °C. It is used primarily for producing oil seals and packaging related to automobiles. Acrylic elastomer can generally be characterized as one of two types. "Old" types include ACM (copolymer of acrylic acid ester and 2-chloroethyl vinyl ether) containing chlorine and ANM (copolymer of acrylic acid ester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |