|
Adam Mackenzie
Captain Adam Mackenzie (died 13 November 1823) was an officer of the British Royal Navy who served during the American, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, being present at numerous fleet actions, as well as serving as successful ship captain. Biography Early career Mackenzie was present as a midshipman in several actions between the British and French during the American War: under Augustus Keppel at Ushant in 1778; under John Byron at Grenada in 1779; under Rodney at Cape St. Vincent and Martinique in 1780; and the relief of Gibraltar under Earl Howe in 1782. He was eventually commissioned as a lieutenant on 3 March 1790, and was present as the first lieutenant of the frigate at the Glorious First of June in 1794. HMS ''Pylades'' Promoted to commander on 22 June 1796, he appointed to command of the 16-gun sloop . In May 1797 he was sent by the Port Admiral at Sheerness to negotiate with the mutineers at the Nore, and also assisted in securing the dockyard from any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent (often abbreviated to Stoke) is a city and unitary authority area in Staffordshire, England, with an area of . In 2019, the city had an estimated population of 256,375. It is the largest settlement in Staffordshire and is surrounded by the towns of Newcastle-under-Lyme, Alsager, Kidsgrove, Biddulph and Stone, which form a conurbation around the city. Stoke is polycentric, having been formed by the federation of six towns in 1910. It took its name from Stoke-upon-Trent where the main centre of government and the principal railway station in the district were located. Hanley is the primary commercial centre; the other four towns which form the city are Burslem, Tunstall, Longton and Fenton. Stoke-on-Trent is the home of the pottery industry in England and known as The Potteries. Formerly a primarily industrial conurbation, it is now a centre for service industries and distribution centres. History Toponymy and etymology The name ''Stoke'' is taken from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Tower And Sword
The Ancient and Most Noble Military Order of the Tower and of the Sword, of the Valour, Loyalty and Merit ( pt, Antiga e Muito Nobre Ordem Militar da Torre e Espada, do Valor, Lealdade e Mérito), before 1910 Royal Military Order of the Tower and Sword ( Portuguese: ''Real Ordem Militar da Torre e Espada''), is a Portuguese order of knighthood and the pinnacle of the Portuguese honours system. It was created by King Afonso V in 1459. The order may be bestowed on people or on Portuguese municipalities. Private Anibal Milhais was the only Portuguese Army private to be awarded the Order of the Tower and the Sword for Valor, for his actions in Lys, Belgium during World War I. History The order was originally created by King Afonso V of Portugal in 1459, under the name of the ''Order of the Sword'', inspired by the legend that Arab rule in Africa would end when a Christian prince would besiege the fortress at Fez. Knighthood in the Order of the Sword was given as reward to thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
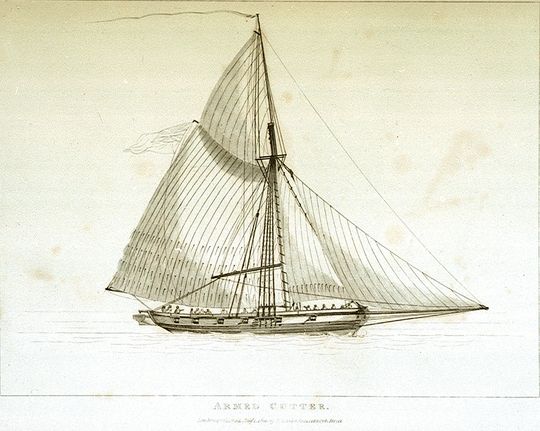
Hired Armed Cutter Courier
His Majesty's hired armed cutter ''Courier'' appears twice in the records of the British Royal Navy. The size and armament suggests that both contracts could represent the same vessel, but other information indicates that the second ''Courier'' had been captured from the French in the West Indies. On the first contract the captain and crew were awarded clasps to the Naval General Service Medal, one for a boat action and one for a single ship action in which they distinguished themselves. First contract The first contract for ''Courier'' was from 6 June 1798 to 1 November 1801.Winfield (2008), p.389. She was of 116 tons ( bm) and carried an armament of twelve 4-pounder guns. She had a crew of 40 men. In 1799 she was under the command of Lieutenant Thomas Searle, in the North Sea. On 15 April he recaptured the ''Nelly'' from the French privateer ''Vengeur''.Ralfe (1972), pp.318-20. On 16 April, ''Courier'' was in company with , and when they captured the Prussian hoy ''Dolphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutter (boat)
A cutter is a type of watercraft. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or Sail plan, sailplan) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cutter), to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships. As a sailing rig, a cutter is a single-masted boat, with two or more headsails. On the eastern side of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, the two headsails on a single mast is the fullest extent of the modern definition. In U.S. waters, a greater level of complexity applies, with the placement of the mast and the rigging details of the bowsprit taken into account so a boat with two headsails may be classed as a sloop. Government agencies use the term "cutter" for vessels employed in patrolling their territorial waters and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hired Armed Vessels
During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries the Royal Navy made use of a considerable number of hired armed vessels. These were generally smaller vessels, often cutters and luggers, that the Navy used for duties ranging from carrying and passengers to convoy escort, particularly in British coastal waters, and reconnaissance.Winfield (2008), p.387. Doctrine The Navy Board usually hired the vessel complete with master and crew rather than bareboat. Contracts were for a specified time or on an open-ended monthly hire basis. During periods of peace, such as the period between the Treaty of Amiens and the commencement of the Napoleonic Wars, the Admiralty returned the vessels to their owners, only to rehire many on the outbreak of war. The Admiralty provided a regular naval officer, usually a lieutenant for the small vessels, to be the commander. The civilian master then served as the sailing master. For purposes of prize money or salvage, hired armed vessels received the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig-sloop
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
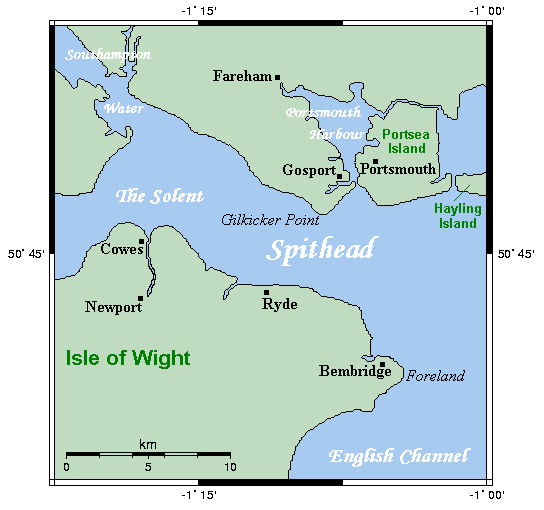
Spithead And Nore Mutinies
The Spithead and Nore mutinies were two major mutinies by sailors of the Royal Navy in 1797. They were the first in an increasing series of outbreaks of maritime radicalism in the Atlantic World. Despite their temporal proximity, the mutinies differed in character. The Spithead mutiny was a simple, peaceful, successful strike action to address economic grievances, while the Nore mutiny was a more radical action, articulating political ideals as well, which failed. The mutinies were extremely problematic for Britain, because at the time the country was at war with Revolutionary France, and the Navy was the main component of the war effort. There were also concerns among the government that the mutinies might be part of wider attempts at revolutionary sedition instigated by societies such as the London Corresponding Society and the United Irishmen. Spithead The mutiny at Spithead (an anchorage near Portsmouth) lasted from 16 April to 15 May 1797. Sailors on 16 ships in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheerness
Sheerness () is a town and civil parish beside the mouth of the River Medway on the north-west corner of the Isle of Sheppey in north Kent, England. With a population of 11,938, it is the second largest town on the island after the nearby town of Minster which has a population of 21,319. Sheerness began as a fort built in the 16th century to protect the River Medway from naval invasion. In 1665 plans were first laid by the Navy Board for Sheerness Dockyard, a facility where warships might be provisioned and repaired. The site was favoured by Samuel Pepys, then Clerk of the Acts of the navy, for shipbuilding over Chatham inland. After the raid on the Medway in 1667, the older fortification was strengthened; in 1669 a Royal Navy dockyard was established in the town, where warships were stocked and repaired until its closure in 1960. Beginning with the construction of a pier and a promenade in the 19th century, Sheerness acquired the added attractions of a seaside resort. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longman
Longman, also known as Pearson Longman, is a publisher, publishing company founded in London, England, in 1724 and is owned by Pearson PLC. Since 1968, Longman has been used primarily as an imprint by Pearson's Schools business. The Longman brand is also used for the Longman Schools in China and the ''Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English, Longman Dictionary''. History Beginnings The Longman company was founded by Thomas Longman (1699–1755), Thomas Longman (1699 – 18 June 1755), the son of Ezekiel Longman (died 1708), a gentleman of Bristol. Thomas was apprenticed in 1716 to John Osborn, a London bookseller, and at the expiration of his apprenticeship married Osborn's daughter. In August 1724, he purchased the stock and household goods of William Taylor (bookseller), William Taylor, the first publisher of ''Robinson Crusoe'', for 9s 6d. Taylor's two shops in Paternoster Row, London, were known respectively as the ''Black Swan (St. Paul's Churchyard), Black Sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe
Admiral of the Fleet Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe, (8 March 1726 – 5 August 1799) was a British naval officer. After serving throughout the War of the Austrian Succession, he gained a reputation for his role in amphibious operations against the French coast as part of Britain's policy of naval descents during the Seven Years' War. He also took part, as a naval captain, in the decisive British naval victory at the Battle of Quiberon Bay in November 1759. In North America, Howe is best known for his service during the American Revolutionary War, when he acted as a naval commander and a peace commissioner with the American rebels; he also conducted a successful relief during the Great Siege of Gibraltar in the later stages of the War. Howe later commanded the victorious British fleet during the Glorious First of June in June 1794 during the French Revolutionary Wars. Early career Howe was born in Albemarle Street, London, the second son of Emanuel Howe, 2nd Visco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |