|
Adam Loftus (politician)
Sir Adam Loftus was an Irish politician and public official of the seventeenth century. He was the eldest son of Sir Dudley Loftus, and part of a powerful Anglo-Irish Leinster family. His mother was Anne Bagenal of a leading Ulster family. He was born and lived at Rathfarnham, County Dublin. He was the cousin of Lord Loftus, the Lord Chancellor of Ireland between 1619 and 1639. Adam was appointed as Vice-Treasurer of Ireland, replacing Lord Mountnorris in the post. He became a client of the Lord Deputy of Ireland Thomas Wentworth, who had him made a member of the Irish Council. Adam's younger brother Nicholas Loftus also received a position at the Treasury as Clerk of the Pells. He sat for the County Wexford seat of Newborough in the 1634 and 1640 Parliaments of Ireland where he was grouped as a supporter of Wentworth. His brother Nicholas, and his son Arthur Loftus, also represented Wexford seats. He was married to Jane Vaughan, the daughter of Walter Vaughan of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politician
A politician is a person who participates in Public policy, policy-making processes, usually holding an elective position in government. Politicians represent the people, make decisions, and influence the formulation of public policy. The roles or duties that politicians must perform vary depending on the level of government they serve, whether Local government, local, national, or international. The ideological orientation that politicians adopt often stems from their previous experience, education, beliefs, the political parties they belong to, or public opinion. Politicians sometimes face many challenges and mistakes that may affect their credibility and ability to persuade. These mistakes include political corruption resulting from their misuse and exploitation of power to achieve their interests, which requires them to prioritize the public interest and develop long-term strategies. Challenges include how to keep up with the development of social media and confronting biase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Loftus
Nicholas Loftus (1592-1666) was an Irish politician and public official. He was the son of Sir Dudley Loftus and the grandson of Adam Loftus, the Archbishop of Dublin and an influential political figure in Tudor Ireland. His mother Anne Bagenal was from a leading Ulster family headed by Sir Nicholas Bagenal. She later remarried to the prominent judge Lord Sarsfield, who thus became Nicholas' stepfather. Nicholas' elder brother Sir Adam Loftus was made Vice-Treasurer of Ireland during the administration of Thomas Wentworth while Nicholas was appointed as an Irish Treasury official, with the title Clerk of the Pells, under him. He was elected as a member of the Parliament of Ireland in 1613 and 1634, representing the seat of Fethard in County Wexford. In the 1640 Parliament he sat for County Wexford seat. In the Parliament elected in 1661, he sat once again for Fethard. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Irish Politicians
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Rathfarnham
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williamite
A Williamite was a follower of King William III of England (r. 1689–1702) who deposed King James II and VII in the Glorious Revolution. William, the Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, replaced James with the support of English Whigs. One of William's aims was to ensure England's entry into his League of Augsburg against France in the Nine Years' War. For Williamites in England, Scotland and Ireland, William was seen as the guarantor of civil and religious liberty and the Protestant monarchy against Catholic absolutism. The term "Williamite" is also commonly used to refer to William's multi-national army in Ireland during the Williamite War in Ireland, 1689–1691. In Ireland itself, William was primarily supported by Protestants and opposed by the native and Anglo-Irish Catholic Jacobites who supported James. Once James II had come to the throne in 1685, he had his viceroy Richard Talbot, Earl of Tyrconnell replace Protestants with Catholics in the government. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
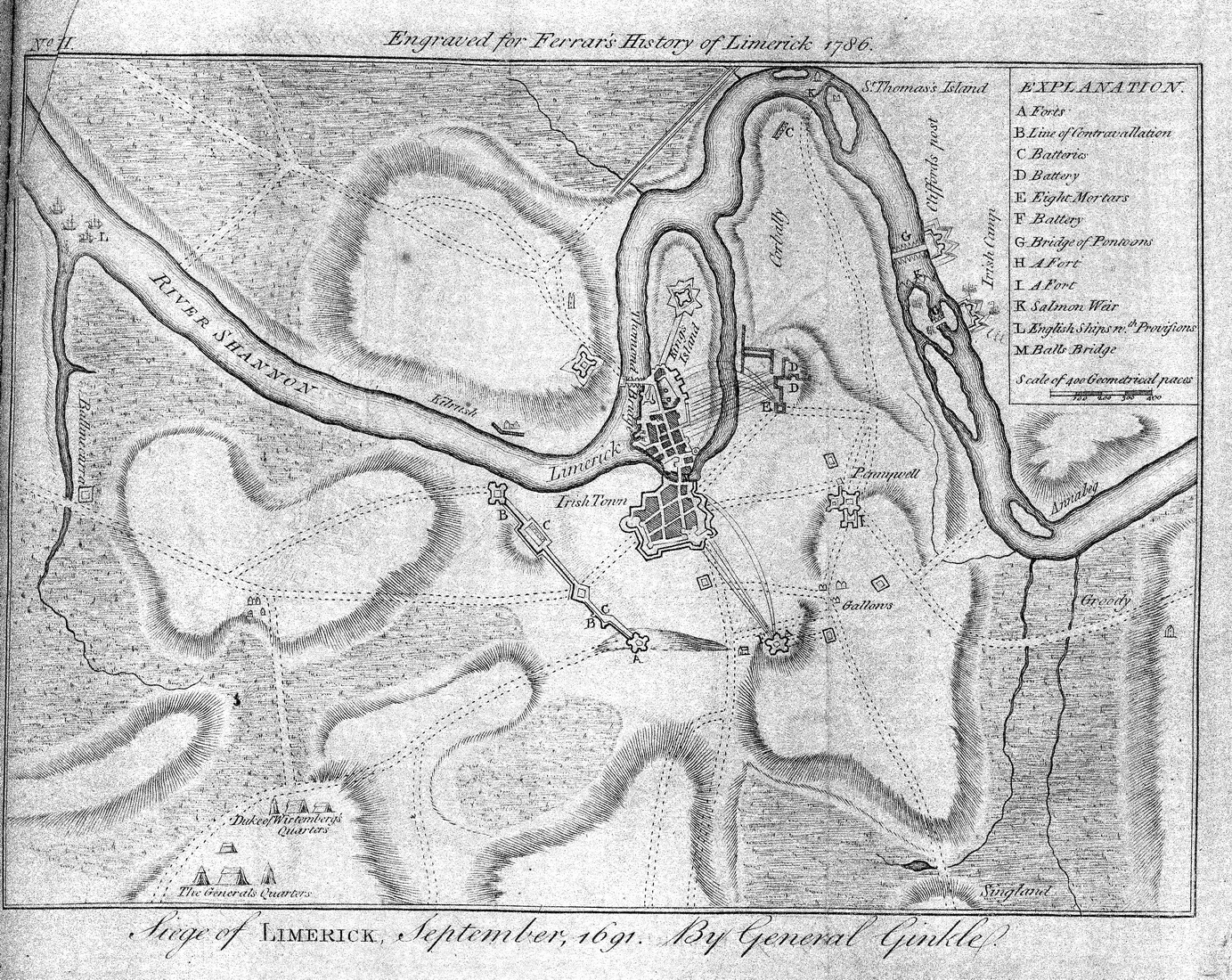
Siege Of Limerick (1691)
The siege of Limerick in western Ireland was a second siege of the town during the Williamite War in Ireland (1689–1691). The city, held by Jacobite forces, was able to beat off a Williamite assault in 1690. However, after a second siege in August–October 1691, it surrendered on favourable terms. Siege By the time of the second siege, the military situation had turned against the Jacobites; their main force had been badly defeated at the Battle of Aughrim in July, with over 4,000 killed, including their commander, Charles Chalmot de Saint-Ruhe, and thousands more either taken prisoner or deserted. The town of Galway capitulated in July 1691; its Jacobite garrison was accorded 'all the honours of war,' which allowed them to retain their weapons and receive a free pass to Limerick. However, although its defences had been considerably strengthened since 1690, morale was now much lower after a series of defeats and retreats. By now, siege warfare was an exact art, the rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Loftus, 1st Viscount Lisburne
Adam Loftus, 1st Viscount Lisburne (1647 – 15 September 1691) was an Anglo-Irish peer and military commander. He was the second son of Sir Arthur Loftus of Rathfarnham, co. Dublin and Lady Dorothy Boyle, daughter of Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork. His paternal grandfather was Adam Loftus. He was Ranger of Phoenix Park and of the King's parks in Ireland and a Master of the Court of Requests. From 1685 he was a member of the Privy Council of Ireland and on 29 January 1686, King James II created him Baron of Rathfarnham and Viscount Lisburne in the Peerage of Ireland. A Roman Catholic, he nevertheless took the Whig side in the Glorious Revolution and in 1689 commanded an English regiment in Ireland as the first Colonel of the 39th (Dorsetshire) Regiment of Foot. On 15 September 1691 he was killed by a cannonball at the Siege of Limerick. He had married twice: firstly Lucy, the second daughter of George Brydges, 6th Baron Chandos, with whom he had a daughter, Lucy and seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudley Loftus
Dr Dudley Loftus (1619 – June 1695) was an Anglo-Irish jurist and noted orientalist. Loftus was born the second son of Sir Adam Loftus and his wife Jane Vaughan, daughter of Walter Vaughan, into a family of 17 siblings on his great-grandfather’s estate of Rathfarnham Castle, Dublin. He graduated from Trinity College, Dublin when 18, then entered Oxford University in 1639 on the advice of Bishop Usher, taking his Master of Arts degree in 1641. In his lifetime he was acclaimed as a linguist, and his reputation as an orientalist was unrivalled thanks to his Latin translations from Ethiopic, Armenian, Syriac, Hebrew, Arabic, and Persian texts. He served four times as a Member of the Irish House of Commons, representing Naas between 1642 and 1648, the combined counties of Kildare and Wicklow in the Third Protectorate Parliament of 1659 at Westminster, Bannow between 1661 and 1666 and Fethard between 1692 and 1693. He was also Vicar General of Ireland, Judge of the Prerogati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Loftus
Sir Arthur Loftus (died 27 May 1665) was an Anglo-Irish politician and landowner. He was the son of Sir Adam Loftus and Jane Vaughan. His grandfather was Sir Dudley Loftus. He served as the Member of Parliament for County Wexford in the 1639–49 parliament and was Provost Marshal of Ulster. He was knighted by Charles II. He lived at Rathfarnham, County Dublin. Loftus married Lady Dorothy Boyle, daughter of Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork and Catherine Fenton, in 1627. However, the Earl of Cork in his diaries records their marriage on Shrove Monday, 13 February 1632 (1631 Old Style). Their son was Adam Loftus, 1st Viscount Lisburne and their daughter, Lettice, married Humphrey Coningsby. References Date of birth unknown 1665 deaths 17th-century Anglo-Irish people 17th-century Irish landowners Irish MPs 1639–1649 Knights Bachelor Arthur Arthur is a masculine given name of uncertain etymology. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland () was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until the end of 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two chambers: the Irish House of Commons, House of Commons and the Irish House of Lords, House of Lords. The Lords were members of the Peerage of Ireland, Irish peerage ('Lords Temporal, lords temporal') and Bishop, bishops ('Lords Spiritual, lords spiritual'; after the Reformation, Church of Ireland bishops). The Commons was directly elected, albeit on a very restricted Suffrage, franchise. Parliaments met at various places in Leinster and Munster, but latterly always in Dublin: in Christ Church Cathedral, Dublin, Christ Church Cathedral (15th century),Richardson 1943 p.451 Dublin Castle (to 1649), Chichester House (1661–1727), the The King's Hospital, Blue Coat School (1729–31), and finally a purpose-built Parliament House, Dublin, Parliament House on College G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |