|
Acres
The acre ( ) is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac, but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".National Institute of Standards and Technolog(n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement . Traditionally, in the Middle Ages, an acre was conceived of as the area of land that could be ploughed by one man using a team of eight oxen in one day. The acre is still a statutory measure in the United States. Both the international acre and the US survey acre are in use, but they differ by only four parts per mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Units
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, related but differing system of United States customary units, customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester measure, Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had metrication, officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod (unit)
The rod, perch, or pole (sometimes also lug) is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units, it is defined as feet, equal to exactly of a mile, or yards (a quarter of a surveyor's chain), and is exactly 5.0292 meters. The rod is useful as a unit of length because integer multiples of it can form one acre of square measure (area). The 'perfect acre' is a rectangular area of 43,560 square feet, bounded by sides 660 feet (a furlong) long and 66 feet (a chain) wide (220 yards by 22 yards) or, equivalently, 40 rods by 4 rods. An acre is therefore 160 square rods or 10 square chains. The name ''perch'' derives from the Ancient Roman unit, the '' pertica''. The measure also has a relationship with the military pike of about the same size. Both measures date from the sixteenth century, when the pike was still utilized in national armies. The tool has been supplanted, first by steel tapes and later by el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain (unit)
The chain (abbreviated ch) is a unit of length equal to 66 feet (22 yards), used in both the US customary and Imperial unit systems. It is subdivided into 100 links. (PDF) There are 10 chains in a furlong, and 80 chains in one statute mile. In metric terms, it is 20.1168 m long. By extension, chainage (running distance) is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, as given by an odometer. The chain has been used since the early 17th century in England, and was brought by British settlers during the colonial period to other countries around the globe. In the United Kingdom, there were 80 chains to the mile, but until the early nineteenth century the Scottish and Irish customary miles were longer than the statute mile; consequently a Scots chain was about 74 (imperial) feet, an Irish chain 84 feet. These longer chains became obsolete following the adoption of the imperial system of units in 1824. In India, "metric chains" of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute Measure
Weights and Measures Acts are acts of the British Parliament determining the regulation of weights and measures. It also refers to similar royal and parliamentary acts of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland and the medieval Welsh states. The earliest of these were originally untitled but were given descriptive glosses or titles based upon the monarch under whose reign they were promulgated. Several omnibus modern acts have the short title " Weights and Measures Act" and are distinguished by the year of their enactment. Background There have been many laws concerned with weights and measures in the United Kingdom or parts of it over the last 1,000 or so years. The acts may catalogue lawful weights and measures, prescribe the mechanism for inspection and enforcement of the use of such weights and measures and may set out circumstances under which they may be amended. Modern legislation may, in addition to specific requirements, set out circumstances under which the incumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furlong
A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one-eighth of a mile, equivalent to any of 660 foot (unit), feet, 220 yards, 40 rod (unit), rods, 10 chain (unit), chains, or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in horse racing, where in many countries it is the standard measurement of race lengths, and agriculture, where it is used to measure rural field lengths and distances. In the United States, some states use older definitions for surveying purposes, leading to variations in the length of the furlong of two parts per million, or about . This variation is small enough to not have practical consequences in most applications. Using the International yard and pound, international definition of the yard as exactly 0.9144 metres, one furlong is 201.168 metres, and five furlongs are about 1 kilometre ( exactly). History The name ''furlong'' derives from the Old Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrication In Australia
Metrication in Australia effectively began in 1966 with the Decimalisation#Australia and New Zealand, conversion to decimal currency under the auspices of the Decimal Currency Board. The conversion of measurements—metrication—started in 1971 under the direction of the Metric Conversion Board, and actively proceeded until the Board was disbanded in 1981. Before 1970, Australia mostly used imperial units of measurement, as a legacy of being a colony of the United Kingdom. Between 1970–88, imperial units were withdrawn from general legal use and replaced with the International System of Units, facilitated through legislation and government agencies. SI units are now the only legal units of measurement in Australia. Australia's largely successful transition to the metric system parallels that of metrication in New Zealand but contrasts with metrication in the United States, metrication in the United Kingdom, and metrication in Canada which was only partial. History Although t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
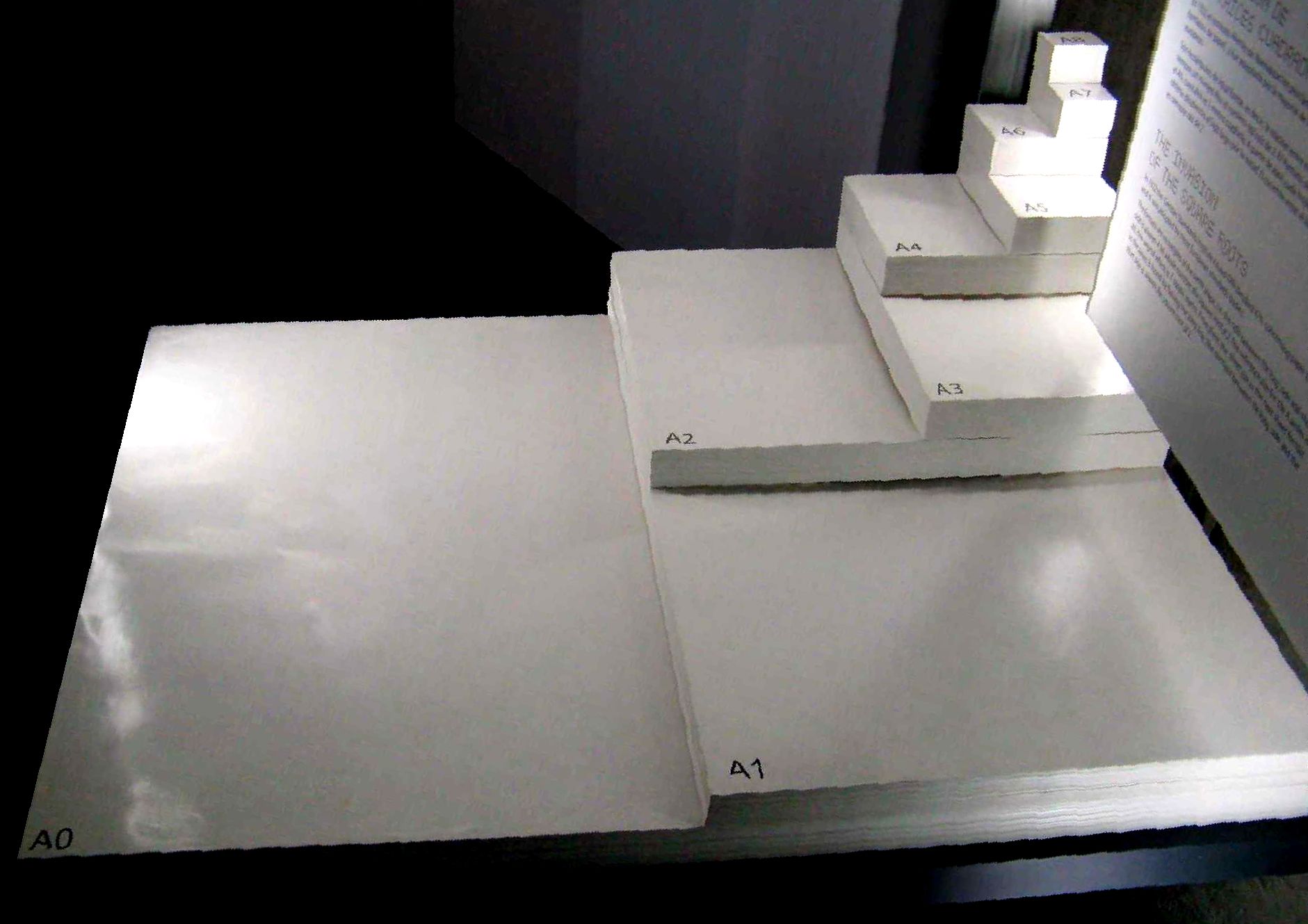
Paper Size
Paper size refers to Technical standard, standardized dimensions for sheets of paper used globally in stationery, printing, and technical drawing. Most countries adhere to the ISO 216 standard, which includes the widely recognized A series (including A4 paper), defined by a consistent aspect ratio of √2. The system, first proposed in the 18th century and formalized in 1975, allows scaling between sizes without distortion. Regional variations exist, such as the #North American paper sizes, North American paper sizes (e.g., Letter (paper size), Letter, Legal paper, Legal, and Ledger paper, Ledger) which are governed by the American National Standards Institute, ANSI and are used in North America and parts of Central and South America. The standardization of paper sizes emerged from practical needs for efficiency. The ISO 216 system originated in late-18th-century Germany as Deutsches Institut für Normung, DIN 476, later adopted internationally for its mathematical precision. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US National Geodetic Survey
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a United States federal agency based in Washington, D.C. that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication, mapping and charting, and a large number of science and engineering applications. Since its founding in 1970, it has been part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a division within the Department of Commerce. History The National Geodetic Survey's history and heritage are intertwined with those of other NOAA offices. It traces its history to the Survey of the Coast, which was formed in 1807 as the first scientific agency of the U.S. federal government. It became the United States Coast Survey in 1836 and the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1878, the latter name change reflecting the increasing role of geodesy in its work. Upon the creation of NOAA in 1970, the Coast and Geodetic Survey was abolished and its responsibilities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Registration
Land registration is any of various systems by which matters concerning ownership, Possession (law), possession, or other rights in Real estate, land are formally recorded (usually with a government agency or department) to provide evidence of title (property), title, facilitate transactions, and prevent unlawful disposal. The information recorded and the protection provided by land registration varies widely by jurisdiction. In common law countries, particularly in jurisdictions in the Commonwealth of Nations, when replacing the deeds registration system, title registrations are broadly classified into two basic types: the Torrens title system and the English system, a modified version of the Torrens system.Lyall, Andrew. ''Land Law in Ireland''. ; Ch. 24 Cadastre, Cadastral systems and land registration are both types of land recording and complement each other.Jo Henssen, BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE MAIN CADASTRAL SYSTEMS IN THE WORLD, Implementations Americas Canada Falk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geodetic Survey
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a List of federal agencies in the United States, United States federal agency based in Washington, D.C. that defines and manages a national geographic coordinate system, coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication, mapping and charting, and a large number of science and engineering applications. Since its founding in 1970, it has been part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a division within the United States Department of Commerce, Department of Commerce. History The National Geodetic Survey's history and heritage are intertwined with those of other NOAA offices. It traces its history to the Survey of the Coast, which was formed in 1807 as the first scientific agency of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government. It became the United States Coast Survey in 1836 and the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1878, the latter name change refle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendenhall Order
The Mendenhall Order marked a decision to change the fundamental standards of length and mass of the United States from the customary standards based on those of England to metric standards. It was issued on April 5, 1893, by Thomas Corwin Mendenhall, superintendent of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, with the approval of the United States Secretary of the Treasury, John Griffin Carlisle. The order was issued as the Survey's ''Bulletin No. 26 – Fundamental Standards of Length and Mass''. Standards before the order In October 1834, the United Kingdom Houses of Parliament were destroyed in a fire, and the British standards of length and mass were also destroyed. "When the new imperial standards to replace them were completed in 1855, two copies of the yard and one copy of the avoirdupois pound were presented to the United States". These were superior to the yard then in use, so one of them was adopted as the United States national standard yard. These yards were tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yard
The yard (symbol: yd) is an English units, English unit of length in both the British imperial units, imperial and US United States customary units, customary systems of measurement equalling 3 foot (unit), feet or 36 inches. Since 1959 it has been by international yard and pound, international agreement standardized as exactly 0.9144 Metre, meter. A distance of 1,760 yards is equal to 1 mile. The theoretical survey foot, US survey yard is very slightly longer. Name The term, ''yard'' derives from the Old English , etc., which was used for branches, staves and measuring rods. It is first attested in the late 7th century Ine of Wessex#Laws, laws of Ine of Wessex, wherein the "yard of land" mentioned is the virgate, yardland, an old English unit of tax assessment equal to hide (unit), hide. Around the same time the Lindisfarne Gospels account of the messengers from John the Baptist in the Gospel of Matthew used it for a branch swayed by the wind. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |