|
Acis
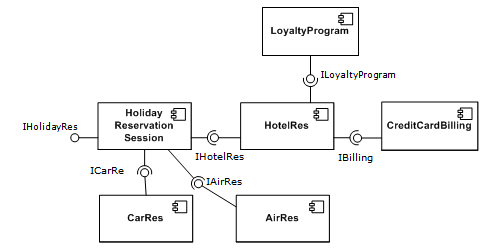
The 3D ACIS Modeler (ACIS) is a geometric modeling kernel developed by Spatial Corporation (formerly Spatial Technology), part of Dassault Systèmes. ACIS is used by software developers in industries such as computer-aided design, computer-aided manufacturing, computer-aided engineering, architecture, engineering and construction, coordinate-measuring machine, 3D animation, and shipbuilding. ACIS provides software developers and manufacturers the underlying 3D modeling functionality. ACIS features an object-oriented C++ architecture with 3D modelling capabilities. ACIS is used to construct applications with hybrid modeling features, since it integrates wireframe model, surface, and solid modeling functionality with both manifold and non-manifold topology, and a set of geometric operations. History As a geometric kernel, ACIS is a second generation system, coming after the first generation Romulus. There are several versions about what the word ACIS actually stands f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Corp
Spatial Corporation was founded in 1986, and had one main product: ACIS, the first commercially available 3D modeling kernel. Through subsequent years, Spatial added products to its portfolio that enabled independent software vendors (ISVs), mostly in the industries of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), known as CAD/CAM, to build applications. These components included extensions and updates to the ACIS modeler, visualization products, and acquisitions in translator technology. In late 2000, Dassault Systèmes purchased Spatial and made it a subsidiary. Flagship products The firm's flagship products include these programs: * 3D ACIS Modeler – features an open, object-oriented C++ architecture that enables robust, 3D modeling abilities. It is a geometric modeling kernel that was developed by Spatial, and is used in industries such as 3Danimation, shipbuilding, and computer-aided design. * CGM Modeler – the 3D modeling kernel used in Dassaul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface (topology)
In the part of mathematics referred to as topology, a surface is a two-dimensional manifold. Some surfaces arise as the boundaries of three-dimensional solid figures; for example, the sphere is the boundary of the solid ball. Other surfaces arise as graphs of functions of two variables; see the figure at right. However, surfaces can also be defined abstractly, without reference to any ambient space. For example, the Klein bottle is a surface that cannot be embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Topological surfaces are sometimes equipped with additional information, such as a Riemannian metric or a complex structure, that connects them to other disciplines within mathematics, such as differential geometry and complex analysis. The various mathematical notions of surface can be used to model surfaces in the physical world. In general In mathematics, a surface is a geometrical shape that resembles a deformed plane. The most familiar examples arise as boundaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in which simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Another way to distinguish between the terms is to define simulation as experimentation with the help of a model. This definition includes time-independent simulations. Often, computer simulation, computers are used to execute the simulation. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance tuning or optimizing, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NURBS
Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is a mathematical model using basis splines (B-splines) that is commonly used in computer graphics for representing curves and surfaces. It offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analytic (defined by common mathematical formulae) and modeled shapes. It is a type of curve modeling, as opposed to polygonal modeling or digital sculpting. NURBS curves are commonly used in computer-aided design (CAD), manufacturing (CAM), and engineering (CAE). They are part of numerous industry-wide standards, such as IGES, STEP, ACIS, and PHIGS. Tools for creating and editing NURBS surfaces are found in various 3D graphics, rendering, and animation software packages. They can be efficiently handled by computer programs yet allow for easy human interaction. NURBS surfaces are functions of two parameters mapping to a surface in three-dimensional space. The shape of the surface is determined by control points. In a compact form, NURB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-spline
In numerical analysis, a B-spline (short for basis spline) is a type of Spline (mathematics), spline function designed to have minimal Support (mathematics), support (overlap) for a given Degree of a polynomial, degree, smoothness, and set of breakpoints (Knot (mathematics), knots that partition its Domain of a function, domain), making it a fundamental building block for all spline functions of that degree. A B-spline is defined as a piecewise polynomial of Order (mathematics), order n, meaning a degree of n - 1. It’s built from sections that meet at these knots, where the continuity of the function and its Derivative, derivatives depends on how often each knot repeats (its multiplicity). Any spline function of a specific degree can be uniquely expressed as a linear combination of B-splines of that degree over the same knots, a property that makes them versatile in mathematical modeling. A special subtype, cardinal B-splines, uses equidistant knots. The concept of B-splines tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Component
A software component is a modular unit of software that encapsulates specific functionality. The desired characteristics of a component are reusability and maintainability. Value Components allow software development to assemble software with reliable parts rather than writing code for every aspect; allowing for implementation to be more like factory assembly than custom building. Attributes Desirable attributes of a component include but are not limited to: * Cohesive encapsulates related functionality * Reusable * Robust * ''Substitutable'' can be replaced by another component with the same interface * Documented * Tested Third-party Some components are built in-house by the same organization or team building the software system. Some are third-party, developed elsewhere and assembled into the software system. Component-based software engineering For large-scale systems, component-based development encourages a disciplined process to manage comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California, where the company would remain headquartered for the remainder of its lifetime; this HP Garage is now a designated landmark and marked with a plaque calling it the "Birthplace of 'Silicon Valley. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components, as well as software and related services, to consumers, small and medium-sized businesses (small and medium-sized enterprises, SMBs), and fairly large companies, including customers in government sectors, until the company officially split into Hewlett Packard Enterprise and HP Inc. in 2015. HP initially produced a line of electronic test and measurement equipment. It won its first big contract in 1938 to provide the HP 200B, a variation of its first product, the HP 200A low-distor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each word in all caps with no punctuation. For some, an initialism or alphabetism connotes this general meaning, and an ''acronym'' is a subset with a narrower definition; an acronym is pronounced as a word rather than as a sequence of letters. In this sense, ''NASA'' () is an acronym, but ''United States, USA'' () is not. The broader sense of ''acronym'', ignoring pronunciation, is its original meaning and in common use. . Dictionary and style-guide editors dispute whether the term ''acronym'' can be legitimately applied to abbreviations which are not pronounced as words, and they do not agree on acronym space (punctuation), spacing, letter case, casing, and punctuation. The phrase that the acronym stands for is called its . The of an acron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |