|
Achim Zeman
Achim Zeman (born 1961 in Stuttgart) is a German painter and installation artist. He is a representative of Op-Art and is based on the rules of Concrete Art. Biography Zeman studied at the Berlin University of the Arts from 1983 to 1989 and was awarded "Master scholar" (Meisterschüler) by Professor Kuno Gonschior. Inspired by him, Zeman discovered the artistic configuration of rooms with the means of painting as an area of his artistic work. In 1990 he received a scholarship from the "Kunststiftung Baden-Württemberg", in the following year a working scholarship from the City state of Berlin. Zeman is a member of the "Westdeutscher Künstlerbund". Since 1992 he lives and works in Cologne, Germany. Artistic work Panel paintings Zeman works with basic geometric shapes such as lines, circles and squares. These can be found not only in his spatial installations, but also in his panel paintings. He does not apply the color on canvases, but to acrylic glass sheets, which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 635,911, making it the sixth largest city in Germany. 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and 5.3 million people in its metropolitan area, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the top 20 European metropolitan areas by GDP; Mercer listed Stuttgart as 21st on its 2015 list of cities by quality of living; innovation agency 2thinknow ranked the city 24th globally out of 442 cities in its Innovation Cities Index; and the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked the city as a Beta-status global city in their 2020 survey. Stuttgart was one of the host cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(methyl Methacrylate)
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. Although not a type of familiar silica-based glass, the substance, like many thermoplastics, is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate. It was developed in 1928 in several different laboratories by many chemists, such as William Chalmers, Otto Röhm, and Walter Bauer, and first brou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Dance
Ice dance (sometimes referred to as ice dancing) is a discipline of figure skating that historically draws from ballroom dancing. It joined the World Figure Skating Championships in 1952, and became a Winter Olympic Games medal sport in 1976. According to the International Skating Union (ISU), the governing body of figure skating, an ice dance team consists of one woman and one man. Ice dance, like pair skating, has its roots in the "combined skating" developed in the 19th century by skating clubs and organizations and in recreational social skating. Couples and friends would skate waltzes, marches, and other social dances. The first steps in ice dance were similar to those used in ballroom dancing. In the late 1800s, American Jackson Haines, known as "the Father of Figure Skating", brought his style of skating, which included waltz steps and social dances, to Europe. By the end of the 19th century, waltzing competitions on the ice became popular throughout the world. By the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
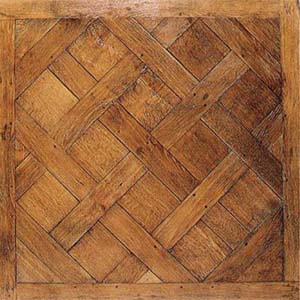
Parquetry
Parquet (; French for "a small compartment") is a geometric mosaic of wood pieces used for decorative effect in flooring. Parquet patterns are often entirely geometrical and angular—squares, triangles, lozenges—but may contain curves. The most popular parquet flooring pattern is herringbone. Etymology The word derives from the Old French ''parchet'' (the diminutive of ''parc''), literally meaning "''a small enclosed space''". History Large diagonal squares known as ''parquet de Versailles'' were introduced in 1684 as ''parquet de menuiserie'' ("woodwork parquet") to replace the marble flooring that required constant washing, which tended to rot the joists beneath the floors. Such ''parquets en losange'' were noted by the Swedish architect Daniel Cronström at Versailles and at the Grand Trianon in 1693. Materials Timber contrasting in color and grain, such as oak, walnut, cherry, lime, pine, maple etc. are sometimes employed, and in the more expensive kinds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Code
A binary code represents text, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system. The two-symbol system used is often "0" and "1" from the binary number system. The binary code assigns a pattern of binary digits, also known as bits, to each character, instruction, etc. For example, a binary string of eight bits (which is also called a byte) can represent any of 256 possible values and can, therefore, represent a wide variety of different items. In computing and telecommunications, binary codes are used for various methods of encoding data, such as character strings, into bit strings. Those methods may use fixed-width or variable-width strings. In a fixed-width binary code, each letter, digit, or other character is represented by a bit string of the same length; that bit string, interpreted as a binary number, is usually displayed in code tables in octal, decimal or hexadecimal notation. There are many character sets and many character encodings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergisch-Gladbach
Bergisch Gladbach () is a city in the Cologne/Bonn Region of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, and capital of the Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis (district). Geography Bergisch Gladbach is located east of the river Rhine, approx. 10 kilometers east of Cologne. Neighbouring municipalities Beginning in the north clockwise the neighbouring municipalities and neighbouring towns are: Odenthal, Kürten, Overath, Rösrath, Cologne and Leverkusen. History Early settlements existed in the 13th century, but the town was officially founded in 1856. The word ''Bergisch'' in the name does not originate from its location in the county of Berg and was not added to distinguish it from Mönchengladbach as believed by many people, but from the counts who gave their name to the region. At the start of the 12th century the counts of Berg settled in the area and it later became the duchy (under Napoleon, the grand duchy) of Berg. This is where the first part of the name (''Bergisch'') comes from, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radevormwald
Radevormwald (; ksh, Radefürmwald) is a municipality in the Oberbergischer Kreis, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is one of the oldest towns in the Bergischen Land, formerly the County and Duchy of Berg. Geography Radevormwald is located about 50 km east of Cologne. At 421 metres above sea level, it was the highest-situated town in the administrative region of Düsseldorf; it is now in the administrative region of Cologne. Neighbouring places * Ennepetal * Breckerfeld * Halver * Wipperfürth * Hückeswagen * Remscheid * Wuppertal * Schwelm Division of the municipality Places submerged by the Wuppertal dam * Dörpe * Friedrichstal * Nagelsberger Gemarke * Oege Wupper villages The river Wupper flows through part of the town lands. In the villages Dahlerau, Vogelsmühle and Dahlhausen – which are located in the Wupper valley and so are known as the "Wupper villages" – this led to the establishment of textile works. These settlements used the water for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors ( fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinisches Landesmuseum Bonn
The Rheinisches Landesmuseum Bonn, or LVR-LandesMuseum Bonn, is a museum in Bonn, Germany, run by the Rhineland Landscape Association. It is one of the oldest museums in the country. In 2003 it completed an extensive renovation. The museum has a number of notable ancient busts and figures dating back to Roman times. History An early forerunner, the "Museum of Antiquities" (''Museum Rheinisch-Westfälischer Alterthümer''), was founded in 1820 by decree of the Prussian state chancellor Karl August von Hardenberg. A more direct ancestor, the "Provincial Museum", was founded in 1874, though it did not get its own building until 1893. This was enlarged in 1907, but the older section was destroyed during World War II and replaced by a new building. The museum was extensively renovated from 1998 to 2003, allowing a new presentation of the exhibits. The "Stone Age Area" was redesigned in 2010. Permanent exhibitions The archaeological exhibits are divided into historical themes, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation. The use of adhesives offers certain advantages over other binding techniques such as sewing, mechanical fastenings, or welding. These include the ability to bind different materials together, the more efficient distribution of stress across a joint, the cost-effectiveness of an easily mechanized process, and greater flexibility in design. Disadvantages of adhesive use include decreased stability at high temperatures, relative weakness in bonding large objects with a small bonding surface area, and greater difficulty in separating objects during testing. Adhesives are typically organized by the method of adhesion followed by ''reactive'' or ''non-reactive'', a term which refers to whether the adhesive chemically reacts in order to harden. Alternatively, they can be organized eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Film
Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces. Plastic films are used in a wide variety of applications. These include: packaging, plastic bags, labels, building construction, landscaping, electrical fabrication, photographic film, film stock for movies, video tape, etc. Materials Almost all plastics can be formed into a thin film. Some of the primary ones are: * Polyethylene – The most common plastic film is made of one of the varieties of polyethylene: low-density polyethylene, medium-density polyethylene, high-density polyethylene, or linear low-density polyethylene. * Polypropylene – Polypropylene can be made a cast film, biaxially oriented film (BOPP), or as a uniaxially oriented film. * Polyester – BoPET is a biaxially oriented polyester film. * Nylon – BOPA/BON ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtractive Color
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and inks are used in color printing and photography where the perception of color is elicited after white light passes through microscopic "stacks" of partially absorbing media allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye and not others. Process The subtractive color mixing model predicts the resultant spectral power distribution of light filtered through overlaid partially absorbing materials on a reflecting or transparent surface. Each layer partially absorbs some wavelengths of light from the illumination spectrum while letting others pass through, resulting in a colored appearance. The resultant spectral power distribution is predicted by sequentially taking the product of the spectral power distributions of the incoming light and transmis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |