|
Ace Lake
The Ace Lake is a deep salt water lake on the Ingrid-Christensen coast of the Princess Elisabeth land in East Antarctica. The lake is located on the Langnes peninsula in the Vestfold Hills near the Organic Lake. Australian biologists at Davis Station explored the lake in 1974 after searching for a saltwater lake with copepods for nine months. The researchers interpreted their discovery as ace, which gave the lake its name. Between 2004 and 2005 a mountain hut was built on the shores of the lake. In 2013, Zhou et al. discovered a new virophage species by metagenomical analysis, the Ace-Lake-Mavirus (ALM), similar to a short time ago in Organic Lake (OLV) and also in Yellowstone Lake (YSLV). ALM belongs to the virophage genus Mavirus; as a virophage, it is a satellite virus that (as a parasite), when co-infected with a helper virus (host), impairs its ability to replicate. ALV presumably parasitizes species of the Mimiviridae virus family.J. Zhou, W. Zhang, S. Yan, J. Xiao, Y. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Elizabeth Land
Princess Elizabeth Land is the sector of Antarctica between longitude 73° east and Cape Penck (at 87°43' east). The sector is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory, although this claim is not widely recognized. Geography Princess Elizabeth Land is located between 64°56'S and 90°00'S and between 73°35' E and 87°43'E. It is divided into two sectors: * Ingrid Christensen Coast, 73°35'E to 81°24'E * Leopold and Astrid Coast, 81°24'E to 87°43'E It is bounded on the west by Amery Ice Shelf, Mac. Robertson Land, and on the east by Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Exploration Princess Elizabeth Land was discovered on 9 February 1931, by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) (1929–31) under Sir Douglas Mawson. Princess Elizabeth Land was named by Mawson after Princess Elizabeth, granddaughter of King George V who reigned at the time as King of Australia, among his other titles. Princess Elizabeth would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Gazetteer Of Antarctica
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Virology
The ''Journal of Virology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers research concerning all aspects of virology. It was established in 1967 and is published by the American Society for Microbiology The American Society for Microbiology (ASM), originally the Society of American Bacteriologists, is a professional organization for scientists who study viruses, bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa as well as other aspects of microbiology. It w .... Research papers are available free online four months after print publication. The editor-in-chief is Rozanne M. Sandri-Goldin (University of California, Irvine, California) (2012–present). Past editors-in-chief include Lynn W. Enquist (2002–2012), Thomas Shenk (1994–2002), and Arnold J. Levine (1984–1994). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimiviridae
''Mimiviridae'' is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family is divided in up to 4 subfamilies., UCPMS ID: 1889607PDF/ref> Fig. 4 and §Discussion: "Considering that tupanviruses comprise a sister group to amoebal mimiviruses…" Viruses in this family belong to the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus clade (NCLDV), also referred to as giant viruses. ''Mimiviridae'' is the sole recognized member of order ''Imitervirales''. '' Phycodnaviridae'' and '' Pandoraviridae'' of '' Algavirales'' are sister groups of ''Mimiviridae'' in many phylogenetic analyses. History The first member of this family, Mimivirus, was discovered in 2003, and the first complete genome sequence was published in 2004. However, the mimivirus Cafeteria roenbergensis virus was isolated and partially characterized in 1995, although the host was misidentified at the time, and the virus was designated BV-PW1. Taxonomy Group: dsDNA Family ''Mimiviridae'' is currentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helper Virus
A helper virus is a virus that allows an otherwise-deficient coinfecting virus to replicate. These can be naturally occurring as with Hepatitis D virus, which requires Hepatitis B virus to coinfect cells in order to replicate. Helper viruses are also commonly used to replicate and spread viral vectors for gene expression and gene therapy. See also * Helper dependent virus * Virophage Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for ... References Virology {{virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Virus
A satellite is a subviral agent that depends on the coinfection of a host cell with a helper virus for its replication. Satellites can be divided into two major classes: satellite viruses and satellite nucleic acids. Satellite viruses, which are most commonly associated with plants, are also found in mammals, arthropods, and bacteria. They encode structural proteins to enclose their genetic material, which are therefore distinct from the structural proteins of their helper viruses. Satellite nucleic acids, in contrast, do not encode their own structural proteins, but instead are encapsulated by proteins encoded by their helper viruses. The genomes of satellites range upward from 359 nucleotides in length for satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA (STobRV). Most viruses have the capability to use host enzymes or their own replication machinery to independently replicate their own viral RNA. Satellites, in contrast, are completely dependent on a helper virus for replication. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mavirus
''Mavirus'' is a genus of double stranded DNA virus that can infect the marine phagotrophic flagellate ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'', but only in the presence of the giant '' CroV'' virus (''Cafeteria roenbergensis''). The genus contains only one species, ''Cafeteriavirus-dependent mavirus''. ''Mavirus'' can integrate into the genome of cells of ''C. roenbergensis'', and thereby confer immunity to the population The name is derived from Maverick virus. The virophage was discovered by Matthias G. Fischer of the University of British Columbia while he was working on Cafeteria roenbergensis virus as part of his PhD. __TOC__ Virology The genome is 19,063 bases in length and encodes 20 predicted coding sequences. Seven have homology to the Maverick/ Polinton family of transposons. The genome encodes a retroviral integrase, an adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), a cysteine protease and a protein primed DNA polymerase B. Classification ''Mavirus'' is a genus in the family ''Lavida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowstone Lake
Yellowstone Lake is the largest body of water in Yellowstone National Park. The lake is above sea level and covers with of shoreline. While the average depth of the lake is , its greatest depth is at least . Yellowstone Lake is the largest freshwater lake above in North America. In winter, ice nearly thick covers much of the lake except where shallow water covers hot springs. The lake freezes over by early December and can remain frozen until late May or early June. History The forest and valleys surrounding Yellowstone Lake had been populated with Native Americans since pre-historic times. Archeologists have found evidence of human presence in the park long before 1872. They found that Native Americans hunted bison and bighorn sheep, fished for Cutthroat Fish, and gathered bitterroot and camas bulbs for at least 11,000 years. Also 26 tribes claim cultural association with Yellowstone today. The first human of European descent to see the lake was trapper John Colter in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
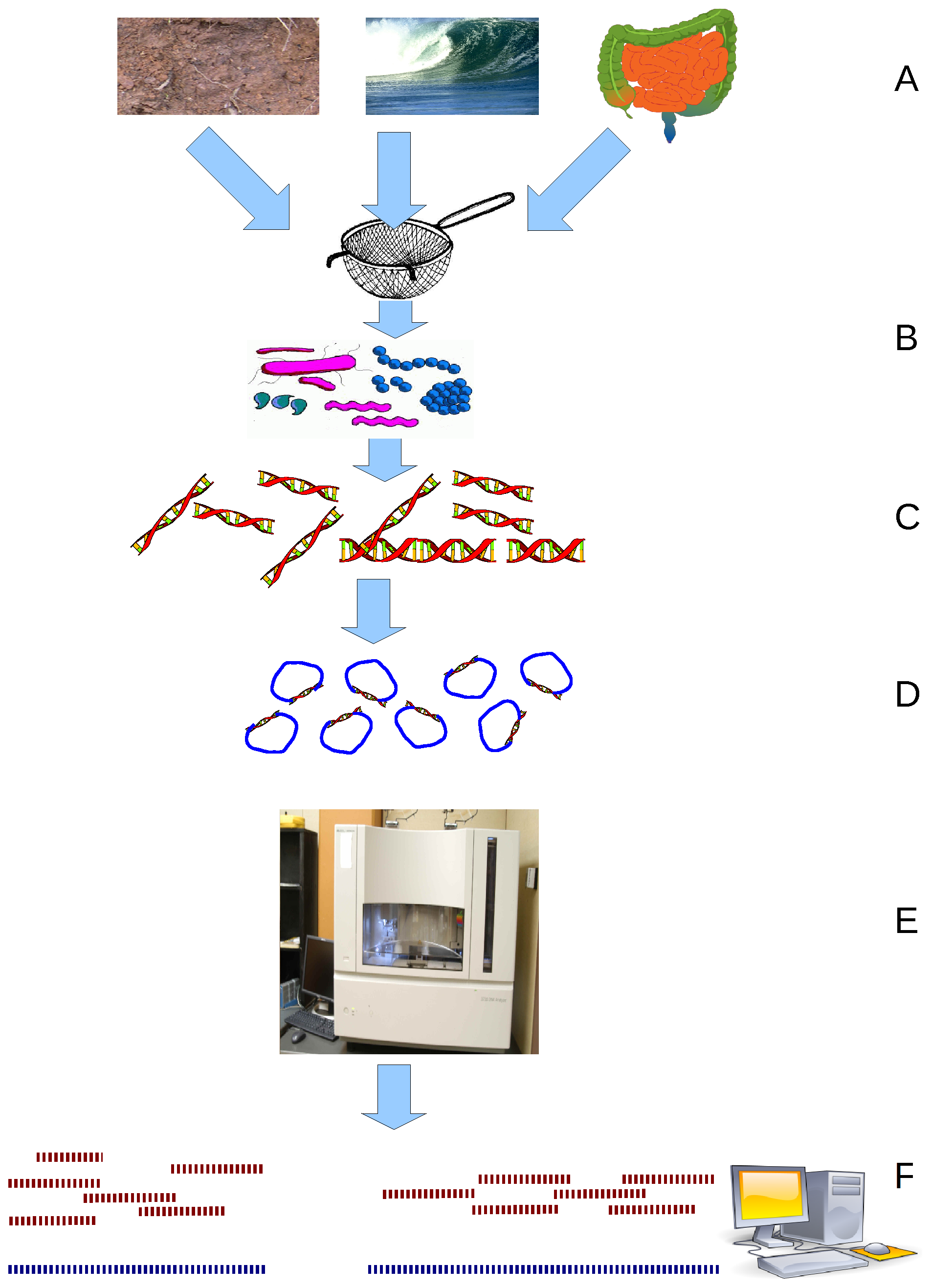
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)