|
Accipiter (horse)
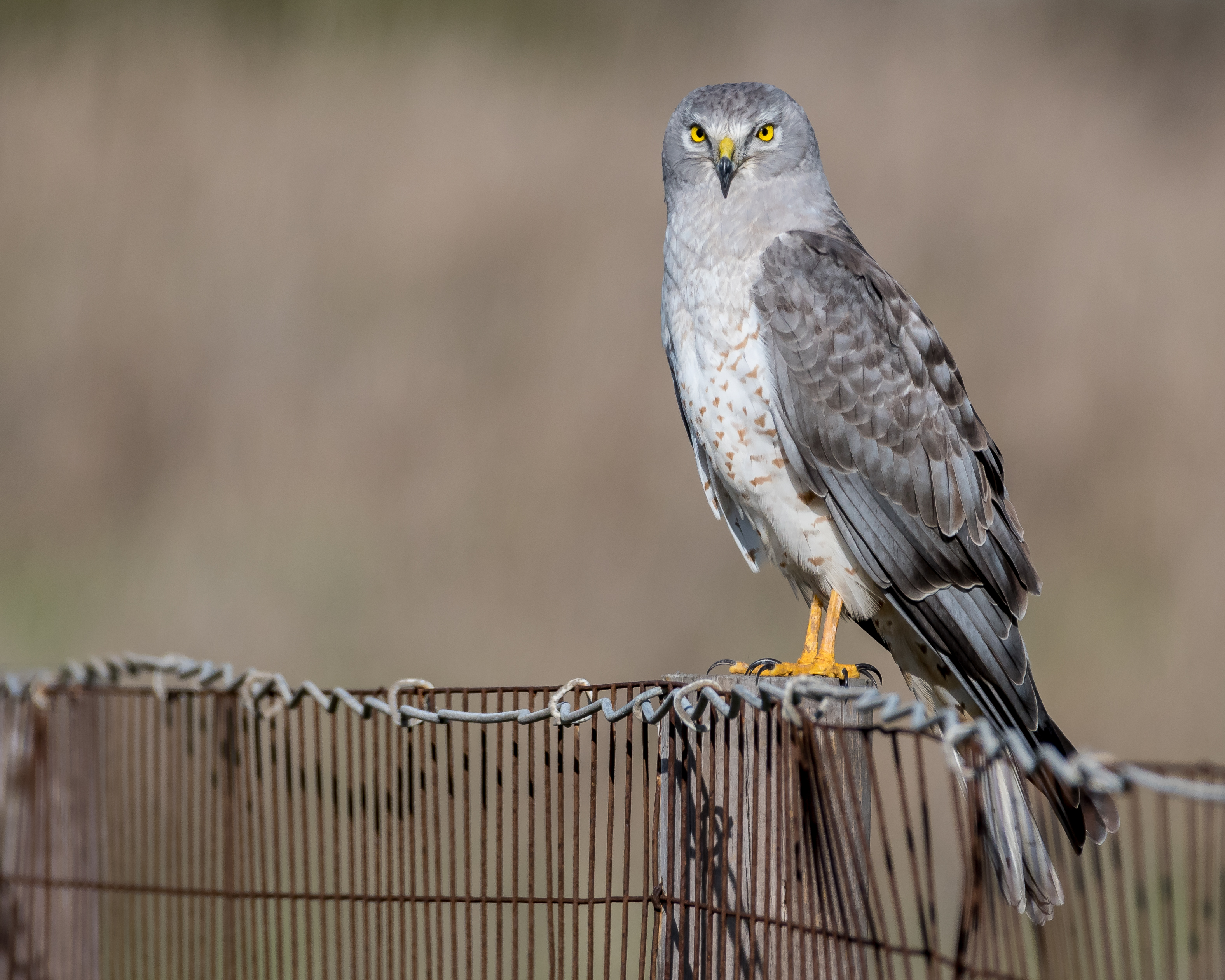
''Accipiter'' () is a genus of birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. With 49 recognized species it is the most diverse genus in its family. Most species are called goshawks or sparrowhawks, although almost all New World species (excepting the northern goshawk) are simply known as hawks. They can be anatomically distinguished from their relatives by the lack of a procoracoid foramen. Two small and aberrant species usually placed here do possess a large procoracoid foramen and are also distinct as regards DNA sequence. They may warrant separation in the old genus ''Hieraspiza''.Olson (2006) Extant accipiters range in size from the little sparrowhawk (''A. minullus''), in which the smallest males measure long, span across the wings and weigh , to the northern goshawk (''A. gentilis''), in which the largest females measure long, span across the wings, and weigh . These birds are slender with short, broad, rounded wings and a long tail which helps them maneuver in flight. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collared Sparrowhawk
The collared sparrowhawk (''Accipiter cirrocephalus'') is a small, slim bird of prey in the family Accipitridae found in Australia, New Guinea and nearby smaller islands. As its name implies the collared sparrowhawk is a specialist in hunting small birds. It is characterised by its slight brow ridges and slender feet. The last segment of their middle toe projects beyond the claws of the other toes. Description The collared sparrowhawk is 29–38 cm (tail about half ), with a wingspan 55–78 cm, the average male weighs 126 g, female 218 g. They are small, fierce, finely built with rounded wings, long square tail, yellow eyes and long legs. Adults have slate-grey upper parts, sometimes with a brown wash, and a chestnut half collar. The underparts are finely barred rufous and white. The under wing and tail are finely barred. The cere is cream to olive-yellow, the eyes yellow and the legs and feet yellow. The sexes are similar in appearance but males are smaller than fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Biology
The term population biology has been used with different meanings. In 1971 Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hastings used the term in 1997 as the title of his book on the mathematics used in population dynamics. The name was also used for a course given at UC Davis in the late 2010s, which describes it as an interdisciplinary field combining the areas of ecology and evolutionary biology. The course includes mathematics, statistics, ecology, genetics, and systematics Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic t .... Numerous types of organisms are studied. The journal '' Theoretical Population Biology'' is published. See also References External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Status
The conservation status of a group of organisms (for instance, a species) indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status exist and are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels as well as for consumer use. International systems IUCN Red List of Threatened Species The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species is the best known worldwide conservation status listing and ranking system. Species are classified by the IUCN Red List into nine groups set through criteria such as rate of decline, population size, area of geographic distribution, and degree of population and distribution fragmentation. Also included are species that have gone e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (which may be shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus '' Homo'' and within this genus to the species '' Homo sapiens''. '' Tyrannosaurus rex'' is likely the most widely known binomial. The ''formal'' introduction of this system of naming species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Sundas Goshawk
The Lesser Sundas goshawk (''Accipiter hiogaster sylvestris'') is a bird of prey native to Indonesia. It is sometimes elevated to species status, but the IOC lumps it together with the variable goshawk The variable goshawk (''Accipiter hiogaster'') is a bird of prey native to Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. It was recently elevated to species status, and was previously lumped together with the grey goshawk The grey gos ... (''A. hiogaster''). References Lesser Sundas goshawk Birds of the Lesser Sunda Islands Lesser Sundas goshawk {{Accipitriformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circus (bird)
A harrier is any of the several species of diurnal hawks sometimes placed in the subfamily Circinae of the bird of prey family Accipitridae. Harriers characteristically hunt by flying low over open ground, feeding on small mammals, reptiles, or birds. The young of the species are sometimes referred to as ring-tail harriers. They are distinctive with long wings, a long narrow tail, the slow and low flight over grasslands and skull peculiarities. The harriers are thought to have diversified with the expansion of grasslands and the emergence of grasses about 6 to 8 million years ago during the Late Miocene and Pliocene. Taxonomy The genus ''Circus'' was introduced by the French naturalist Bernard Germain de Lacépède in 1799. The type species was subsequently designated as the western marsh harrier. Most harriers are placed in this genus. The word ''Circus'' is derived from the Ancient Greek ''kirkos'', referring to a bird of prey named for its circling flight (''kirkos'', "c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megatriorchis
Doria's goshawk or Doria's hawk, (''Megatriorchis doriae'') is a raptor, the only member of the genus ''Megatriorchis''. Description At up to 69 cm long, it is among the biggest hawks in the broad sense. It is greyish-brown with a black-barred crown and upperparts, whitish underparts, a black streak behind the eye, dark brown irises, a blackish bill and greenish-yellow legs. The sexes are similar. The female is slightly larger than the male. Habitat and distribution Doria's goshawk is endemic to lowland rainforests of New Guinea and Batanta Island. Its diet consists mainly of birds, including the lesser bird of paradise, and other small animals. Conservation Due to ongoing habitat loss, Doria's goshawk is evaluated as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. It is listed on Appendix II of CITES. Etymology In the genus name, "Mega-" is from the Greek word for "big". "Triorchis" was Greek for a kind of hawk thought to have three testicles — see '' Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrotriorchis
''Erythrotriorchis'' is a genus of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It contains the following species: * Chestnut-shouldered goshawk (''Erythrotriorchis buergersi'') * Red goshawk (''Erythrotriorchis radiatus'') Etymology "Erythro-" is from a Greek word for "red", and "triorchis" meant a kind of hawk thought to have three testicles. For further details see '' Eutriorchis''. Taxonomy Latham described the red goshawk as ''Falco radiatus'' in 1801. Sharpe definedAs cited by Peters: ''Erythrotriorchis'' in 1875 as a new monotypic genus for ''Falco radiatus''. Peters also included ''E. doriae'' in the genus, p225/ref> though Doria's goshawk Doria's goshawk or Doria's hawk, (''Megatriorchis doriae'') is a raptor, the only member of the genus ''Megatriorchis''. Description At up to 69 cm long, it is among the biggest hawks in the broad sense. It is greyish-brown with a black-bar ... is now classified separately as ''Megatriorchis doriae''. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
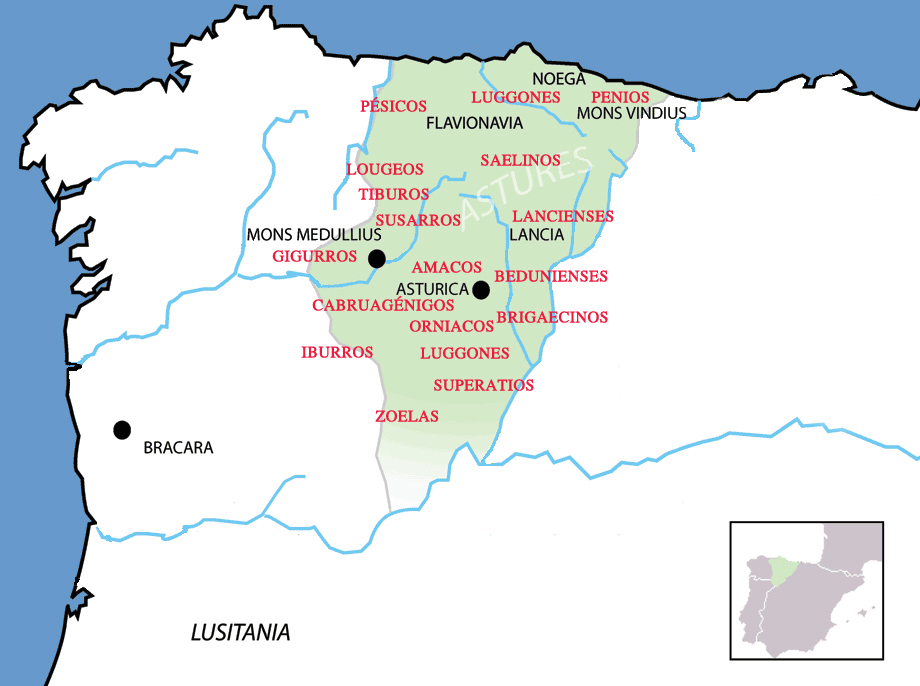
Astur (genus)
The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the Hispano-Celtic inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community of Principality of Asturias, the modern province of León, and the northern part of the modern province of Zamora (all in Spain), and eastern Trás os Montes in Portugal. They were a horse-riding highland cattle-raising people who lived in circular huts of stone drywall construction. The Albiones were a major tribe from western Asturias. Isidore of Seville gave an etymology as coming from a ''river Asturia'', identified by David Magie with Órbigo river in the plain of León, by others the modern Esla river. Location The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of Asturias and the León, eastern Lugo, Orense, and northern Zamora provinces, along with the northeastern tip of the Portuguese region of Trás-os-Montes. Here they held the towns of ''Lancia'' (Villasabariego – Le� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |