|
Accessory Cephalic Vein
The accessory cephalic vein is a variable vein that passes along the radial border of the forearm to join the cephalic veinhttp://dictionary.reference.com/browse/accessory+cephalic+vein (10/15/10) distal/inferior to the elbow. It may arise from a dorsal forearm venous plexus, or from the ulnar/medial side of the dorsal venous network of hand. In some cases the accessory cephalic springs from the cephalic above the wrist and joins it again higher up. A large oblique branch frequently connects the basilic and cephalic veins on the back of the forearm. See also * Cephalic vein In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (also called the antecubital vein) is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, a ... References Veins of the upper limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Vein
Superficial veins are veins that are close to the surface of the body, as opposed to deep veins, which are far from the surface. Superficial veins are not paired with an artery, unlike the deep veins, which are typically associated with an artery of the same name. Superficial veins are important physiology, physiologically for cooling of the body. When the body is too hot, the body shunts blood from the deep veins to the superficial veins to facilitate heat transfer to the body's surroundings. Superficial veins are often visible underneath the skin. Those below the level of the heart tend to bulge out, which can be readily witnessed in the hand, where the veins bulge significantly less after the arm has been raised above the head for a short time. Veins become more visually prominent when lifting heavy weight, especially after a period of proper strength training. Physiologically, the superficial veins are not as important as the deep veins (as they carry less blood) and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Venous Network Of Hand
The dorsal venous network of the hand is a venous network on the Dorsum (anatomy), dorsum (backside) of hand. It is formed by the dorsal metacarpal veins (three in number), a dorsal digital vein from the radial (lateral) side of the index finger and one from the ulnar (medial) side of the little finger, and both dorsal digital veins of the thumb. The venous network gives rise to the cephalic vein and the basilic vein; an accessory cephalic vein may arise from it as well. References Veins of the upper limb {{Circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (also called the antecubital vein) is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the elbow, it communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein. Anatomy The cephalic vein is situated within the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. Origin The cephalic vein forms at the roof of the anatomical snuffbox at the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand. Course and relations From its origin, it ascends up the lateral aspect of the radius. Near the shoulder, the cephalic vein passes between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles ( deltopectoral groove) through the clavipectoral triangle, where it empties into the axillary vein. Anastomoses It communicates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
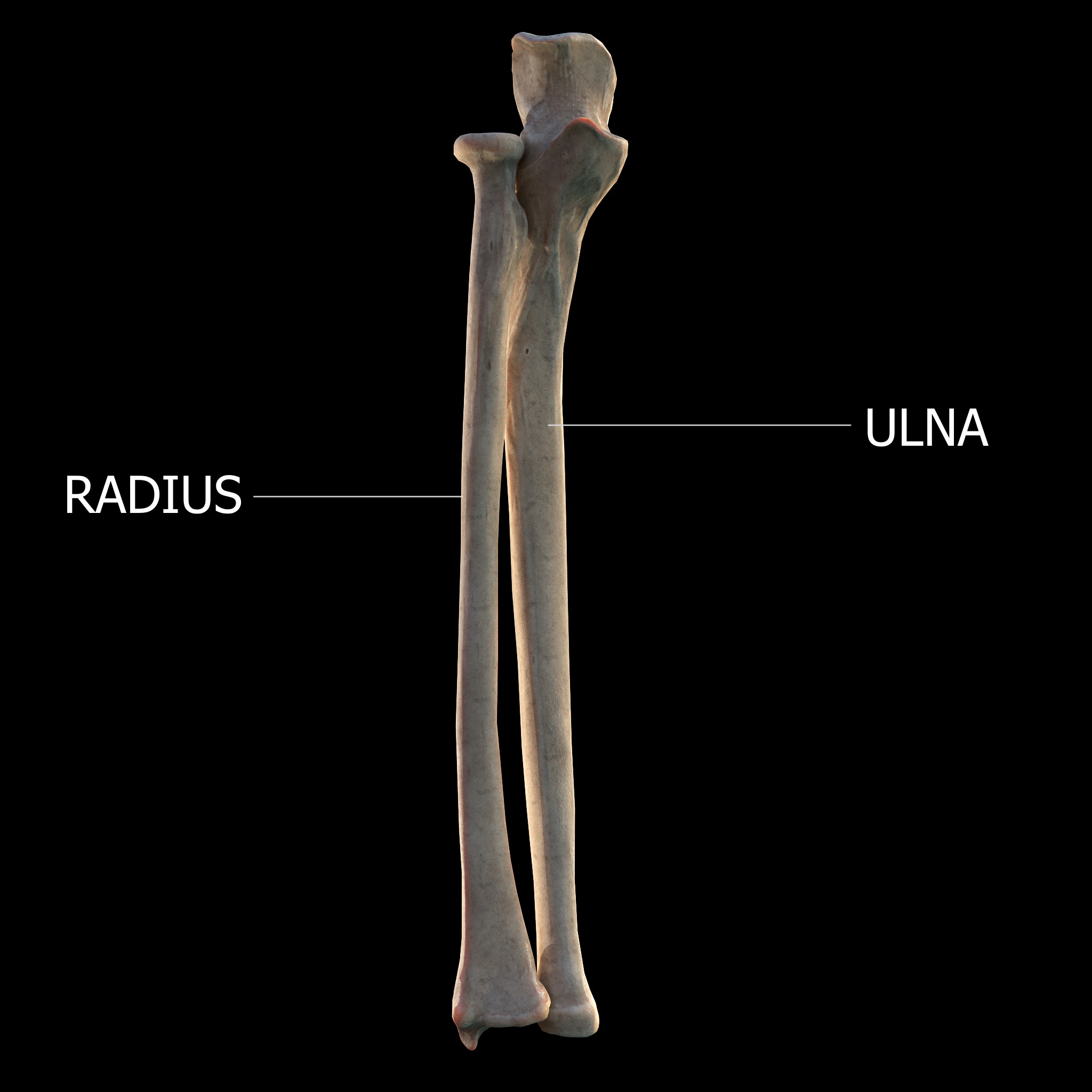
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow ( brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (also called the antecubital vein) is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the elbow, it communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein. Anatomy The cephalic vein is situated within the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. Origin The cephalic vein forms at the roof of the anatomical snuffbox at the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand. Course and relations From its origin, it ascends up the lateral aspect of the radius. Near the shoulder, the cephalic vein passes between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles ( deltopectoral groove) through the clavipectoral triangle, where it empties into the axillary vein. Anastomoses It communicates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Venous Network Of Hand
The dorsal venous network of the hand is a venous network on the Dorsum (anatomy), dorsum (backside) of hand. It is formed by the dorsal metacarpal veins (three in number), a dorsal digital vein from the radial (lateral) side of the index finger and one from the ulnar (medial) side of the little finger, and both dorsal digital veins of the thumb. The venous network gives rise to the cephalic vein and the basilic vein; an accessory cephalic vein may arise from it as well. References Veins of the upper limb {{Circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilic Vein
The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. It originates on the medial ( ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm, where its course is generally visible through the skin as it travels in the subcutaneous fat and fascia lying superficial to the muscles. The basilic vein terminates by uniting with the brachial veins to form the axillary vein. Anatomy Course As it ascends the medial side of the biceps in the arm proper (between the elbow and shoulder), the basilic vein normally perforates the brachial fascia ( deep fascia) in the middle of the medial bicipital groove, and run upwards medial to the brachial artery to the lower border of teres major, continuing as the axillary vein. Tributaries and anastomoses Near the region anterior to the cubital fossa (in the bend of the elbow joint), the basilic vein usually communicates with the cephalic vein (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |