|
Acanthicolepis
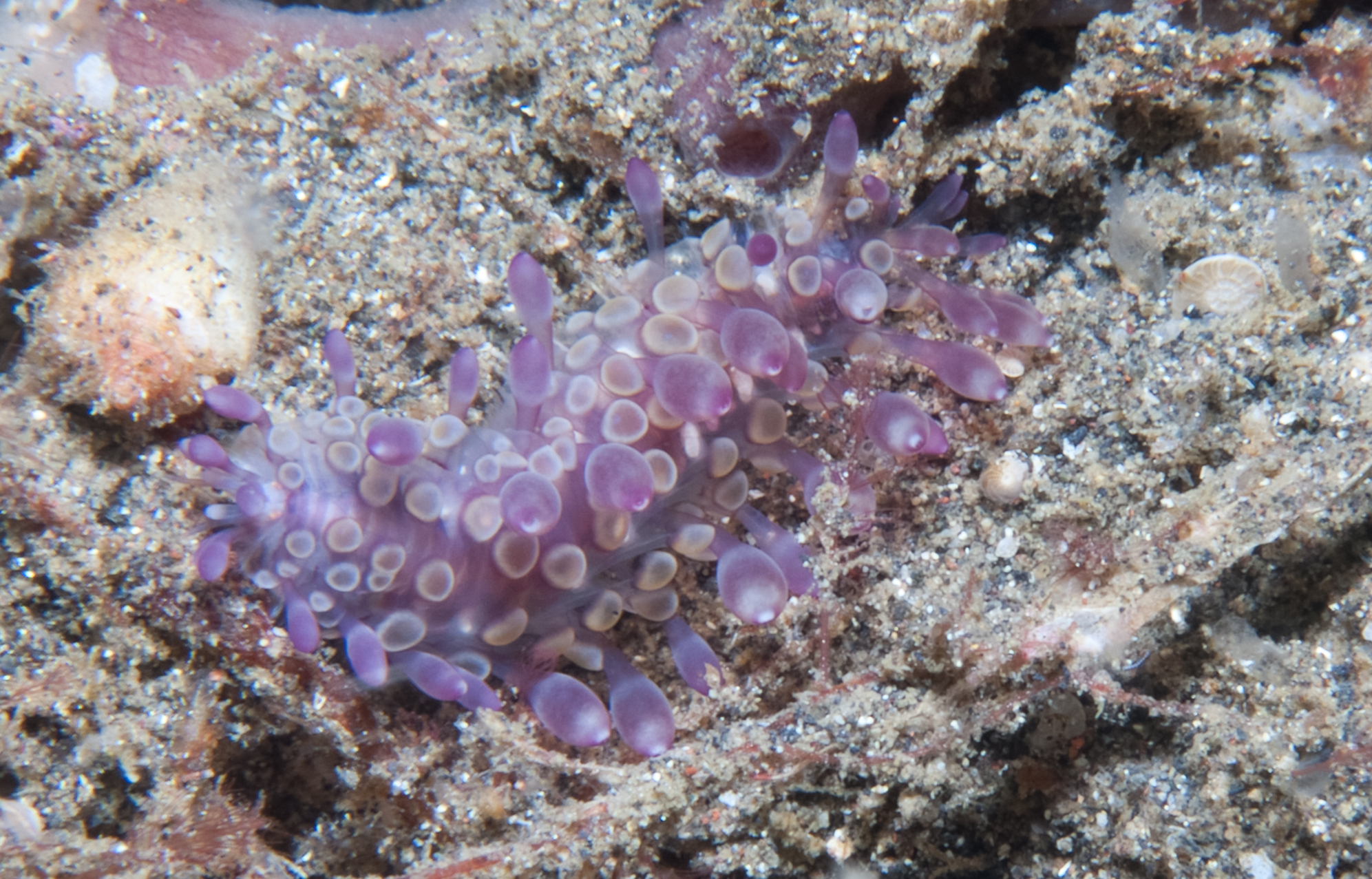
''Acanthicolepis'' is a genus of marine annelids in the family Polynoidae (scale worms). The genus was described in 1990 and includes two short-bodied species with up to 50 segments and which occur in the Mediterranean Sea and North-east Atlantic Ocean. Description Body short, with up to 50 segments and 18 pairs of elytra on segments 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 26, 29, 32, 34, 35, and 38. The prostomium has a pair of anterior peaks and the lateral antennae are inserted terminoventrally. Parapodia with both dorsal (notopodial) and ventral (neuropodial) acicula penetrating epidermis. The notochaetae are stout, with numerous rows of spines; the neurochaetae are more slender and include both unidentate (lack a secondary tooth at the tips) and bidentate forms (see Barnich & Fiege, 2010 for detailed diagnosis). Species Two valid species of ''Acanthicolepis'' are recognised as of June 2020: * ''Acanthicolepis asperrima ''Acanthicolepis'' is a genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthicolepis Asperrima
''Acanthicolepis'' is a genus of marine annelids in the family Polynoidae (scale worms). The genus was described in 1990 and includes two short-bodied species with up to 50 segments and which occur in the Mediterranean Sea and North-east Atlantic Ocean. Description Body short, with up to 50 segments and 18 pairs of elytra on segments 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 26, 29, 32, 34, 35, and 38. The prostomium has a pair of anterior peaks and the lateral antennae are inserted terminoventrally. Parapodia with both dorsal (notopodial) and ventral (neuropodial) acicula penetrating epidermis. The notochaetae are stout, with numerous rows of spines; the neurochaetae A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such ... are more slender and include both unidentate (lack a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthicolepis Zibrowii
''Acanthicolepis'' is a genus of marine annelids in the family Polynoidae (scale worms). The genus was described in 1990 and includes two short-bodied species with up to 50 segments and which occur in the Mediterranean Sea and North-east Atlantic Ocean. Description Body short, with up to 50 segments and 18 pairs of elytra on segments 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 26, 29, 32, 34, 35, and 38. The prostomium has a pair of anterior peaks and the lateral antennae are inserted terminoventrally. Parapodia with both dorsal (notopodial) and ventral (neuropodial) acicula penetrating epidermis. The notochaetae are stout, with numerous rows of spines; the neurochaetae are more slender and include both unidentate (lack a secondary tooth at the tips) and bidentate forms (see Barnich & Fiege, 2010 for detailed diagnosis). Species Two valid species of ''Acanthicolepis'' are recognised as of June 2020: * ''Acanthicolepis asperrima ''Acanthicolepis'' is a genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
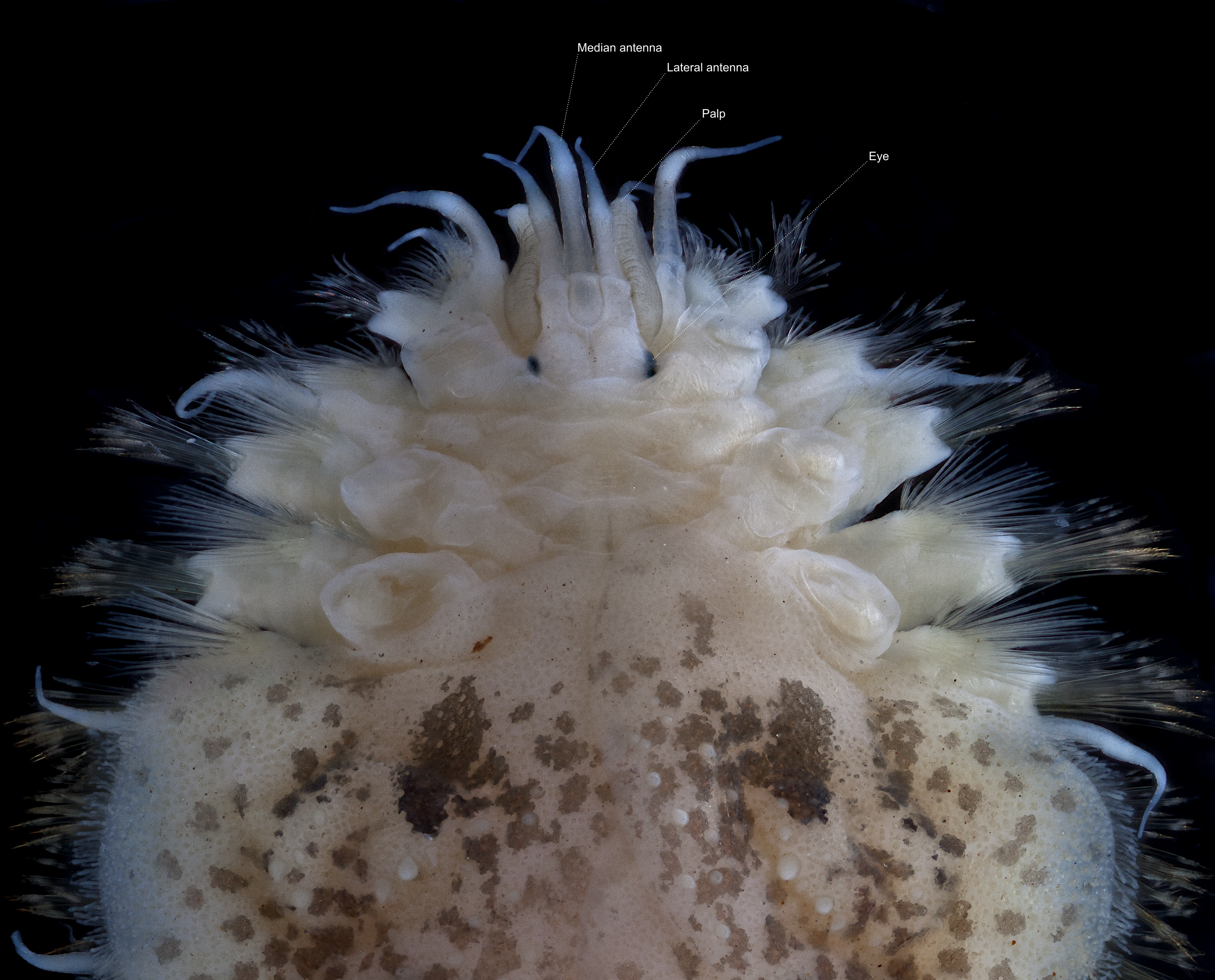
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in '' Eulagisca gigantea'' and '' Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoe Asperrima
In Greek mythology, Polynoe or Poulynoe () was one of the 50 Nereids, marine- nymph daughters of the ' Old Man of the Sea' Nereus and the Oceanid Doris.Hesiod, '' Theogony'' 258 Her name means 'giver of reason' or 'richness of mind, thoughtful'. Notes References * Hesiod Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ..., ''Theogony'' from ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica'' with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White, Cambridge, MA.,Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914Online version at the Perseus Digital Library. * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elytron (Annelida)
In annelids, elytra (; from Greek ἔλυτρον "sheath, cover"; singular: elytron ) are shield-like scales that are attached dorsally, one pair on each of a number of alternating segments and entirely or partly cover the dorsum. Elytra are modified dorsal cirri, and their number, size, location, and ornamentation are important taxonomic characters. The basal part of the elytra is known as the elytrophore; if (as is often the case) elytra are lost their presence is indicated by the elytrophore which is still present and visible. Annelids possessing elytra are also known as "scale worms". Possession of elytra is characteristic of the annelid suborder Aphroditiformia. Gallery File:Eunoe leiotentaculata lower res.jpg, A ''Eunoe leiotentaculata'' specimen showing its 15 pairs of elytra. File:Euphione sp. dorsal.jpg, ''Euphione ''Euphione'' is a genus of polychaetes belonging to the family Polynoidae. The species of this genus are found in Australia, Malesia Malesia is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; plural: parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed lateral outgrowths that bear the chaetae. In several groups of sea snails and sea slugs, 'parapodium' refers to lateral fleshy protrusions. __TOC__ Annelid parapodia Most species of polychaete annelids have paired, fleshy parapodia which are segmentally arranged along the body axis. Parapodia vary greatly in size and form, reflecting a variety of functions, such as gas exchange, anchorage, protection and locomotion. General description Parapodia in polychaetes can be uniramous (consisting of one lobe or ramus) but are usually biramous (two lobes or rami). In the latter case, the dorsal lobes are called notopodia and the ventral lobes neuropodia. Both neuropodia and notopodia may possess a bundle of chaetae (neurochaetae and notoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acicula
Acicula (singular: aciculum) are strong, stout internal chaetae that provide support to parapodia In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; plural: parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed ... in polychaete annelids. References {{reflist Annelid anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium, multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of Epithelium#Cell types, columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes (cell proliferation, proliferating basal and cell differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods). Polychaete annelids, ('polychaeta' literally meaning "many bristles") are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals. Use in taxonomy and identification The ultrastructure of chaetae is fundamentally similar for all taxa but there is vast diversity in chaetal morphology. Moreover, chaetae bear precise characters for determination of species and taxonomic assessment. The shape, absolute and relative size, number, position, ornamentation and type are important taxonomic characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |