|
AcacH
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer . The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds. Properties Tautomerism The keto and enol tautomers of acetylacetone coexist in solution. The enol form has C2v symmetry, meaning the hydrogen atom is shared equally between the two oxygen atoms. In the gas phase, the equilibrium constant, ''K''keto→enol, is 11.7, favoring the enol form. The two tautomeric forms can be distinguished by NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy and other methods. The equilibrium constant tends to be high in nonpolar solvents; when ''K''keto→enol is equal or greater than 1, the enol form is favoured. The keto form becomes more fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keto–enol Tautomerism
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of functional group or chemical intermediate, intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula (R = many substituents). The term ''enol'' is an abbreviation of ''alkenol'', a portmanteau deriving from "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol". Many kinds of enols are known. Keto–enol tautomerism refers to a chemical equilibrium between a "keto" form (a carbonyl, named for the common ketone case) and an enol. The interconversion of the two forms involves the transfer of an alpha hydrogen atom and the reorganisation of bonding electrons. The keto and enol forms are tautomerism, tautomers of each other. Enolization organic compound, Organic esters, ketones, and aldehydes with an α-hydrogen ( bond adjacent to the carbonyl group) often form enols. The reaction involves migration of a proton () from carbon to oxygen: : In the case of ketones, the conversion is called a keto-enol tautomerism, although this name is often more generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diketone
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical (dialdehydes, diketones, diesters, ''etc.'') or unsymmetrical (keto-esters, keto-acids, ''etc.''). 1,2-Dicarbonyls 1,2-Dialdehyde The only 1,2-dialdehyde is glyoxal, . Like many alkyldialdehydes, glyoxal is encountered almost exclusively as its hydrate and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave equivalently to the aldehydes since hydration is reversible. Glyoxal condenses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IR Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing Chemical bond, bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance structures'' or ''canonical structures'') into a resonance hybrid (or ''hybrid structure'') in valence bond theory. It has particular value for analyzing delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis structure. The resonance hybrid is the accurate structure for a molecule or ion; it is an average of the theoretical (or hypothetical) contributing structures. Overview Under the framework of valence bond theory, resonance is an extension of the idea that the bonding in a chemical species can be described by a Lewis structure. For many chemical species, a single Lewis structure, consisting of atoms obeying the octet rule, possibly bearing formal charges, and connected by bonds of positive integer order, is suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
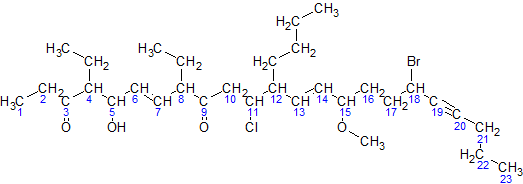
IUPAC Nomenclature Of Organic Chemistry
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the '' Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry'' (informally called thBlue Book. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry. To avoid long and tedious names in normal communication, the official IUPAC naming recommendations are not always followed in practice, except when it is necessary to give an unambiguous and absolute definition to a compound. IUPAC names can sometimes be simpler than older names, as with ethanol, instead of ethyl alcohol. For relatively simple molecules they can be more easily understood than non-systematic names, which must be learnt or looked over. However, the common or trivial name is often substantially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylacetonate Anion
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer . The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds. Properties Tautomerism The keto and enol tautomers of acetylacetone coexist in solution. The enol form has C2v symmetry, meaning the hydrogen atom is shared equally between the two oxygen atoms. In the gas phase, the equilibrium constant The equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction is the value of its reaction quotient at chemical equilibrium, a state approached by a dynamic chemical system after sufficient time has elapsed at which its composition has no measurable tendency ..., ''K''keto→enol, is 11.7, favoring the enol form. The two tautomeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− ( hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak Acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula , to dissociate into a proton, , and an anion, . The dissociation or ionization of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. : Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (), perchloric acid (), nitric acid () and sulfuric acid (). A weak acid is only partially dissociated, or is partly ionized in water with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present, in solution, in equilibrium with each other. : Acetic acid () is an example of a weak acid. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant, K_a value. The strength of a weak organic acid may depend on substituent effects. The strength of an inorganic acid is dependent on the oxidation state for the atom to which the proton may be attached. Acid strength is solvent-dependent. For example, hydrogen chloride is a strong acid in aqueous solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |