|
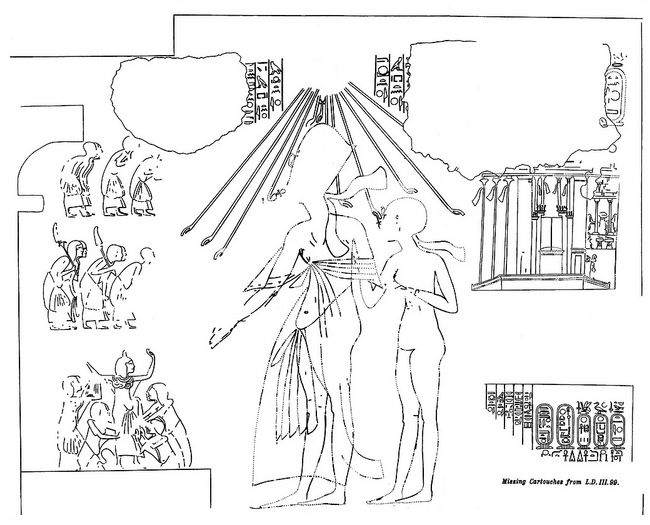
Abydos King List (Ramesses II)
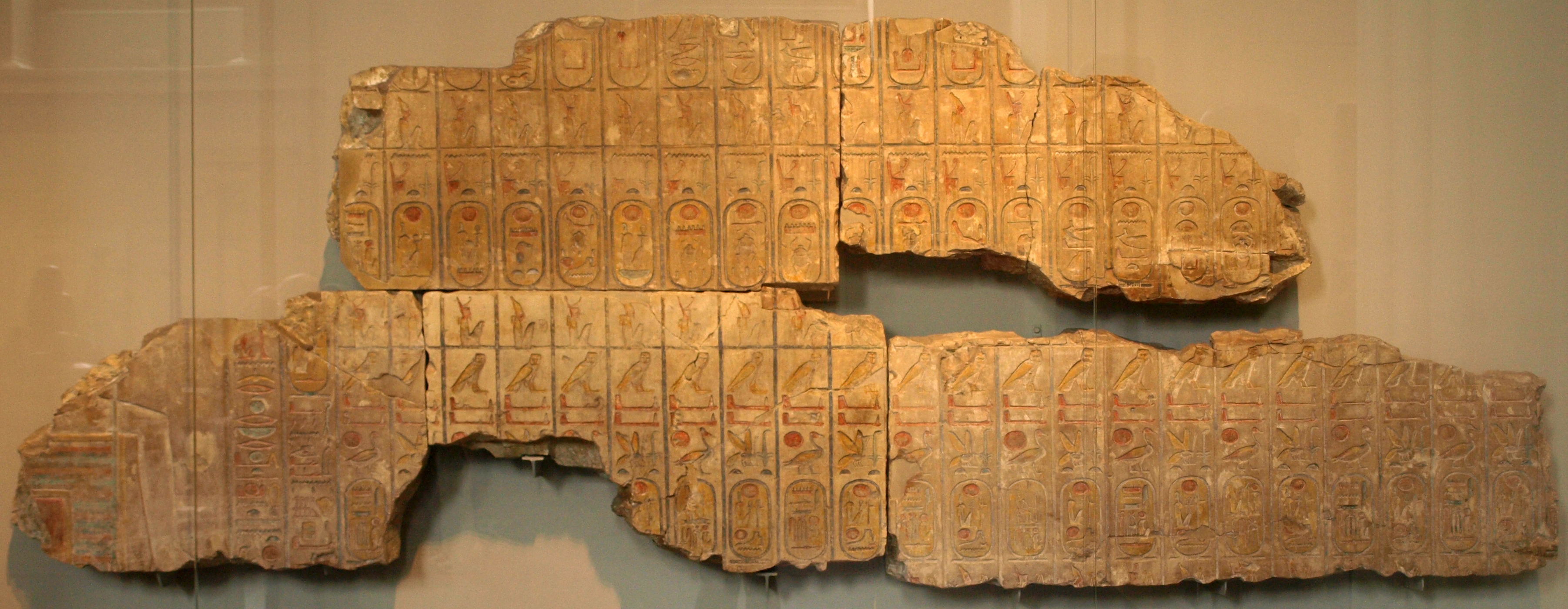
The Abydos King List of Ramesses II, also known as the Fragmentary Abydos King List, the Fragmentary Abydos King Table or the Fragmentary Abydos Tablet, is a list of Ancient Egyptian kings down to Ramesses' own time. Originally located in the temple of Ramesses II at Abydos in Egypt, it was built in the 13th century BC. The list is similar to the one inscribed in the temple built at the site by Ramesses' father and predecessor, Seti I, but with the addition of Ramesses' own throne name and nomen. The list was found by William John Bankes William John Bankes (11 December 1786 – 15 April 1855) was an English politician, explorer, Egyptologist and adventurer. The second, but first surviving, son of Henry Bankes MP, he was a member of the Bankes family of Dorset and he had Sir Ch ... in 1818 and the surviving fragments were removed in 1837 by the French consul in Egypt, dismantled and the blocks sold to the British. Severely damaged, it is now on display at the British Museum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyksos
The Hyksos (; Egyptian language, Egyptian ''wikt:ḥqꜣ, ḥqꜣ(w)-wikt:ḫꜣst, ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''heqau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands"), in modern Egyptology, are the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC). Their seat of power was the city of Avaris in the Nile Delta, from where they ruled over Lower Egypt and Middle Egypt up to Cusae. In the ''Aegyptiaca'', a history of Egypt written by the Greco-Egyptian priest and historian Manetho in the 3rd century BC, the term Hyksos is used ethnically to designate people of probable West Semitic, Levantine origin. While Manetho portrayed the Hyksos as invaders and oppressors, this interpretation is questioned in modern Egyptology. Instead, Hyksos rule might have been preceded by groups of Canaanite peoples who gradually settled in the Nile Delta from the end of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt, Twelfth Dynasty onwards and who may have seceded from the crumbling and unstable Egyptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merenre Nemtyemsaf II
Merenre Nemtyemsaf II (died 2213 BC) was an ancient Egyptian king, the sixth and penultimate ruler of the 6th Dynasty. He reigned for 1 year and 1 month in the first half of the 22nd century BC, at the very end of the Old Kingdom period. Nemtyemsaf II likely ascended the throne as an old man, succeeding his long-lived father Pepi II Neferkare at a time when the power of the pharaoh was crumbling. Attestations Merenre Nemtyemsaf II is attested on the 4th line, column 6 of the Turin canon, a king list redacted in the early Ramesside Period. Although his name is lost in the canon, the duration of its reign is still readable as 1 year and 1 month, following the reign of Pepi II Neferkare.Darrell D. Baker: ''The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I - Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC'', Stacey International, , 2008, p. 211–212 Nemtyemsaf II is also attested on the 39th entry of the Abydos King List, which dates to the reign of Seti I and constitutes one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenemhat III
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.'' Amenemhat III (Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet III, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the sixth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was elevated to throne as co-regent by his father Senusret III, with whom he shared the throne as the active king for twenty years. During his reign, Egypt attained its cultural and economic zenith of the Middle Kingdom. The aggressive military and domestic policies of Senusret III, which re-subjugated Nubia and wrested power from the nomarchs, allowed Amenemhat III to inherit a stable and peaceful Egypt. He directed his efforts towards an extensive building program with particular focus on Faiyum. Here he dedicated a temple to Sobek, a chapel to Renenutet, erected two colossal statues of himself in Biahmu, and contributed to excavation of Lake Moeris. He built for himself two pyramids at Dahshur and Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senusret III
Khakaure Senusret III (also written as Senwosret III or the hellenised form, Sesostris III) was a pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth dynasty of Egypt, Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to rule at the height of the Middle Kingdom. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of nomarch, regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development."''The Pyramids: Their Archeology and History''", Miroslav Verner, Translated by Steven Rendall, p386–387 & p416–421, Atlantic, Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a List of pharaohs deified during lifetime, cult during their own lifet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senusret II
Senusret II or Sesostris II was the fourth pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. His pyramid was constructed at El-Lahun. Senusret II took a great deal of interest in the Faiyum oasis region and began work on an extensive irrigation system from Bahr Yussef through to Lake Moeris through the construction of a dike at El-Lahun and the addition of a network of drainage canals. The purpose of his project was to increase the amount of cultivable land in that area. The importance of this project is emphasized by Senusret II's decision to move the royal necropolis from Dahshur to El-Lahun where he built his pyramid. This location would remain the political capital for the 12th and 13th Dynasties of Egypt. Senusret II was known by his prenomen Khakheperre, which means "The Ka of Re comes into being". The king also established the first known workers' quarter in the nearby town of Senusrethotep ( Kahun). Reign Co-regency Co-regencies are a major issue for Egyptologists' understandi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenemhat II
Nubkaure Amenemhat II, also known as Amenemhet II, was the third pharaoh of the 12th Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Although he ruled for at least 35 years, his reign is rather obscure, as well as his family relationships. Family Archaeological findings have provided the name of Amenemhat's mother, the "king's mother" Neferu III, but not the name of his father. Nevertheless, it is commonly assumed that he was a son of his predecessor Senusret I. An early attestation of Amenemhat may have come from the tomb of the namesake nomarch Amenemhat, buried at Beni Hasan. This nomarch, who lived under Senusret I, escorted the "King's son Ameny" in an expedition to Nubia, and it is believed that this prince Ameny was no other than Amenemhat II in his youth. The identity of Amenemhat's queen consort is unknown. Many royal women were buried within his pyramid complex, but their relationships with the king are unclear: a queen Keminub must be dated to the later 13th Dynasty, and three "king's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallery Of Antiquities, Selected From The British Museum (1842) Plate 29 (cropped)
Gallery or The Gallery may refer to: * Gallery (surname), a surname Arts, entertainment, and media * Art gallery ** Contemporary art gallery ** Online art gallery Music * Gallery (band), an American soft rock band of the 1970s Albums * ''Gallery'' (Elaiza album), 2014 album * ''Gallery'' (Great White album), a 1999 compilation album * ''Gallery'', an album by Bert Kaempfert 1974 * ''The Gallery'' (album), a 1995 album by Dark Tranquility * ''Gallery'', 2017 album by Arizona Songs * "Gallery" (Mario Vazquez song) * "Gallery" (Yōko Oginome song) * "Gallery", a 2018 track by Toby Fox from ''Deltarune Chapter 1 OST'' from the video game ''Deltarune'' * "Gallery", a 2021 song by Park Ji-hoon on the EP ''My Collection'' * "The Gallery", a song on the Joni Mitchell album ''Clouds'' * "The Gallery", a song on the Bradley Joseph album ''Rapture'' Television * ''Gallery'' (TV series), Canadian documentary series on CBC Television (1973–1979) * ''Gallery Girls'', a reality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ay (pharaoh)
Ay was the penultimate pharaoh of ancient Egypt's Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty. He held the throne of Egypt for a brief four-year period in the late 14th century BC. Prior to his rule, he was a close advisor to two, and perhaps three, other pharaohs of the dynasty. It is speculated that he was the power behind the throne during child ruler Tutankhamun's reign, although there is no evidence for this aside from Tutankhamun's youthfulness. His ''Prenomen (Ancient Egypt), prenomen'' ''Kheperkheperure'' means "Everlasting are the Manifestations of Ra", while his ''nomen (Ancient Egypt), nomen'' ''Ay it-netjer'' reads as "Ay, Father of the God". Records and monuments that can be clearly attributed to Ay are rare, both because his reign was short and because his successor, Horemheb, instigated a campaign of ''damnatio memoriae'' against him and the other pharaohs associated with the unpopular Amarna Period. Origins and family Ay is believed to have been from Akhmim. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutankhamen
Tutankhamun or Tutankhamen, (; ), was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled during the late Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Born Tutankhaten, he instituted the restoration of the traditional polytheistic form of ancient Egyptian religion, undoing a previous shift to the religion known as Atenism. Tutankhamun's reign is considered one of the greatest restoration periods in ancient Egyptian history. His endowments and restorations of cults were recorded on what is today known as the Restoration Stela. The cult of the god Amun at Thebes was restored to prominence, and the royal couple changed their names to "Tutankhamun" and "Ankhesenamun", replacing the -aten suffix. He also moved the royal court from Akhenaten's capital, Amarna, back to Memphis almost immediately on his accession to the kingship. He reestablished diplomatic relations with the Mitanni and carried out military campaigns in Nubia and the Near East. Tutankhamun was one of only a few kings who was worshipped as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neferneferuaten
Ankhkheperure-Merit-Neferkheperure/Waenre/Aten Neferneferuaten (), or "Neferneferuaten", is the name of a queen regnant ('female pharaoh, king') of ancient Egypt who reigned in her own right near the end of the Amarna Period during the Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. Her name features feminine Grammatical gender, gender traces; and one of her epithets was ''Akhet-en-hyes'' ("Effective for her husband"). This epithet also features in one version of her Nomen (ancient Egypt), nomen (birth name) cartouche. (See Ancient Egyptian royal titulary.) She is distinguished from the king Smenkhkare, with whom she shared the prenomen (throne name) ''Ankhkheperure'', by the presence of epithets in both cartouches. It has been suggested that she was in fact Smenkhkare's wife Meritaten or his predecessor Akhenaten's widow Nefertiti. The Golden Nut Pectoral (Carter no. 261p1) The golden Nut Pectoral (Ancient Egypt), pectoral (Carter no. 261p1) was also reused for the funeral o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smenkhkare
Smenkhkare (alternatively romanized Smenkhare, Smenkare, or Smenkhkara; meaning "Vigorous is the soul of Re") was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of unknown background who lived and ruled during the Amarna Period of the 18th Dynasty. Smenkhkare was husband to Meritaten, the daughter of his likely co-regent, Akhenaten. Since the Amarna period was subject to a large-scale condemnation of memory by later pharaohs, very little can be said of Smenkhkare with certainty, and he has hence been subject to immense speculation. Origin and family Smenkhkare's origins are unknown. It is assumed he was a member of the royal family, likely either a brother or son of the pharaoh Akhenaten. If he is Akhenaten's brother, his mother was likely either Tiye or Sitamun. If a son of Akhenaten, he was presumably an older brother of Tutankhamun, as he succeeded the throne ahead of him; his mother was likely an unknown, lesser wife. An alternative suggestion, based on objects from the tomb of Tutankhamun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |