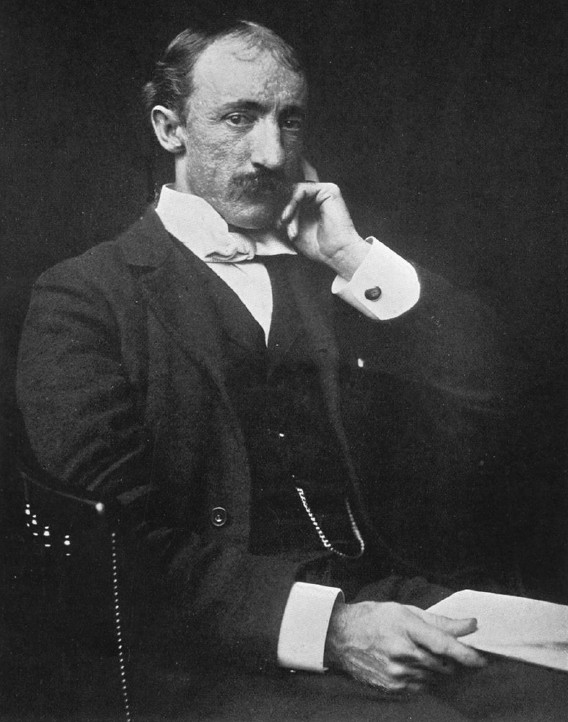|
Aby Warburg
Aby Moritz Warburg (June 13, 1866 – October 26, 1929) was a German art historian and cultural theorist who founded the ''Kulturwissenschaftliche Bibliothek Warburg'' (Warburg Library for Cultural Studies), a private library, which was later moved to the Warburg Institute, London. At the heart of his research was the legacy of the classical world, and the transmission of classical representation, in the most varied areas of Western culture through to the Renaissance. Warburg described himself as: "''Amburghese di cuore, ebreo di sangue, d'anima Fiorentino''" ('Hamburger at heart, Jew by blood, Florentine in spirit'). Early life and education Aby Warburg was born in Hamburg into the wealthy Warburg family of German Jewish bankers. His ancestors had come to Germany from Italy in the 17th century and settled in the town of Warburg in Westphalia, taking on the town's name as their family name. In the 18th century the Warburgs moved to Altona near Hamburg. Two brothers Warburg f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-largest in the European Union with a population of over 1.9 million. The Hamburg Metropolitan Region has a population of over 5.1 million and is the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, eighth-largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. At the southern tip of the Jutland Peninsula, Hamburg stands on the branching River Elbe at the head of a estuary to the North Sea, on the mouth of the Alster and Bille (Elbe), Bille. Hamburg is one of Germany's three city-states alongside Berlin and Bremen (state), Bremen, and is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The Port of Hamburg is Germany's largest and Europe's List of busiest ports in Europe, third-largest, after Port of Rotterdam, Rotterda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Lamprecht
Karl Gotthard Lamprecht (25 February 1856 – 10 May 1915) was a German historian who specialized in German art and economic history. Biography Lamprecht was born in Jessen in the Province of Saxony. As a student, he trained in history, political science, economics, and art at the universities of Göttingen, Leipzig, and Munich. Lamprecht taught at the university in Marburg and later at Leipzig, where he founded the ''Institut für Kultur und Universalgeschichte'' center dedicated to comparative world and cultural history. Lamprecht was employee at the successful edition project “The Chronicles of the German Cities” under the leadership of the well-known and highly reputated German historian Karl von Hegel.Marion Kreis (2012)''Karl Hegel. Geschichtswissenschaftliche Bedeutung und wissenschaftsgeschichtlicher Standort''(= ''Schriftenreihe der Historischen Kommission bei der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften.'' Bd. 84). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Göttingen, , pp. 314 ff. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aby Warburg 1896
Aby or ABY may refer to: Aviation * IATA airport code for Southwest Georgia Regional Airport in Albury, State of Georgia, USA Places * Aby, Ivory Coast * Aby Lagoon, a lagoon in Ivory Coast * Abyy or Aby, Sakha Republic, Russia ** Aby Lowland * Aby, Lincolnshire, a village in England, UK * Åby, Norrköping Municipality, Sweden * Åby, Växjö Municipality, Sweden Transport * Ashburys railway station's station code Other uses * ''Aby'' (film), a 2017 Malayalam-language Indian film * Aby (name), a given name and surname, including a list of people with the name * Abyssinian cat, or Abys, a shorthair cat breed * Aneme Wake language's ISO 639-3 code * ABY, a system of measuring fictional dates in ''Star Wars'' relative to the Battle of Yavin See also * Aaby (other) (for Åby) * Abby (other) Abby is a given name. Abby may also refer to: * Abby (film), ''Abby'' (film), a 1974 blaxploitation/horror film about a woman possessed by an African demon * Abby (TV s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Loeb
James Loeb (; ; August 6, 1867 – May 27, 1933) was an American banker, Hellenist and philanthropist Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives for the public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material .... Biography James Loeb, of German-Jewish descent, was the second son of Solomon Loeb and Betty Loeb. James Loeb joined his father at Kuhn, Loeb & Co. in 1888 and was made partner in 1894, but he retired from the bank in 1901 due to severe illness. In memory of his former lecturer and friend Charles Eliot Norton, Loeb created The Charles Eliot Norton Memorial Lectureship in 1907. In 1911, he founded and endowed the Loeb Classical Library. He assembled a team of Anglo-American classicists to oversee the series, and arranged for publication through Heinemann (publisher) in London When James Loeb died, he bequeathed the Loeb Classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Hamilton Cushing
Frank Hamilton Cushing (July 22, 1857 in North East Township, Erie County, Pennsylvania – April 10, 1900 in Washington, D.C.) was an American anthropologist and ethnologist. He made pioneering studies of the Zuni Indians of New Mexico by entering into their culture; his work helped establish participant observation as a common anthropological research strategy. In recent years, however, questions have emerged about Cushing's activities among the Zuni. Consequently, Frank Cushing's work provides an important case study for considering the ethics of both ethnographic research and the generation of museum collections. Early life Cushing was born in the borough of North East, Pennsylvania. He later moved with his family to Western New York. As a boy he took an interest in the Native American artifacts in the surrounding countryside and taught himself how to knap flint (make arrowheads and such from flint). He published his first scientific paper when he was 17. After a brief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Mooney
James Mooney (February 10, 1861 – December 22, 1921) was an American ethnographer who lived for several years among the Cherokee. Known as "The Indian Man", he conducted major studies of Southeastern Indians, as well as of tribes on the Great Plains. "Register to the Papers of James Mooney" , National Anthropological Archives, Smithsonian Institution, accessed 10 Nov 2009 He did ethnographic studies of the Ghost Dance, a spiritual movement among various Native American culture groups, after |
Solomon Loeb
Solomon Loeb (born Salomon Löb, June 29, 1828 – December 12, 1903) was a German-born American banker and businessman. He was a merchant in textiles and later a banker with Kuhn, Loeb & Co. Biography His father, a devout Jew, had been a small corn- and wine-dealer in Worms, which belonged to the Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine. Solomon Loeb immigrated to the United States in 1849. He settled in Cincinnati with the textiles merchant Kuhn, Netter & Co. He moved to New York City in 1865 and with his partner, Abraham Kuhn, started the banking house of Kuhn, Loeb and Co. His second born son, James Loeb, joined the bank in 1888 (and left in 1901). Solomon Loeb gradually retired from running the business but left Kuhn, Loeb & Co. only in 1899. He then started to move into the real estate business. In addition, he was also a generous philanthropist. Among his donations was the Hebrew Charities Building that formerly stood at Second Avenue and 21st Street in New York City. Fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Berlin
The Humboldt University of Berlin (, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin, Germany. The university was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humboldt, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher as the University of Berlin () in 1809, and opened in 1810. From 1828 until its closure in 1945, it was named the (Royal) Friedrich Wilhelm University of Berlin (FWU Berlin; ). During the Cold War, the university found itself in East Berlin and was ''de facto'' split in two when the Free University of Berlin opened in West Berlin. The university received its current name in honour of Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1949. The university is divided into nine faculties including its medical school shared with the Freie Universität Berlin. The university has a student enrollment of around 35,000 students, and offers degree programs in some 171 disciplines from und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erwin Panofsky
Erwin Panofsky (March 30, 1892 – March 14, 1968) was a German-Jewish art historian whose work represents a high point in the modern academic study of iconography, including his hugely influential ''Renaissance and Renascences in Western Art'' and his seminal '' Early Netherlandish Painting''.Shone, Richard and Stonard, John-Paul, eds. ''The Books that Shaped Art History'', chapter 7. London: Thames & Hudson, 2013. Panofsky's ideas were highly influential in intellectual history in general,Chartier, Roger. ''Cultural History'', pp. 23–24 (from "Intellectual History and the History of ''Mentalités''"). Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1988 particularly in his use of historical ideas to interpret artworks and vice versa. Many of his books are still in print, including ''Studies in Iconology: Humanist Themes in the Art of the Renaissance'' (1939), ''Meaning in the Visual Arts'' (1955), and his 1943 study ''The Life and Art of Albrecht Dürer''. His academic career was pursue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconology
Iconology is a method of interpretation in cultural history and the history of the visual arts used by Aby Warburg, Erwin Panofsky and their followers that uncovers the cultural, social, and historical background of themes and subjects in the visual arts. Though Panofsky differentiated between iconology and iconography, the distinction is not very widely followed, "and they have never been given definitions accepted by all iconographers and iconologists". Few 21st-century authors continue to use the term "iconology" consistently, and instead use iconography to cover both areas of scholarship. To those who use the term, iconology is derived from synthesis rather than scattered analysis and examines symbolic meaning on more than its face value by reconciling it with its historical context and with the artist's body of work – in contrast to the widely descriptive iconography, which, as described by Panofsky, is an approach to studying the content and meaning of works of art th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct from artistic style. The word ''iconography'' comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek ("image") and ("to write" or ''to draw''). A secondary meaning (based on a non-standard translation of the Greek and Russian equivalent terms) is the production or study of the religious images, called "Icon, icons", in the Byzantine art, Byzantine and Eastern Orthodox Churches, Orthodox Christian tradition. This usage is mostly found in works translated from languages such as Greek or Russian, with the correct term being "icon painting". In art history, "an iconography" may also mean a particular depiction of a subject in terms of the content of the image, such as the number of figures used, their placing and gestures. The term is also used in many academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |